Chapter. 비동기
🍩 비동기
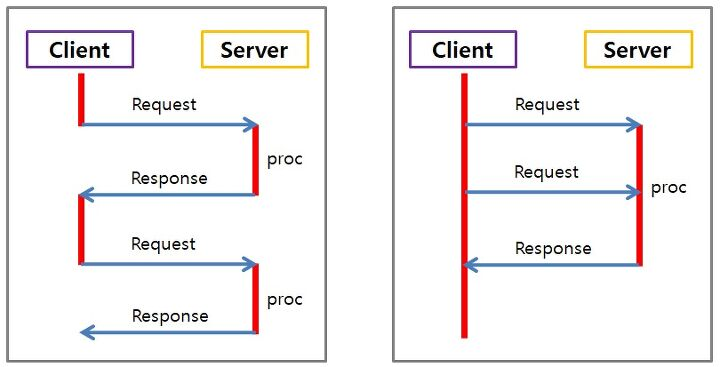
동기 : 순차적으로 일을 처리하는 것
비동기 : 일처리를 하면서 동시다발적으로 각각 일을 처리하는 것
ie) 백그라운드 실행, 로딩창 / 인터넷에서 서버로 요청을 보내고 응답을 기다리기 / 큰 용량의 파일을 로딩
🍩 callback
어떤 함수에 인자로 쓰이는 함수
fs.readFile(path or filename, [options], callback);🍩 promise
프로미스가 생성될 시점에 꼭 알 수 있지는 않은 값을 위한 대리자
비동기 처리에 사용되는 객체
비동기 연산이 종료된 이후의 결과값 혹은 실패 이유를 처리하기 위한 처리기를 연결
API가 실행될 때 서버에서 데이터를 받아오기도 전에 데이터를 다 받아온 것 처럼
화면에 데이터를 표시하려고 하면 오류나 빈 화면이 렌더링 되는데,
이 문제점을 해결하기 위한 방법 중 하나
- pending : 이행하거나 거부되지 않은 초기 상태
- fufilled : 연산이 성공적으로 완료됨
- rejected : 연산이 실패함
생성자 Promise()
const promise1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(()=> {
resolve('result')
},1000)
})🍩 promise 메서드
Promise.all([promise1, promise2, ...])
순회 가능한 객체에 주어진 모든 프로미스가 이행한 후, 혹은
프로미스가 주어지지 않았을 때 이행하는 Promise를 반환
여러 프로미스의 결과를 집계할 때 사용
const promise1 = Promise.resolve(3);
const promise2 = 42;
const promise3 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(resolve, 100, 'foo');
});
Promise.all([promise1, promise2, promise3]).then((values) => {
console.log(values);
});
// expected output: Array [3, 42, "foo"]Promise.reace([promise1, promise2, ...])
iterable 안의 프로미스 중 가장 먼저 완료된 것으로 이행 혹은 거부
const promise1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(resolve, 500, 'one');
});
const promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(resolve, 100, 'two');
});
Promise.race([promise1, promise2]).then((value) => {
console.log(value);
// Both resolve, but promise2 is faster
});
// expected output: "two"
Promise.reject(reason)
주어진 이유로 거부하는 Promise 객체 반환
Promise.reject("Testing static reject").then(function(reason) {
// 호출되지 않음
}, function(reason) {
console.log(reason); // "Testing static reject"
});Promise.resolve(value)
주어진 값으로 이행하는 Promise.then 객체 반환
const promise1 = Promise.resolve(123);
promise1.then((value) => {
console.log(value);
// expected output: 123
});
🍩 Promise 프로토타입
- callback =>promise
const getDataFromFilePromise = filePath => {
return new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{//Promise 생성 매개변수에 resolve,reject 넣기
fs.readFile(filePath, 'utf8',(err, data)=>{
if(err){
reject(err);// 에러가 났을땐 reject함수가 에러값 반환
}else{
resolve(data);// 성공시엔 resolve함수가 데이터값 반환
}
})
})
};- promise chaining
const user1Path = path.join(__dirname, 'files/user1.json');
const user2Path = path.join(__dirname, 'files/user2.json');
const readAllUsersChaining = () => {
return getDataFromFilePromise(user1path)
.then(user1 =>{//.then으로 연결 정상적인 값만 반환 user1에 user1path값이 들어 있다.
