참고한 블로그 🙏
스위프트 | "(최소)힙 구현"하기 (Swift5 | Heap - MinHeap)
힙의 정의
최댓값 혹은 최솟값의 연산을 빠르게 하기 위해서 고안된 완전이진트리를 기반으로 한 자료구조를 의미합니다.
힙의 이진트리는 부모 node가 자식 node보다 더 작은 (혹은 큰) 구조를 유지하고 있습니다. 새로운 데이터가 들어 올 때 이 원칙으로 트리를 다시 정렬하고 데이터가 나갈 때도 마찬가지입니다.
간단하게 이야기하면 힙은 안에 데이터를 넣기만 하면 자동으로 정렬을 해주는 자료구조라고 볼 수 있습니다. 시간 복잡도는 O(logn)입니다.
힙의 원리
insert
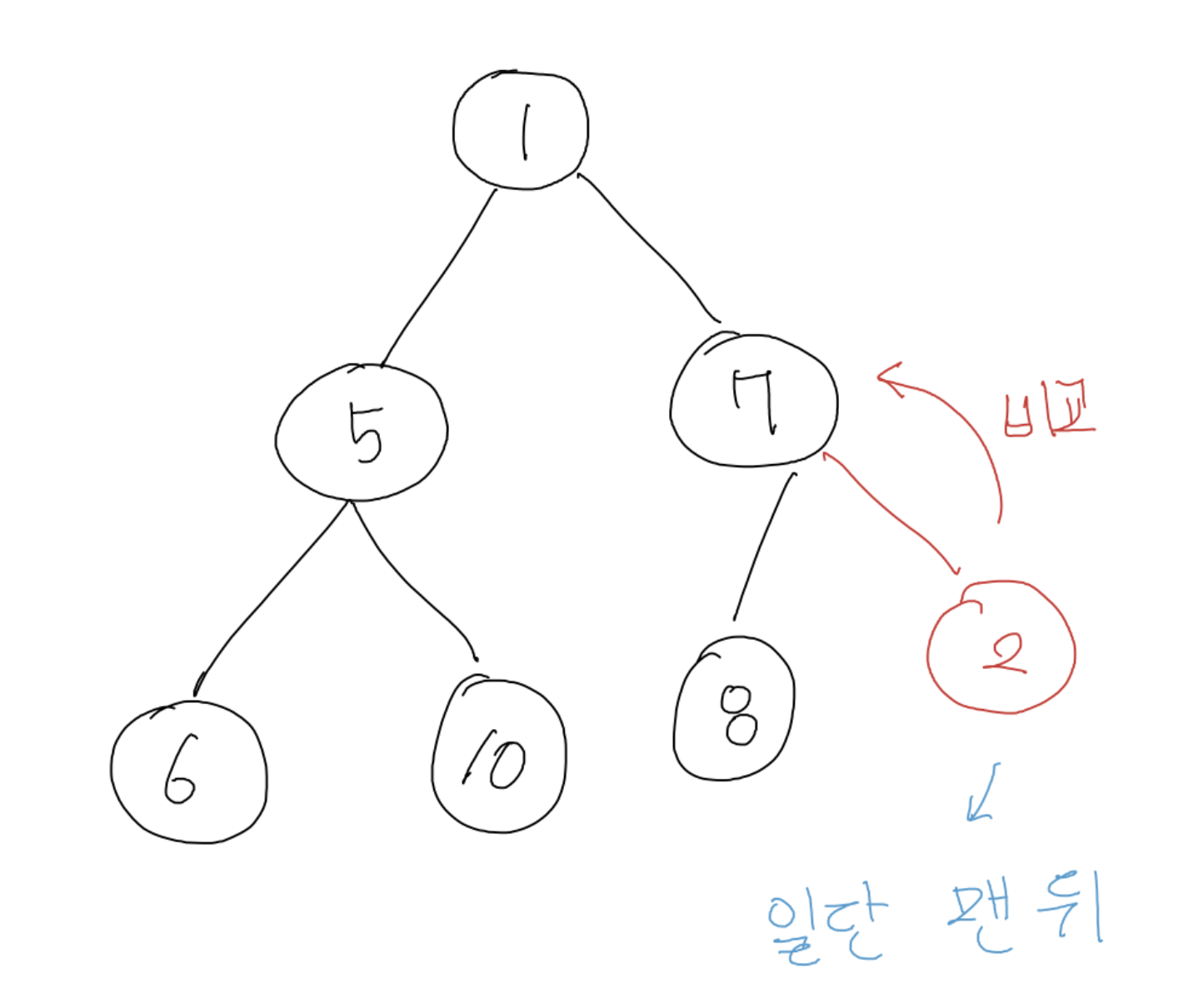
새로운 데이터를 insert할 때는 일단 힙의 맨 아래에 insert합니다. 그 이후에 부모 node와의 비교를 통해 부모 node보다 작으면 위로 올라가고 부모 node보다 크면 그대로 있는 방식으로 제자리를 찾아갑니다.
