Heap
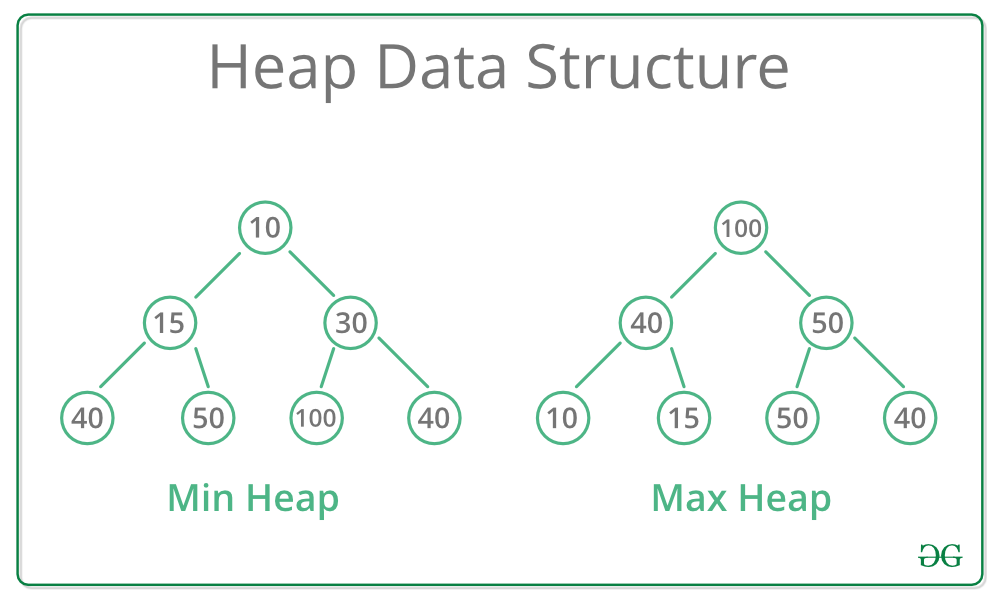
힙은 최대 힙과 최소 힙 두 종류를 가지고 있는 자료 구조 이다.
모든 부모는 자식보다 (크고 (최대 힙) /작고 (최소 힙)) 이 조건은 모든 노드에 적용된다.
쉽게 말해서 최대 힙일 때는 최댓값이 root이고 최소 힙일 때는 최솟값이 root이다.
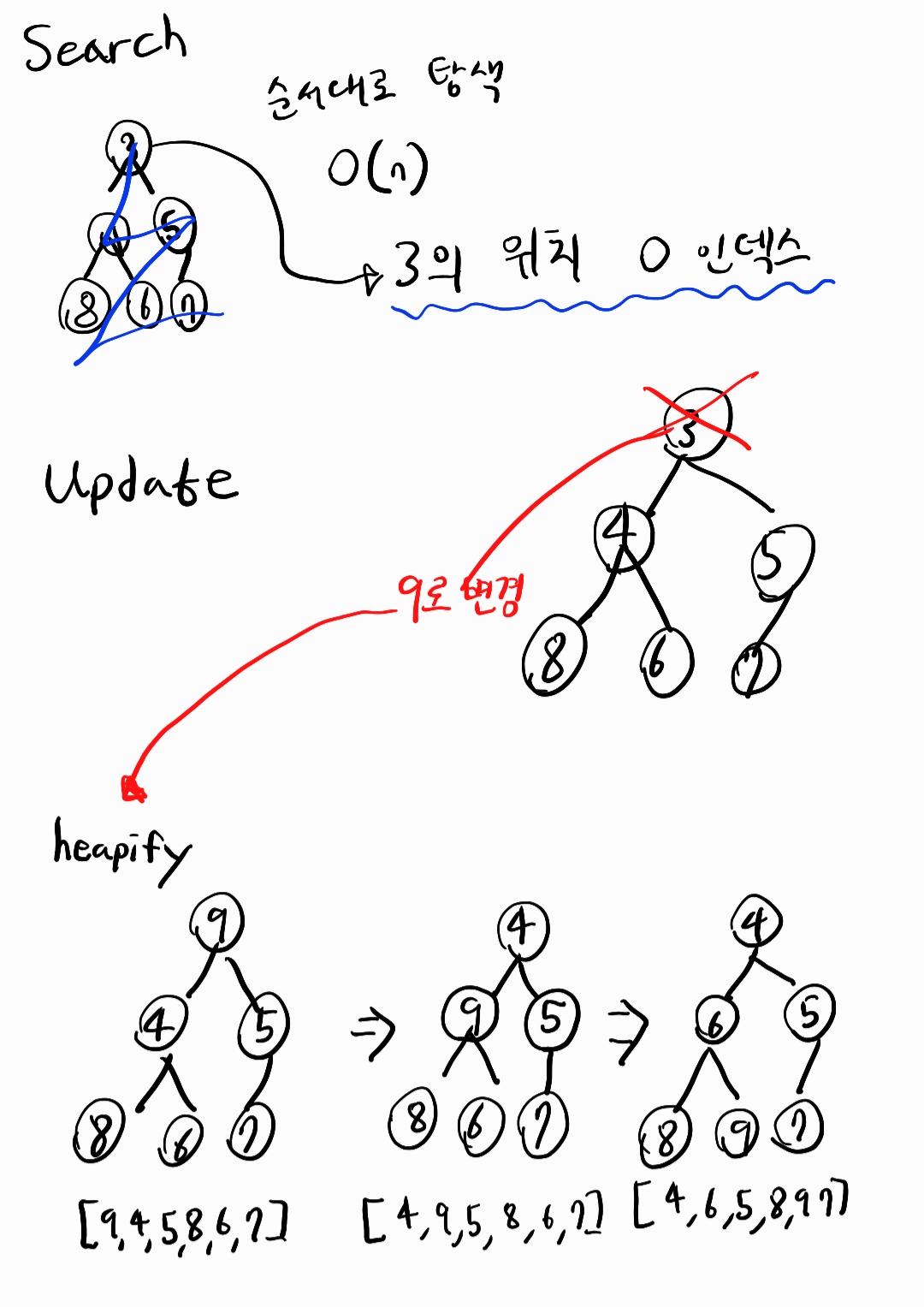
삽입, 삭제는 O(logn)이고 조회, 수정은 O(n)의 시간복잡도를 가지고 있다.
그 이유는 다음과 같다.
삽입,삭제는 변화 후 두 자식 트리중에 변화가 필요한 자식 트리만 선택해서 heapify시킨다.
여기서 logn의 시간 복잡도를 갖게 된다.조회, 수정은 전체 트리(두 자식 모두)를 탐색해야 하기 때문에 n의 시간 복잡도를 갖는다.
heapify란 말그대로 heap화 시킨다고 보면 된다. 해당 트리가 힙의 조건을 만족시키도록 변화시키는 것이다.
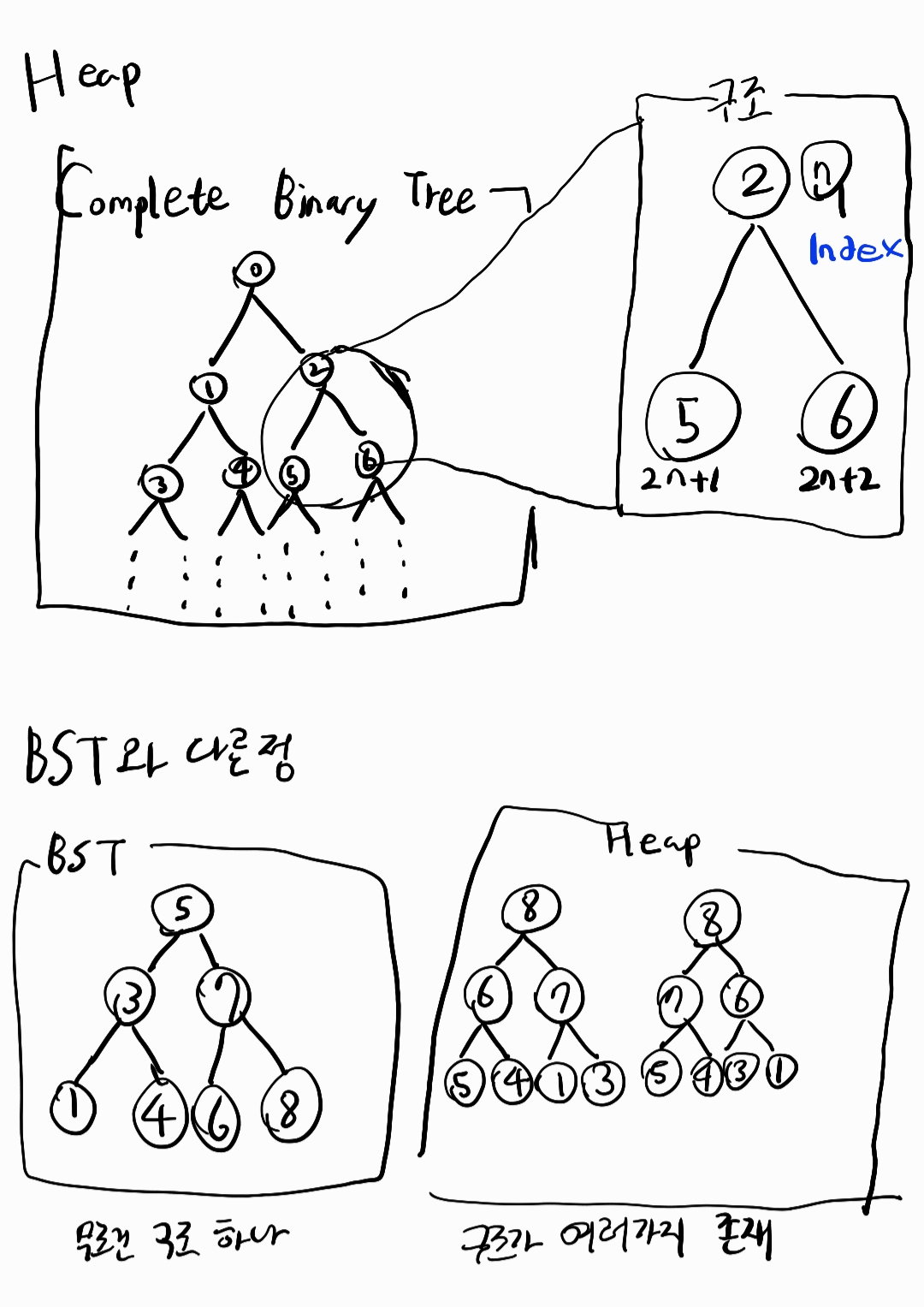
BST와 다른 점
다음 그림과 같이 구조의 개수가 다르다. (다양성이 존재한다.)
JS 구현
class Heap {
arr = [];
#upheap(index) {
if (index > 0) {
