Canvas API
Javascript와 HTML <canvas> 엘리먼트를 통해 그래픽을 그리기 위한 수단을 제공하는데 애니메이션, 게임 그래픽, 데이터 시각화, 실시간 비디오 처리 등의 목적으로 사용이 가능하다.
<canvas id="tutorial" width="150" height="150"></canvas><canvas>는 처음에는 src 및 alt 속성이 없다는 점만 제외하면 <img> 요소처럼 보입니다. 실제로 <canvas> 요소에는 width와 height의 두 속성만 있으며 직접 명시하거나 DOM 프로퍼티를 통해 설정할 수 있다. (기본값 width: 300px, height: 150px)
렌더링 컨텍스트
<canvas> 엘리먼트는 고정 크기의 드로잉 영역을 생성하고 하나 이상의 렌더링 컨텍스(rendering contexts)를 노출하여, 출력할 컨텐츠를 생성하고 다루게 됩니다. 이 포스팅에서는 2D 렌더링 컨텍스트를 집중적으로 다룹니다.
캔버스는 처음에 비어있고 무언가를 표시하기 위해서 <canvas> 요소는 getContext() 메서드를 이용해 랜더링 컨텍스트와 그리기 함수들을 사용할 수 있습니다.
getContext() 메서드는 렌더링 컨텍스트 타입을 지정하는 하나의 파라미터를 가집니다. 2D 그래픽의 경우, CanvasRenderingContext2D을 얻기위해 "2d"로 지정합니다.
const canvas = document.getElementById("tutorial");
const ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");경로기반 그리기
경로는 점들의 집합이며, 선의 한 부분으로 연결되어 여러가지 도형, 곡선을 이루고 두께와 색을 나타내게 된다. 경로를 이용하여 도형을 만들 때에는 몇가지 추가적인 단계를 거쳐야 한다.
beginPath(): 경로(path) 초기화, 이전의 경로를 모두 지우고 새로운 경로 생성closePath(): 경로(path) 종료, 시작점과 현재 점까지 연결된 직선을 추가한다.stroke(): 경로를 윤곽선을 이용하여 연결하는 도형을 그린다.fill(): 경로의 내부를 채운 도형을 그린다. fill의 경우 별도로closePath()호출을 하지 않아도 된다.
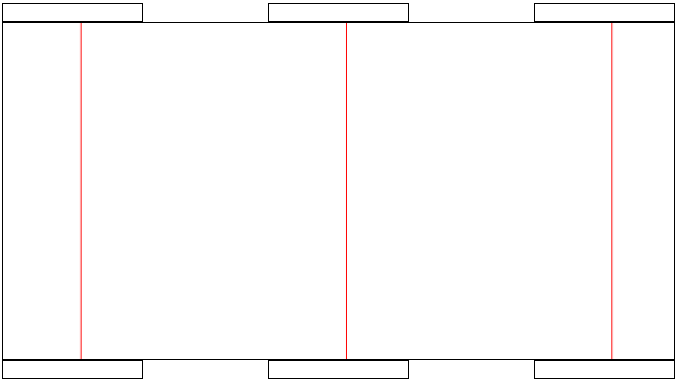
가변 크기의 캔버스
canvas 엘리먼트에 명시적으로 width, height 속성을 지정하지 않은 경우 별도로 css를 통해 크기를 제어한다면 그리기 메소드들의 좌표위치값들이 왜곡이 일어날 수 있으므로 자바스크립트를 통한 요소의 크기를 동적으로 제어해줘야 한다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ko">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./styles.css" />
<script src="./index.js" defer></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="container-input">
<input type="text" class="player" />
<input type="text" class="player" />
<input type="text" class="player" />
</div>
<canvas id="tutorial"></canvas>
<div class="container-input">
<input type="text" class="destination" />
<input type="text" class="destination" />
<input type="text" class="destination" />
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>// css
#tutorial {
border: solid 1px black;
}
.container {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
.container-input {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
}
input {
border: solid 1px black;
width: 20%;
}// js
const playerList = document.querySelectorAll(".player");
const destination = document.querySelectorAll(".destination");
const canvas = document.getElementById("tutorial");
const canvasRect = canvas.getBoundingClientRect();
const ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
// 동적 크기를 반드시 할당하자.
canvas.width = canvasRect.width;
canvas.height = canvasRect.height;
ctx.strokeStyle = "red";
for (let i = 0; i < playerList.length; i++) {
const startRect = playerList[i].getBoundingClientRect();
const endRect = destination[i].getBoundingClientRect();
const startX = startRect.left + startRect.width / 2;
const startY = 0;
const endX = endRect.left + endRect.width / 2;
const endY = canvasRect.height;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(startX, startY);
ctx.lineTo(endX, endY);
ctx.stroke();
ctx.closePath();
}