No. 2178
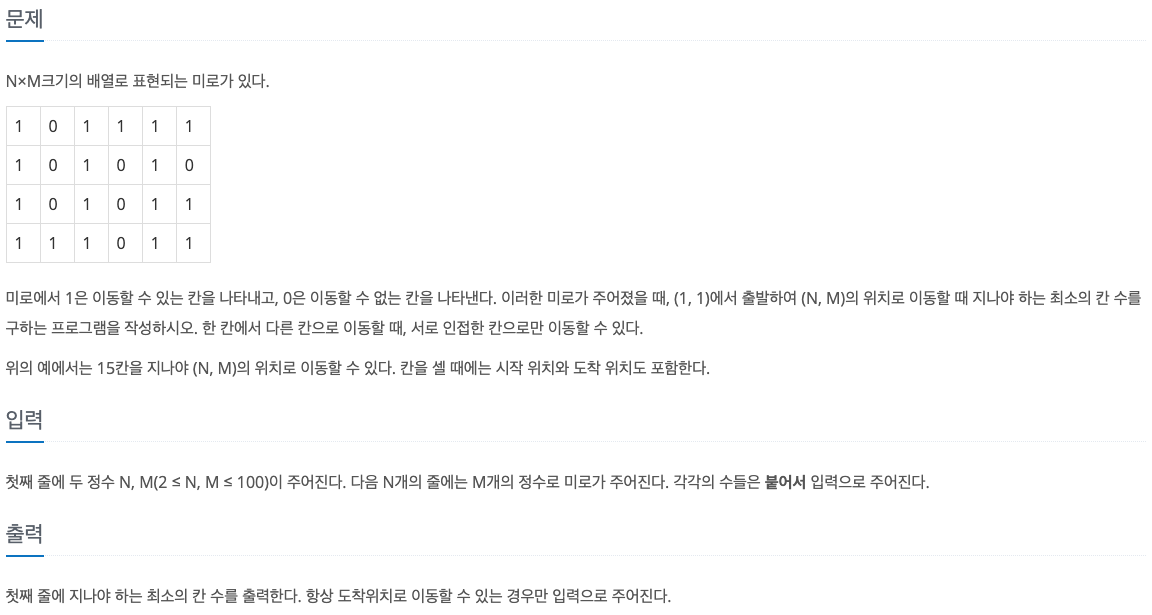
1. Problem
2. My Solution
- BFS 알고리즘을 이용하여 문제 해결
- 전형적인 BFS 알고리즘의 문제 유형 (최단거리)
- 첫 번째 방법
import sys
from collections import deque
def bfs(x,y):
queue = deque()
queue.append((x,y))
while(queue):
x,y = queue.popleft()
if x == n-1 and y == m-1:
print(maze[x][y])
exit()
for dx, dy in move:
nx = x + dx
ny = y + dy
if 0 <= nx < n and 0<= ny < m and maze[nx][ny] == 1:
queue.append((nx,ny))
maze[nx][ny] += maze[x][y]
n,m = map(int,sys.stdin.readline().rstrip().split())
maze = []
move = [(-1,0),(1,0),(0,-1),(0,1)]
for _ in range(n):
maze.append(list(map(int,list(sys.stdin.readline().rstrip()))))
bfs(0,0)- 두 번째 방법
- 매번 x == n-1 and y == m-1 비교하는 연산을 줄 일 수 있음
import sys
from collections import deque
def bfs(x,y):
queue = deque()
queue.append((x,y))
while(queue):
x,y = queue.popleft()
for dx, dy in move:
nx = x + dx
ny = y + dy
if 0 <= nx < n and 0<= ny < m and maze[nx][ny] == 1:
queue.append((nx,ny))
maze[nx][ny] += maze[x][y]
return maze[n-1][m-1]
n,m = map(int,sys.stdin.readline().rstrip().split())
maze = []
move = [(-1,0),(1,0),(0,-1),(0,1)]
for _ in range(n):
maze.append(list(map(int,list(sys.stdin.readline().rstrip()))))
print(bfs(0,0))No. 7576
1. Problem


2. My Solution
- 익은 사과들을 동시에 bfs 수행
- level 을 내려갈 때 마다 누적합 수행
import sys
from collections import deque
def bfs():
queue = deque()
# 익은 사과들 모두 동시에 bfs 수행
for i in start:
queue.append(i)
while(queue):
x,y = queue.popleft()
for dx, dy in move:
nx = x + dx
ny = y + dy
if 0 <= nx < n and 0 <= ny < m and tomatoes[nx][ny] == 0:
queue.append((nx,ny))
tomatoes[nx][ny] = tomatoes[x][y] + 1
m,n = map(int,sys.stdin.readline().rstrip().split())
tomatoes = []
start = []
move = [(-1,0),(1,0),(0,-1),(0,1)]
max_day = 0
for _ in range(n):
tomatoes.append(list(map(int,sys.stdin.readline().rstrip().split())))
