📌 About
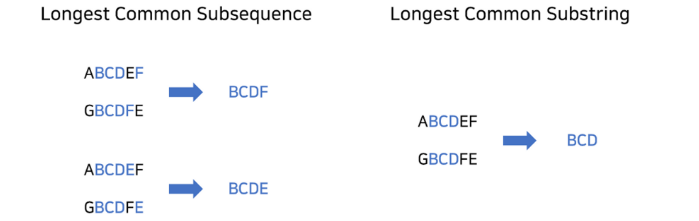
LCS 알고리즘은 Longest Common Subsequence의 약자로 두 문자열에 대해 공통 문자로 이루어진 최장 길이 문자열을 구하는 알고리즘이다. Longest Common Substring의 약자이기도 하나 일반적으로는 subsequence를 의미한다. 두 알고리즘의 차이는 아래와 같다.
📌 Algorithm
LCS 알고리즘은 2차원 배열의 DP 방식으로 이루어진다.
String strI = 문자열
String strJ = 문자열
int[][] lsc = new int[strI.length() + 1][strJ.length()];📍 Compare Chars
이중 for문으로 lcs 배열을 탐색하면서 알고리즘에 따라 아래대로 DP를 수행하면 된다.
- Longest Common Subsequence
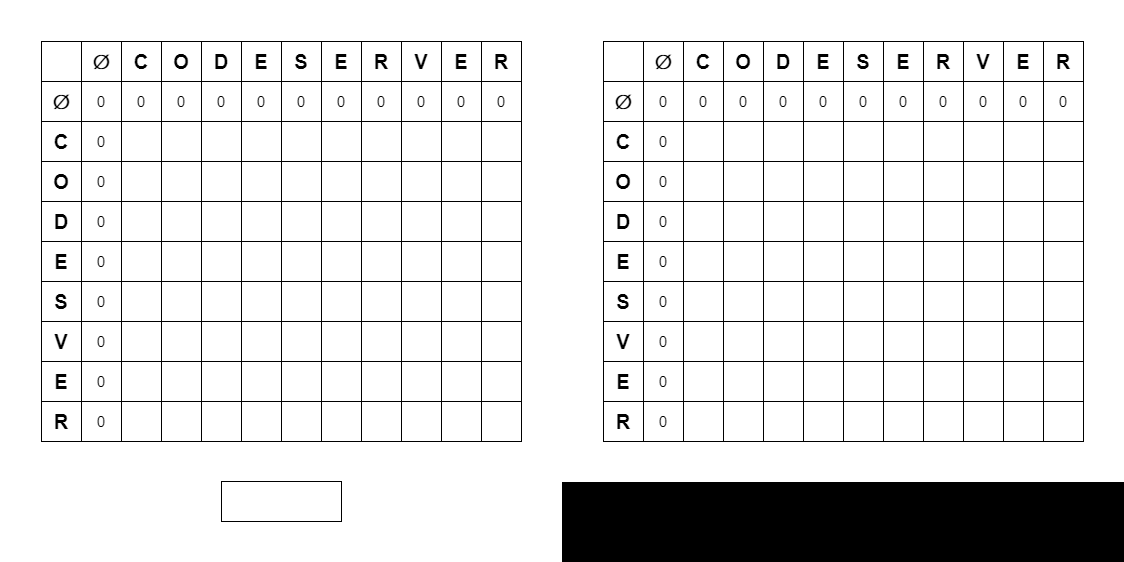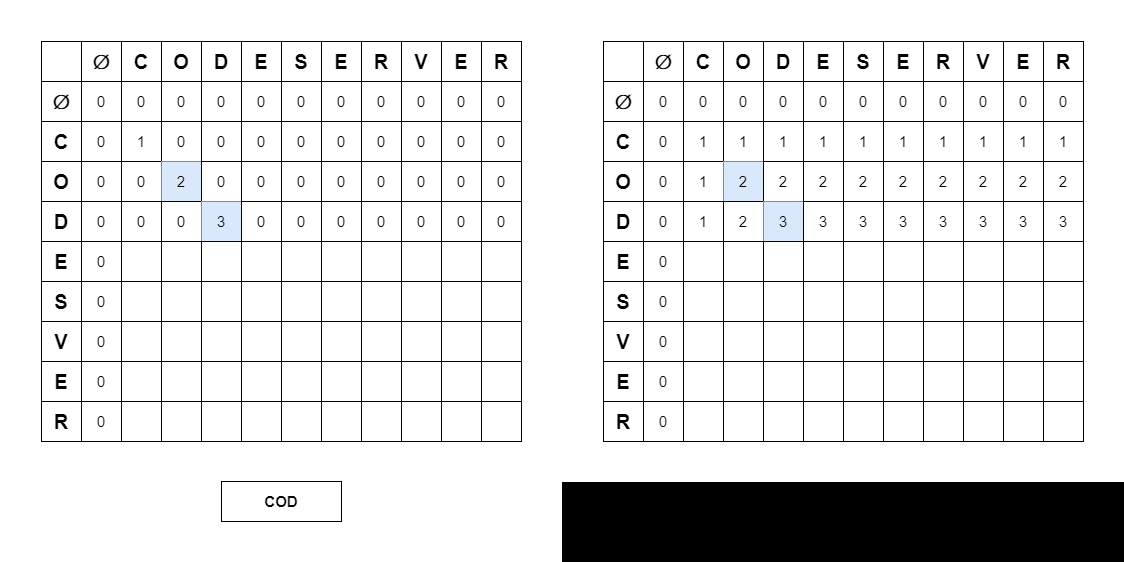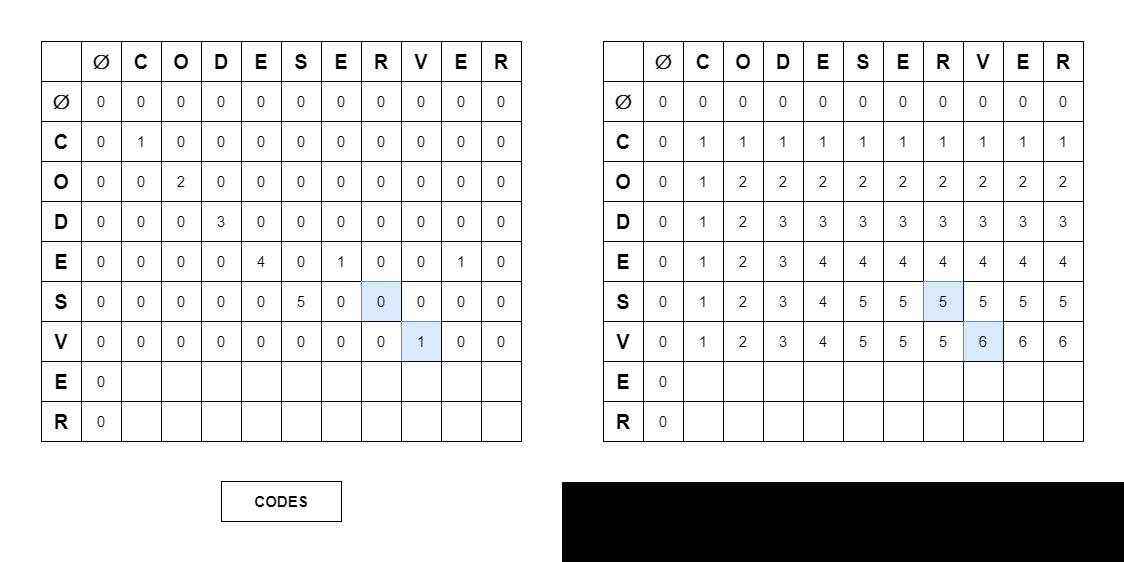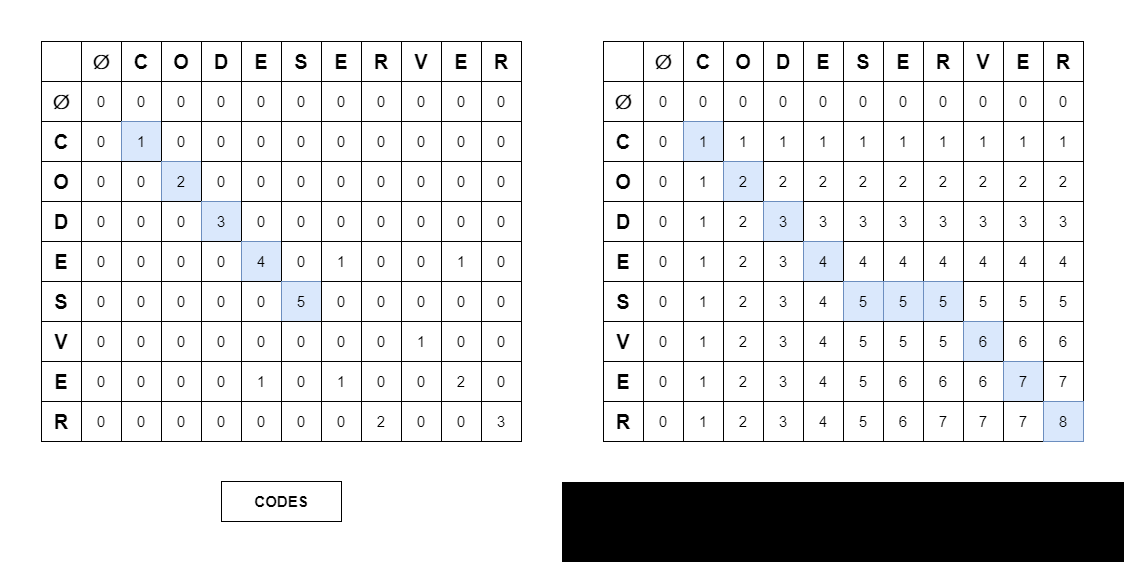
if (strI.charAt(i - 1) == strJ.charAt(j - 1))
lcs[i][j] = lcs[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
else lcs[i][j] = Math.max(lcs[i - 1][j], lcs[i][j - 1]);- Longest Common Substring
if (strI.charAt(i - 1) == strJ.charAt(j - 1))
lcs[i][j] = lcs[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
// else lcs[i][j] = 0; -> 배열을 처음부터 0으로 초기화되기 때문에 해당 코드는 불필요하다.📍 Search Common String
위의 방식으로 최장 길이는 구할 수 있지만 최장 공통 문자열은 따로 구해야 한다.
LCS(Subsequence)는 lcs[strI.length()][strJ.length()]가 최장 길이이다.
여기서부터 역으로 찾아올라가면 된다.