// 경우의 수가 (n-1)/2 이거나 (n-2)/2이기 때문에
// 내림으로 처리한다.
const parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
if (this.arr[index] < this.arr[parentIndex]) {
const temp = this.arr[index];
this.arr[index] = this.arr[parentIndex];
this.arr[parentIndex] = temp;
this.#upheap(parentIndex);
}
}
}
insert(value) {
let index = this.arr.length;
this.arr[index] = value;
this.#upheap(index);
return this.arr;
}
#downheap(index) {
if (index < this.arr.length) {
const [childrenIndex1, childrenIndex2] = [index * 2 + 1, index * 2 + 2];
const smallerIndex =
this.arr[childrenIndex1] > this.arr[childrenIndex2]
? childrenIndex2
: childrenIndex1;
if (this.arr[smallerIndex] < this.arr[index]) {
let temp = this.arr[smallerIndex];
this.arr[smallerIndex] = this.arr[index];
this.arr[index] = temp;
this.#downheap(smallerIndex);
}
}
}
remove() {
// 루트만 삭제
const result = this.arr[0];
this.arr[0] = this.arr[this.arr.length - 1];
this.arr.splice(this.arr.length - 1, 1);
this.#downheap(0);
return result;
}
search(value) {
for (let index = 0; index < this.arr.length; index++) {
if (this.arr[index] === value) {
return index;
}
}
return null;
}
sort() {
// 힙 정렬
const sortedArray = [];
while (this.arr.length > 0) {
sortedArray.push(this.remove());
}
return sortedArray;
}
update(value, newValue) {
const index = this.search(value);