return getDataFromFilePromise(user2path)
.then(user2 =>{//user2에 user2path 값이 들어있다.
return `[${user1},${user2}]`
})
})
.then(data => JSON.parse(data)) // 문자열을 객체화 시켜주기위해
}- Promise all
const readAllUsers = () => {
return Promise.all([
getDataFromFilePromise(user1Path),
getDataFromFilePromise(user2Path)
])
.then(([user1,user2]) =>{
return `[${user1},${user2}]`
})
.then(data => JSON.parse(data));
}Promise.catch()
거부된 케이스를 다루며 Promise를 리턴함
then.과 같은 방식으로 사용됨
const promise1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
throw 'Uh-oh!';
});
promise1.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
});
// expected output: Uh-oh!
Promise.then()
성공한 케이스의 콜백함수와 실패한 케이스의 콜백함수를 인자로 받아 Promise를 리턴
const promise1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('Success!');
});
promise1.then((value) => {
console.log(value);
// expected output: "Success!"
});Promise.filnally()
마지막으로 실행할 값을 받아 반환
🍩 async & await
비동기 코드를 쓰고 Promise를 더 읽기 쉽도록 만드는 문법
function() 앞에 async 키워드를 추가하여 await 키워드가 비동기 코드를 호출할 수 있게 함
async 키워드를 사용하면 return 을 반환함
fetch('coffee.jpg')
.then(response => response.blob())
.then(myBlob => {
let objectURL = URL.createObjectURL(myBlob);
let image = document.createElement('img');
image.src = objectURL;
document.body.appendChild(image);
})
.catch(e => {
console.log('There has been a problem with your fetch operation: ' + e.message);
});
}=>
async function myFetch() {
let response = await fetch('coffee.jpg');
let myBlob = await response.blob();
let objectURL = URL.createObjectURL(myBlob);
let image = document.createElement('img');
image.src = objectURL;
document.body.appendChild(image);
}
myFetch()
.catch(e => {
