
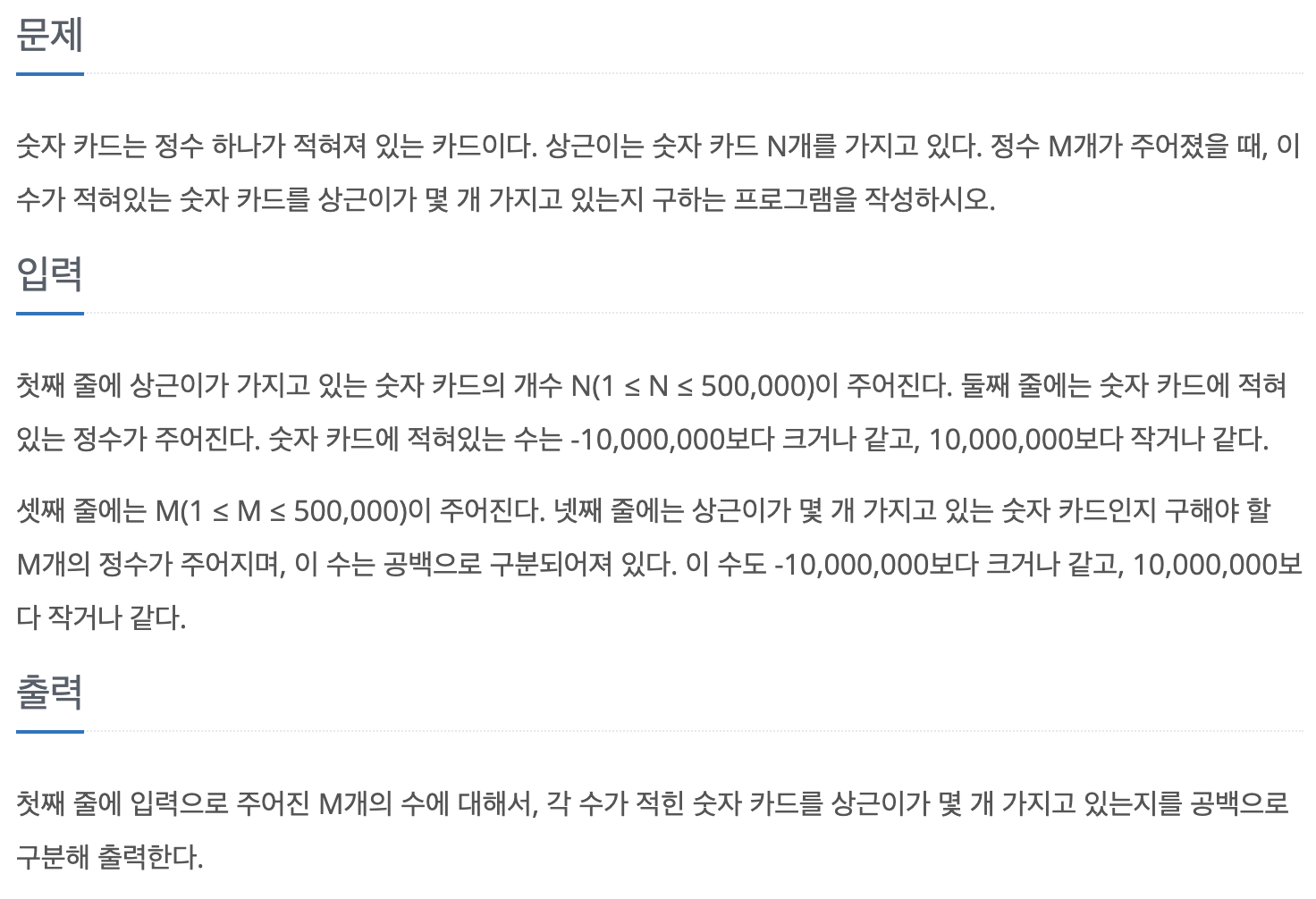
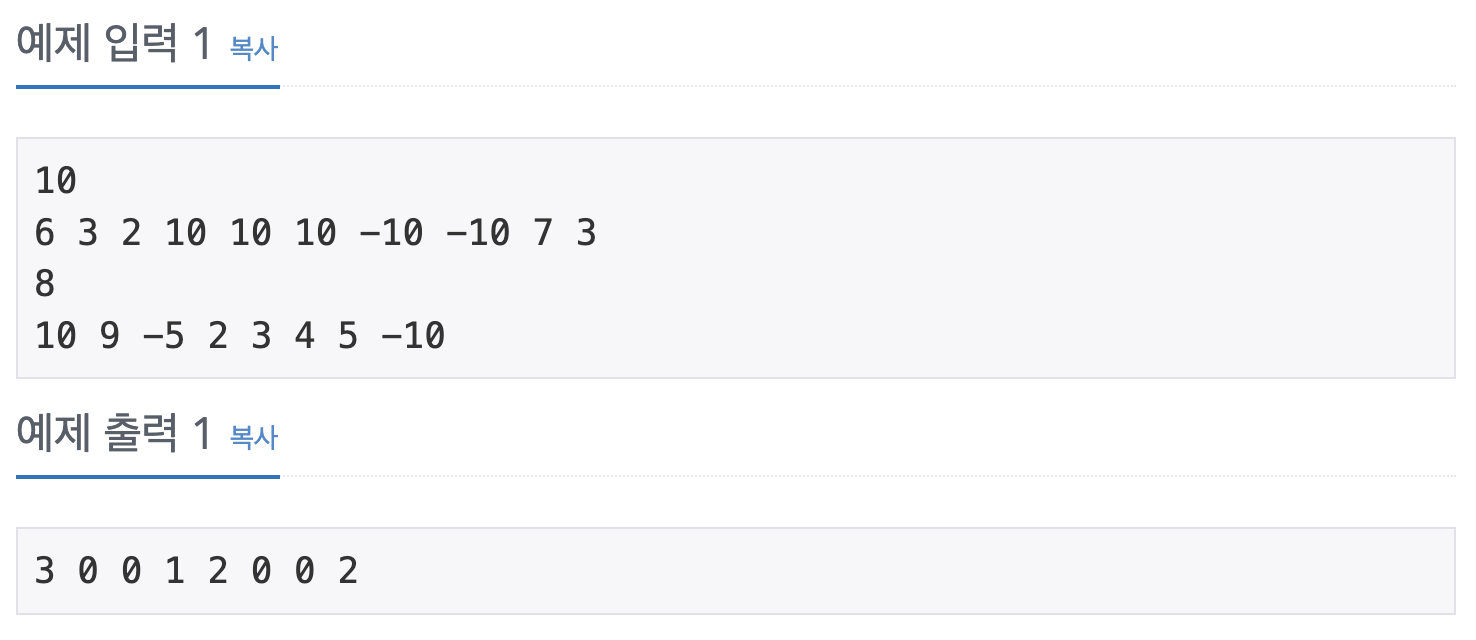
 https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/10816
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/10816
구현 과정
가지고 있는 전체 카드 중에서 해당 카드를 찾고, 해당 카드의 개수를 증가시키는 이 문제에서는 효율적인 검색 방법을 골라야 한다. 두 언어 모두 이분 탐색으로 구현해봤다.
주어진 배열을 일단 정렬하고 나면, 같은 숫자의 카드가 쭈르륵 붙어있기 때문에 해당 숫자가 (마지막으로 나타나는 위치 - 처음 나타나는 위치) 를 구하면 그게 해당 숫자 카드의 개수가 된다.
C에서의 구현
처음 나타나는 위치를 찾는 함수, 마지막으로 나타나는 위치를 찾는 함수를 따로 구현해준다.
Python에서의 구현
이진 탐색 기능을 제공하는 bisect 모듈을 사용했다.
bisect.bisect_left(arr, x)- x값 이상이 처음 나타나는 위치를 반환bisect.bisect_right(arr, x)- x값을 초과하는 첫 위치를 찾음
이렇게 left, right 인덱스를 구한 뒤, 그 값의 차로 x값의 개수를 구할 수 있다.
전체 코드
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int compare(const void *a, const void *b) {
int num1 = *(int *)a;
int num2 = *(int *)b;
return num1 - num2; // 오름차순 정렬
}
int lower_bound(int array[], int n, int target) {
int low = 0, high = n - 1;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (array[mid] < target)
low = mid + 1;
else
high = mid;
}
return low;
}
int upper_bound(int array[], int n, int target) {
int low = 0, high = n - 1;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) / 2 + 1;
if (array[mid] > target)
high = mid - 1;
else
low = mid;
}
return low;
}
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
int *cards = (int *)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &cards[i]);
}
qsort(cards, n, sizeof(int), compare);
int m;
scanf("%d", &m);
while (m--) {
int num;
scanf("%d", &num);
int low = lower_bound(cards, n, num);
int high = upper_bound(cards, n, num);
if (cards[low] == num && cards[high] == num)
printf("%d ", high - low + 1);
else
printf("0 ");
}
printf("\n");
free(cards);
return 0;
}Python
import sys
import bisect
input = sys.stdin.read
data = input().split()
n = int(data[0])
cards = list(map(int, data[1:n+1]))
m = int(data[n+1])
nums = list(map(int, data[n+2:n+2+m]))
cards.sort()
def countCards(arr, x):
left = bisect.bisect_left(arr, x)
right = bisect.bisect_right(arr, x)
return right - left
res = [countCards(cards, num) for num in nums]
print(" ".join(map(str, res)))