mutating func insert(_ element: T) {
//✅ 빈 heap이라면 init과 똑같은 동작
if heap.isEmpty {
heap.append(element)
heap.append(element)
return
}
//✅ 일단 맨 뒤에 넣고
heap.append(element)
//✅ 부모 node와 비교해서 올라갈지 여부를 결정하는 함수
func isMoveUp(_ insertIndex: Int) -> Bool {
if insertIndex <= 1 { //❓ 맨 위 (root node까지 올라왔을 때)
return false //❗️ 더 이상 올라갈 때 없으므로 false
}
let parentIndex = insertIndex / 2 //👉 부모 node의 index (짝수, 홀수 관계 없이 Int니까 반올림)
return heap[insertIndex] < heap[parentIndex] ? true : false //👉 부모 node와 값 비교
}
var insertIndex = heap.count - 1 //👉 가장 마지막 node의 index
//✅ 부모 node와 비교하면서 제자리를 찾아간다.
while isMoveUp(insertIndex) {
let parentIndex = insertIndex / 2
heap.swapAt(insertIndex, parentIndex) //👉 시간 복잡도 O(1)
insertIndex = parentIndex //👉 부모 node와 자리 바꾸었으므로 insertIndex 갱신
}
}pop
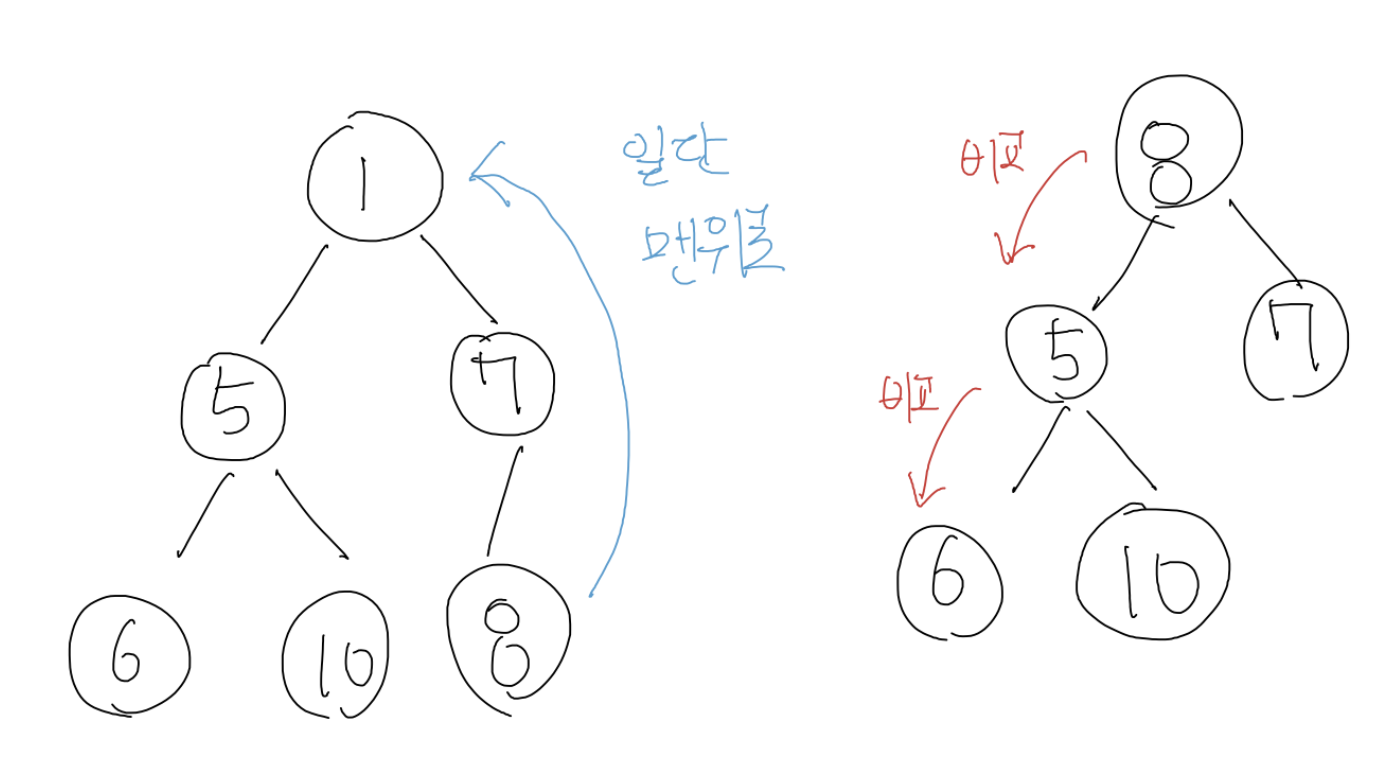
일단 pop할 node (이진 트리의 가장 상위에 위치한 데이터)를 가장 마지막 node와 바꾸고 pop합니다. 가장 상위 node를 자식 node들과 비교해 하면서 제자리를 찾아갑니다.