# 익은 사과를 찾아서 해당 위치를 저장
for x in range(n):
for y in range(m):
if tomatoes[x][y] == 1:
start.append((x,y))
bfs()
for i in tomatoes:
if 0 in i:
print(-1)
exit()
max_day = max(max_day, max(i))
# start 사과부터 1일이라고 가정했으므로 -1
print(max_day-1)
No. 11725
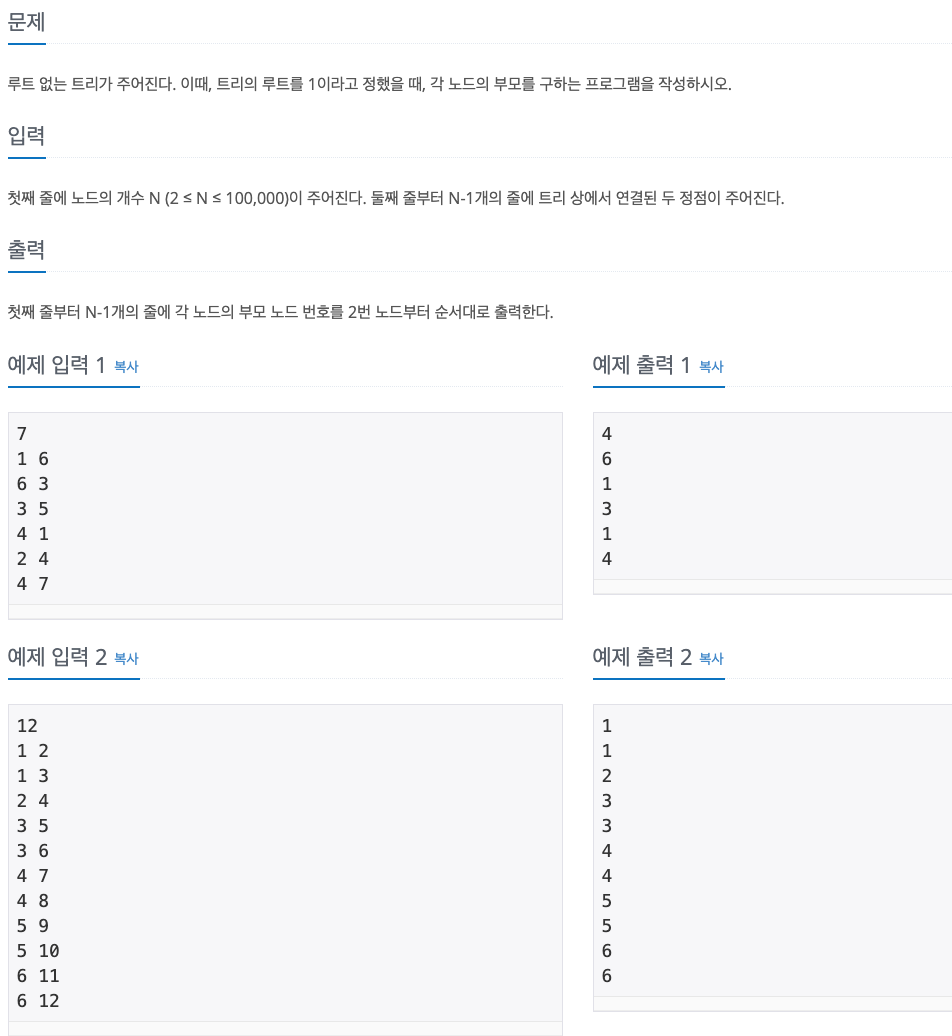
1. Problem
2. My Solution
- 각 노드의 연결된 노드 정보를 저장하고 있는 tree 리스트 생성
- 1을 루트라고 가정하면 1을 시작으로하는 bfs
import sys
from collections import deque
def bfs(v):
queue = deque()
queue.append(v)
visited[v] = True
while(queue):
v = queue.popleft()
for u in tree[v]:
if visited[u] == True:
continue
# 정점 v와 연결된 u의 부모를 v로 설정함
res[u] = v
queue.append(u)
visited[u] = True
n = int(sys.stdin.readline())
tree = [[] for _ in range(n+1)]
visited = [False] * (n+1)
res = [0] * (n+1)
for _ in range(n-1):
a,b = map(int,sys.stdin.readline().rstrip().split())
tree[a].append(b)
tree[b].append(a)
bfs(1)
for i in range(2,n+1):
print(res[i]) No. 2775
1. Problem
2. My Solution
- 첫 번째 방법
- 층, 호수, 누적합을 위해서 3중 for 문을 구현
import sys
test_n = int(sys.stdin.readline())
for _ in range(test_n):
k = int(sys.stdin.readline())
n = int(sys.stdin.readline())
apartment = [[0]*(n+1) for _ in range(k+1)]
apartment[0] = [i for i in range(n+1)]
for i in range(1,k+1):
for j in range(1,n+1):
for z in range(1,j+1):
apartment[i][j] += apartment[i-1][z]
print(apartment[k][n])- 최종 코드
- 여러 테스트 케이스가 입력으로 들어올 때는 답을 미리 구해 놓으면 속도가 더 빠름
- index 순서대로 누적합을 구할 때는 sum + slicing 기법을 이용
import sys
room = [list(range(1,15))] # 0층 주민들
for i in range(14):
room.append([sum(room[i][0:j]) for j in range(1,15)])
test_n = int(sys.stdin.readline().strip())
for i in range(test_n):
k = int(sys.stdin.readline().strip())
n = int(sys.stdin.readline().strip())
print(room[k][n-1])
3. Learned
- index 순서대로 누적합을 구할 때는 sum + slicing 기법을 이용하자
- 리스트를 append 하면서 리스트를 만들어나가도 됨