console.log('There has been a problem with your fetch operation: ' + e.message);
});
Chapter. Node.js
🍪 Node.js
로컬 환경에서 자바스크립트를 실행할 수 있는 비동기 이벤트 기반 자바스크립트 런타임
<script src="불러오고싶은_스크립트.js"></script>
로 HTML에서 JavaScript파일을 불러옴
반면 Node.js는 자바스크립트 코드 상단에 require를 사용하여 다른 파일을 불러옴
const fs = require('fs'); // 파일 시스템 모듈을 불러옵니다
const dns = require('dns'); // DNS 모듈을 불러옵니다
3rd party module은 built-in module이 아닌 외부모듈로,
npm install을 통해 설치함
Chapter. fetch
🥛 fetch
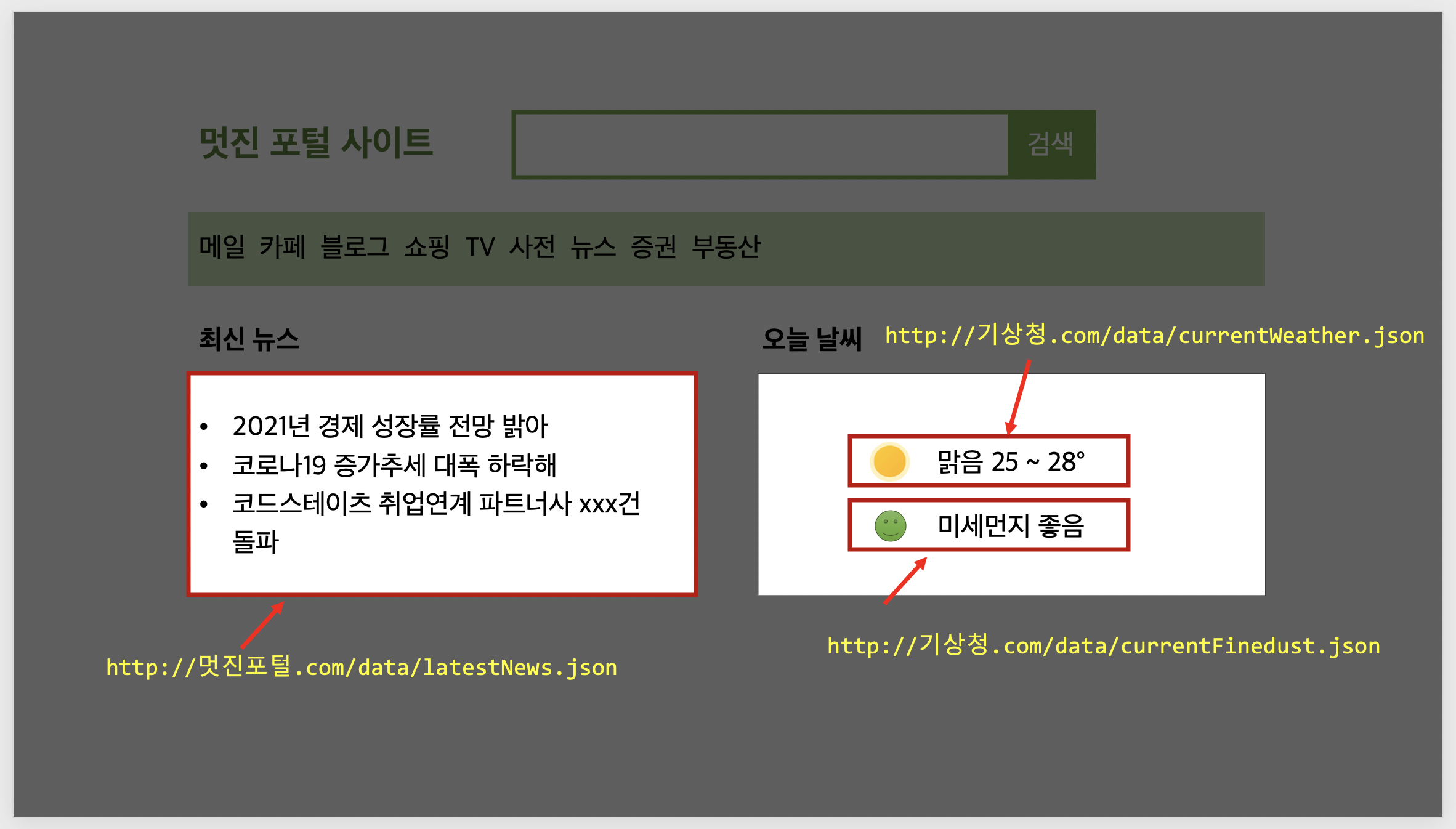
네트워크를 통해 비동기적으로 리소스를 가져오는 쉽고 논리적 방법을 제공
fetch API = Url로 요청하는 걸 가능하게 함
fetch()은 하나의 인수(가져올 리소스에 대한 경로)를 취하고 응답(Response객체)을 포함하는 promise를 반환함
fetch(url)
.then((response) => response.json()) // 자체적으로 json() 메소드가 있어, 응답을 JSON 형태로 변환시켜서 다음 Promise로 전달합니다
.then((json) => console.log(json)) // 콘솔에 json을 출력합니다
.catch((error) => console.log(error)); // 에러가 발생한 경우, 에러를 띄웁니다var newsURL = 'http://localhost:3000/data/latestNews';
var weatherURL = 'http://localhost:3000/data/weather';
function getNewsAndWeather() {
let obj = {};
return fetch(newsURL)
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
obj['news'] = data.data;
return fetch(weatherURL);
})
.then((response)=> response.json())
.then(data => {
obj['weather'] = data;
return obj;
})
}=>Promise.all
function getNewsAndWeatherAll() {
return Promise.all([
fetch(newsURL).then(response => response.json()),
fetch(weatherURL).then(response => response.json())
])
.then((data) =>{
return {news: data[0].data, weather : data[1]};
})
}=>async/await
async function getNewsAndWeatherAsync() {
let news = await fetch(newsURL).then(response => response.json())
let weather = await fetch(weatherURL).then(response => response.json())
return {news: news.data, weather : weather};
}