//✅ 어느 자식 node와 자리를 바꿀지
enum moveDownDirection { case left, right, none }
//✅ 자료 빼기
//👉 일단 맨 위로 올리고 제자리 찾아가기
mutating func pop() -> T? {
//✅ heap이 비었을 때
if heap.count <= 1 {
return nil
}
//✅ root node에 있는 자료를 리턴
let returnData = heap[1]
heap.swapAt(1, heap.count - 1) //👉 root node 맨 뒤로 보내고
heap.removeLast() //👉 pop하기
//✅ root node와 자리를 바꾼 맨 마지막 node의 원래 자리를 찾아주기 위한 함수
func moveDown(_ poppedIndex: Int) -> moveDownDirection {
//✅ 자식 node들의 index
let leftChildIndex = poppedIndex * 2 //👉 왼쪽은 2배
let rightChildIndex = leftChildIndex + 1 //👉 오른쪽은 2배 + 1
//1️⃣ 자식 node가 없는 경우 (왼쪽 자식만 확인하면 됨)
if leftChildIndex >= heap.count {
return .none //👉 더 이상 내려갈 곳이 없다. (제자리)
}
//2️⃣ 왼쪽 자식 node만 있는 경우
if rightChildIndex >= heap.count {
return heap[leftChildIndex] < heap[poppedIndex] ? .left : .none
//👉 왼쪽 자식 node와 비교해서 내가 더 크면 왼쪽과 swap
}
//3️⃣ 자식 node가 둘 다 있다.
