📚 자바의 정석을 정리한 내용입니다.
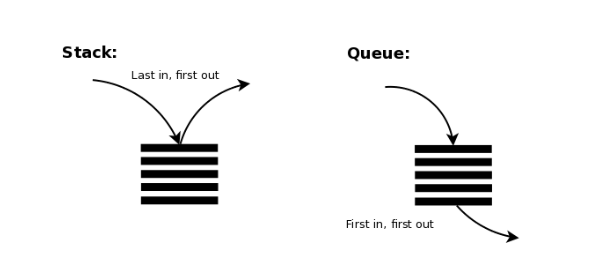
스택은 마지막에 저장한 데이터를 가장 먼저 꺼내는 Last in first out(LIFO)구조.
큐는 처음 저장한 데이터를 가장 먼저 꺼내는 First in first out(FIFO)구조다.
참고로 Stack은 클래스, Queue는 인터페이스다.
Stack의 메서드
| method | 설명 |
|---|---|
| boolean empty() | Stack이 비었는지 확인 |
| Object peek() | Stack 맨 위에 저장된 객체를 반환 pop과 달리 꺼내는 것은 아님 비어 있다면 EmptyStackException |
| Oject pop() | 맨 위에 저장된 객체를 꺼낸다. 비었다면 역시 EmptyStackExcption |
| Object push(Object item) | Stack에 객체를 저장한다 |
| int search(Object o) | 주어진 객체o를 찾아서 index를 반환 배열과 달리 0이 아닌 1부터 시작 |
Queue의 메서드
| method | 설명 |
|---|---|
| boolean add(Object o) | 지정한 객체o를 Queue에 추가. 저장 공간이 부족하면 IllegalStateException |
| Ojbect remove() | 객체를 꺼내 반환. 비어 있으면 NoSuchElementException |
| Object element() | 삭제 없이 요소를 읽는다. peek과 달리 비었을 때 NoSuchElementException |
| boolean offer(Object o) | 객체 저장 |
| Object poll() | 객체를 꺼내 반환, 비었으면 null |
| Object peek() | 삭제 없이 요소 읽는다. 비었으면 null. |
Stack vs. Queue
package com.javaex.ch11;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackAndQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack stack = new Stack();
Queue queue = new LinkedList(); //Queue인터페이스 구현체인 LinkedList
stack.push("0");
stack.push("1");
stack.push("2");
queue.offer("0");
queue.offer("1");
queue.offer("2");
System.out.println("=========Stack=========");
while (!stack.empty()) {
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
System.out.println("=========Queue=========");
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(queue.poll());
}
}
}
/*결과
=========Stack=========
2
1
0
=========Queue=========
0
1
2
*/Queue의 변형
Dequeue
Stack과 Queue의 결합. 양끝에서 저장offer과 삭제poll가능.
구현 클래스:ArrayDeque, LinkedList
PriorityQueue
우선순위 큐. 우선순위가 높은 것부터 꺼냄
null저장 불가.
입력 3,1,5,2,4 -> 출력 1,2,3,4,5
Blocking Queue
비어 있을 때 꺼내기와 가득 차 있을 때 넣기를
지정된 시간동안 지연block시킴