private String findCommonString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
int i = strI.length();
int j = strJ.length();
while (lcs[i][j] != 0) {
if (lcs[i - 1][j] == lcs[i][j]) i--;
else if (lcs[i][j - 1] == lcs[i][j]) j--;
else {
builder.append(strI.charAt(i - 1));
i--;
j--;
}
}
return builder.reverse().toString();
}LCS(Substring)과 같은 경우는 문자들을 비교할 때 같이 찾으면 된다.
private String compareSubstringChars() {
String common = "";
for (int i = 1; i <= strI.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= strJ.length(); j++) {
if (strI.charAt(i - 1) == strJ.charAt(j - 1)) {
lcs[i][j] = lcs[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
String string = strI.substring(i - lcs[i][j], i);
if (common.length() < string.length()) common = string;
}
}
}
return common;
}📌 Code
public class LCS {
private final String strI;
private final String strJ;
private int[][] lcs;
public LCS(String strI, String strJ) {
this.strI = strI;
this.strJ = strJ;
}
public String runSubsequence() {
initializeLCSArray();
compareSubsequenceChars();
return findCommonString();
}
public String runSubstring() {
initializeLCSArray();
return compareSubstringChars();
}
private void initializeLCSArray() {
lcs = new int[strI.length() + 1][strJ.length() + 1];
}
private void compareSubsequenceChars() {
for (int i = 1; i <= strI.length(); i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= strJ.length(); j++)
lcs[i][j] = strI.charAt(i - 1) == strJ.charAt(j - 1) ?
lcs[i - 1][j - 1] + 1 :
Math.max(lcs[i - 1][j], lcs[i][j - 1]);
}
private String compareSubstringChars() {
String common = "";
for (int i = 1; i <= strI.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= strJ.length(); j++) {
if (strI.charAt(i - 1) == strJ.charAt(j - 1)) {
lcs[i][j] = lcs[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
String string = strI.substring(i - lcs[i][j], i);
if (common.length() < string.length()) common = string;
}
}
}
return common;
}
private String findCommonString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
int i = strI.length();
int j = strJ.length();
while (lcs[i][j] != 0) {
if (lcs[i - 1][j] == lcs[i][j]) i--;
else if (lcs[i][j - 1] == lcs[i][j]) j--;
else {
builder.append(strI.charAt(i - 1));
i--;
j--;
}
}
return builder.reverse().toString();
}
}