//3️⃣ - 1 : 모든 자식 node들이 나보다 큰 경우
if (heap[leftChildIndex] > heap[poppedIndex]) && (heap[rightChildIndex] > heap[poppedIndex]) {
return .none //👉 swap할 필요가 없음
}
//3️⃣ - 2 : 모든 자식 node들이 나보다 작은 경우
if (heap[leftChildIndex] < heap[poppedIndex]) && (heap[rightChildIndex] < heap[poppedIndex]) {
return heap[leftChildIndex] < heap[rightChildIndex] ? .left : .right
//👉 두 자식 node 중에서 더 작은 쪽과 swap (작은 쪽이 부모로 올라가야 하니까)
}
//3️⃣ - 3 : 둘 중에 하나만 나보다 작은 경우
if (heap[leftChildIndex] < heap[poppedIndex]) || (heap[rightChildIndex] < heap[poppedIndex]) {
return heap[leftChildIndex] < heap[rightChildIndex] ? .left : .right
//👉 작은 쪽과 swap
}
return .none
}
//✅ heap 맨 위에서 제자리를 찾아가는 과정
var poppedIndex = 1
while true {
switch moveDown(poppedIndex) {
case .none:
return returnData
case .left:
let leftChildIndex = poppedIndex * 2
heap.swapAt(poppedIndex, leftChildIndex)
poppedIndex = leftChildIndex
case .right:
let rightChildIndex = (poppedIndex * 2) + 1
heap.swapAt(poppedIndex, rightChildIndex)
poppedIndex = rightChildIndex
}
}
}힙의 구현
🤔 index를 왜 1부터 시작할까? → 0부터 시작하게 되면 자식 node를 구할 때 예외처리를 해주어야 함. (0은 2배를 해도 0이므로)
// 최소힙 구현
import Foundation
struct MinHeap<T: Comparable> {
var heap: [T] = []
var isEmpty: Bool {
return heap.count <= 1 ? true : false
}
init() {}
// 첫 node를 가지고 init할 때
init(_ element: T) {
heap.append(element) //👉 0번 index 일부러 채우기 (아니면 예외처리 해야함)
heap.append(element) //👉 1번 index가 root node
}
//✅ 자료 넣기
// 👉 일단 자료에 넣고서 부모 node와 비교해가면서 위로 올린다.
mutating func insert(_ element: T) {
//✅ 빈 heap이라면 init과 똑같은 동작
if heap.isEmpty {
heap.append(element)
heap.append(element)
return
}
//✅ 일단 맨 뒤에 넣고
heap.append(element)
//✅ 부모 node와 비교해서 올라갈지 여부를 결정하는 함수
func isMoveUp(_ insertIndex: Int) -> Bool {
if insertIndex <= 1 { //❓ 맨 위 (root node까지 올라왔을 때)
return false //❗️ 더 이상 올라갈 때 없으므로 false
}
let parentIndex = insertIndex / 2 //👉 부모 node의 index (짝수, 홀수 관계 없이 Int니까 반올림)
return heap[insertIndex] < heap[parentIndex] ? true : false //👉 부모 node와 값 비교
}
var insertIndex = heap.count - 1 //👉 가장 마지막 node의 index
//✅ 부모 node와 비교하면서 제자리를 찾아간다.
while isMoveUp(insertIndex) {
let parentIndex = insertIndex / 2
heap.swapAt(insertIndex, parentIndex) //👉 시간 복잡도 O(1)
insertIndex = parentIndex //👉 부모 node와 자리 바꾸었으므로 insertIndex 갱신
}
}
//✅ 어느 자식 node와 자리를 바꿀지
enum moveDownDirection { case left, right, none }
//✅ 자료 빼기
//👉 일단 맨 위로 올리고 제자리 찾아가기
mutating func pop() -> T? {
//✅ heap이 비었을 때
if heap.count <= 1 {
return nil
}
//✅ root node에 있는 자료를 리턴
let returnData = heap[1]
heap.swapAt(1, heap.count - 1) //👉 root node 맨 뒤로 보내고
heap.removeLast() //👉 pop하기
//✅ root node와 자리를 바꾼 맨 마지막 node의 원래 자리를 찾아주기 위한 함수
func moveDown(_ poppedIndex: Int) -> moveDownDirection {
//✅ 자식 node들의 index
let leftChildIndex = poppedIndex * 2 //👉 왼쪽은 2배
let rightChildIndex = leftChildIndex + 1 //👉 오른쪽은 2배 + 1
//1️⃣ 자식 node가 없는 경우 (왼쪽 자식만 확인하면 됨)
if leftChildIndex >= heap.count {
return .none //👉 더 이상 내려갈 곳이 없다. (제자리)
}
//2️⃣ 왼쪽 자식 node만 있는 경우
if rightChildIndex >= heap.count {
return heap[leftChildIndex] < heap[poppedIndex] ? .left : .none
//👉 왼쪽 자식 node와 비교해서 내가 더 크면 왼쪽과 swap
}
//3️⃣ 자식 node가 둘 다 있다.