if (index === null){
return false;
}
this.arr.splice(index,1,newValue);
for (let i=0;i<Math.floor((this.arr.length)/2-1);i++){
this.#heapify(i);
}
}
removeValue(value) {
const index = this.search(value);
if (index === null) {
return false;
}
this.arr.splice(index, 1);
this.#heapify();
}
#heapify(index) {
const [childrenIndex1, childrenIndex2] = [index * 2 + 1, index * 2 + 2];
const smallerIndex =
(this.arr[childrenIndex1]||0) > (this.arr[childrenIndex2]||0)
? childrenIndex2
: childrenIndex1;
if (this.arr[smallerIndex] < this.arr[index]) {
let temp = this.arr[smallerIndex];
this.arr[smallerIndex] = this.arr[index];
this.arr[index] = temp;
}
}
}
const heap = new Heap();
console.log(heap.insert(3));
console.log(heap.insert(1));
console.log(heap.insert(7));
console.log(heap.insert(4));
console.log(heap.insert(6));
console.log(heap.insert(5));
console.log(heap.insert(8));
console.log("--------------------------");
heap.remove();
console.log("삭제 후 : "+heap.arr);
console.log("3 인덱스 검색 : "+heap.search(3));
heap.update(3, 9);
console.log("3 > 9 수정 : "+heap.arr);
console.log("힙 정렬 : " + heap.sort());
console.log("--------------------------");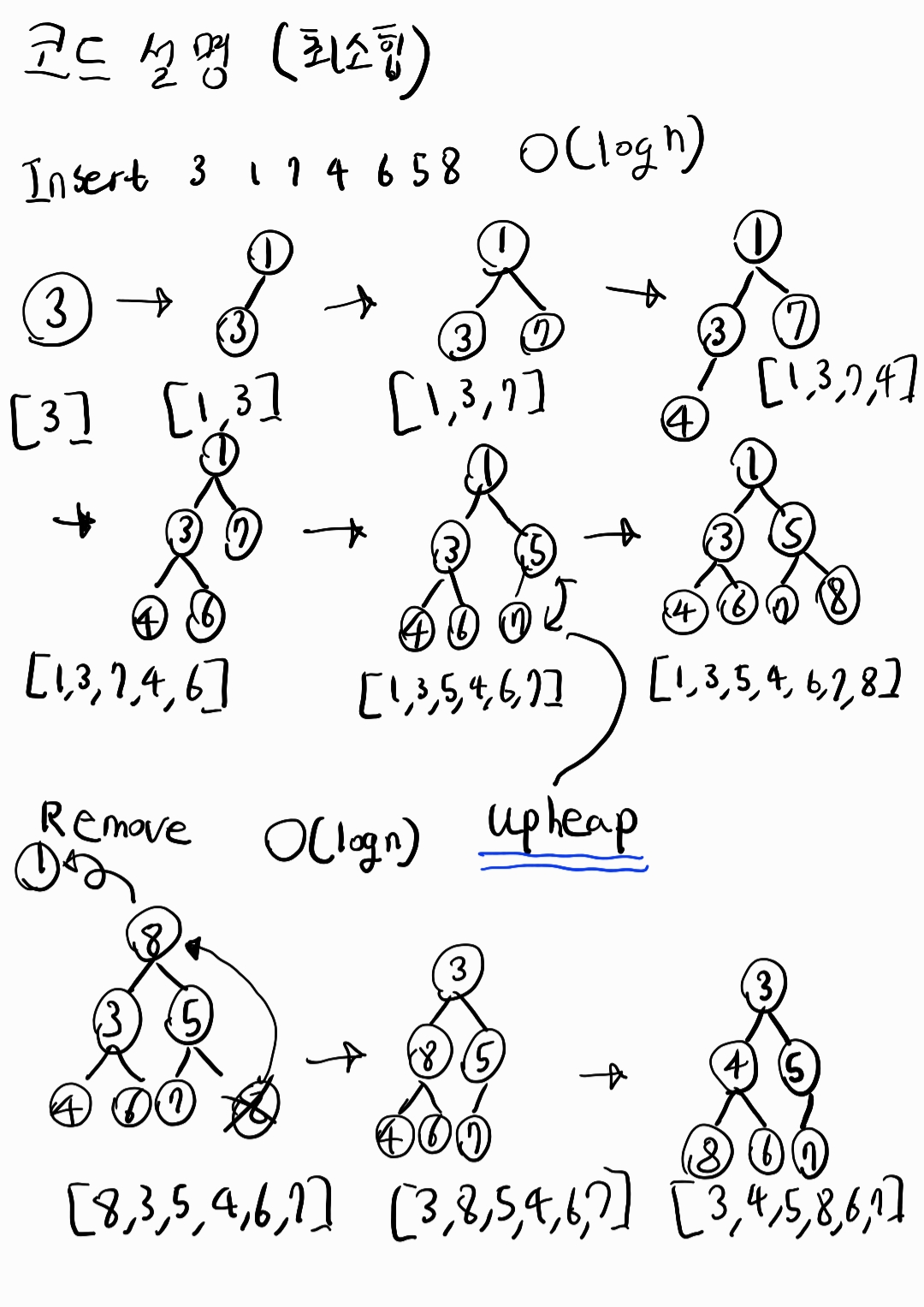
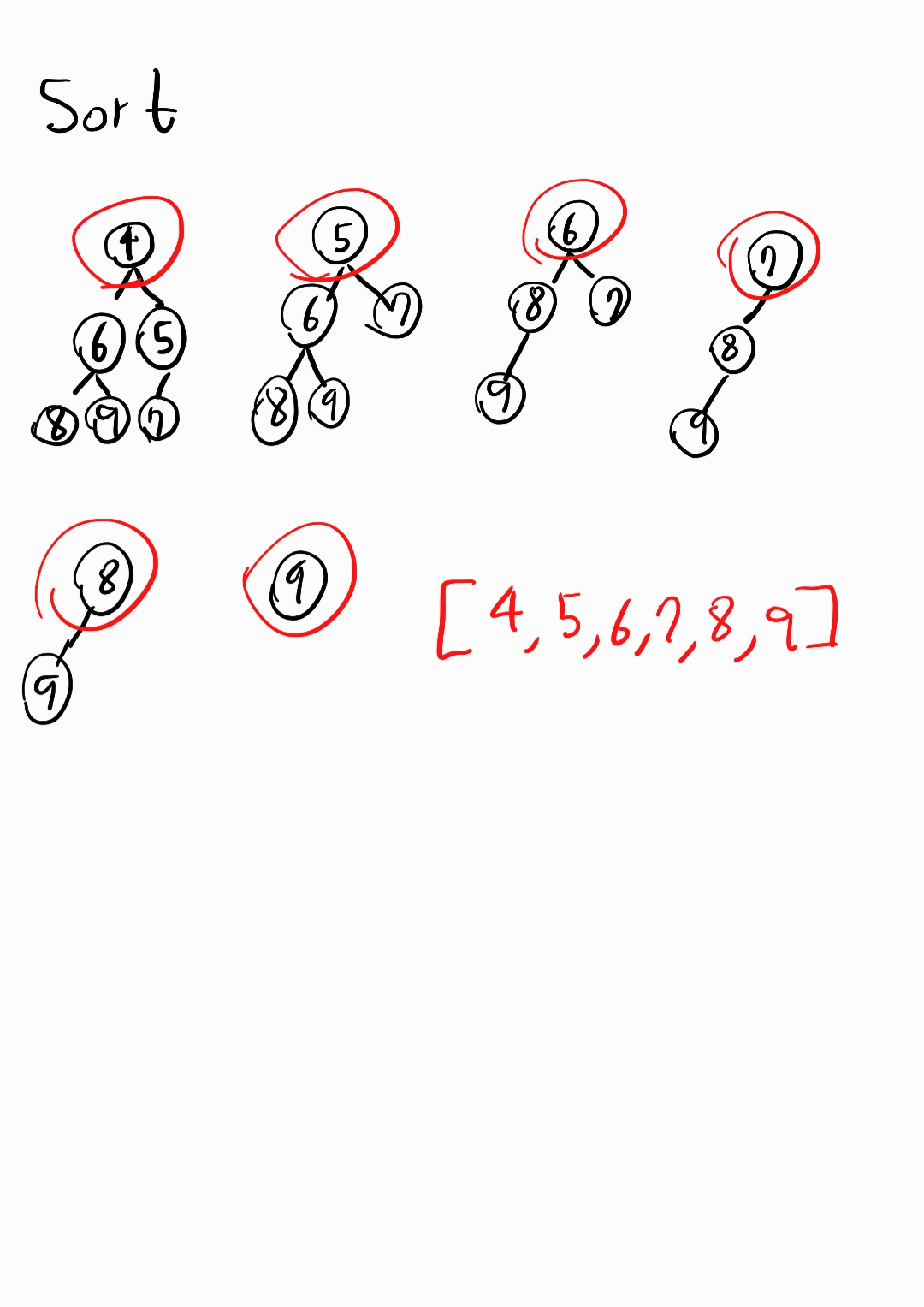
Reference
인프런 - 비전공자의 전공자 따라잡기 (제로초)
C언어로 쉽게 풀어쓴 자료구조 - 천인국,공용해,하상호