//3️⃣ - 1 : 모든 자식 node들이 나보다 큰 경우
if (heap[leftChildIndex] > heap[poppedIndex]) && (heap[rightChildIndex] > heap[poppedIndex]) {
return .none //👉 swap할 필요가 없음
}
//3️⃣ - 2 : 모든 자식 node들이 나보다 작은 경우
if (heap[leftChildIndex] < heap[poppedIndex]) && (heap[rightChildIndex] < heap[poppedIndex]) {
return heap[leftChildIndex] < heap[rightChildIndex] ? .left : .right
//👉 두 자식 node 중에서 더 작은 쪽과 swap (작은 쪽이 부모로 올라가야 하니까)
}
//3️⃣ - 3 : 둘 중에 하나만 나보다 작은 경우
if (heap[leftChildIndex] < heap[poppedIndex]) || (heap[rightChildIndex] < heap[poppedIndex]) {
return heap[leftChildIndex] < heap[rightChildIndex] ? .left : .right
//👉 작은 쪽과 swap
}
return .none
}
//✅ heap 맨 위에서 제자리를 찾아가는 과정
var poppedIndex = 1
while true {
switch moveDown(poppedIndex) {
case .none:
return returnData
case .left:
let leftChildIndex = poppedIndex * 2
heap.swapAt(poppedIndex, leftChildIndex)
poppedIndex = leftChildIndex
case .right:
let rightChildIndex = (poppedIndex * 2) + 1
heap.swapAt(poppedIndex, rightChildIndex)
poppedIndex = rightChildIndex
}
}
}
}주석 제거 버전
// 최소힙 구현
import Foundation
struct MinHeap<T: Comparable> {
var heap: [T] = []
var isEmpty: Bool {
return heap.count <= 1 ? true : false
}
init() {}
init(_ element: T) {
heap.append(element)
heap.append(element)
}
mutating func insert(_ element: T) {
if heap.isEmpty {
heap.append(element)
heap.append(element)
return
}
heap.append(element)
func isMoveUp(_ insertIndex: Int) -> Bool {
if insertIndex <= 1 {
return false
}
let parentIndex = insertIndex / 2
return heap[insertIndex] < heap[parentIndex] ? true : false
}
var insertIndex = heap.count - 1
while isMoveUp(insertIndex) {
let parentIndex = insertIndex / 2
heap.swapAt(insertIndex, parentIndex)
insertIndex = parentIndex
}
}
enum moveDownDirection { case left, right, none }
mutating func pop() -> T? {
if heap.count <= 1 {
return nil
}
let returnData = heap[1]
heap.swapAt(1, heap.count - 1)
heap.removeLast()
func moveDown(_ poppedIndex: Int) -> moveDownDirection {
let leftChildIndex = poppedIndex * 2
let rightChildIndex = leftChildIndex + 1
if leftChildIndex >= heap.count {
return .none
}
if rightChildIndex >= heap.count {
return heap[leftChildIndex] < heap[poppedIndex] ? .left : .none
}
if (heap[leftChildIndex] > heap[poppedIndex]) && (heap[rightChildIndex] > heap[poppedIndex]) {
return .none
}
if (heap[leftChildIndex] < heap[poppedIndex]) && (heap[rightChildIndex] < heap[poppedIndex]) {
return heap[leftChildIndex] < heap[rightChildIndex] ? .left : .right
}
if (heap[leftChildIndex] < heap[poppedIndex]) || (heap[rightChildIndex] < heap[poppedIndex]) {
return heap[leftChildIndex] < heap[rightChildIndex] ? .left : .right
}
return .none
}
var poppedIndex = 1
while true {
switch moveDown(poppedIndex) {
case .none:
return returnData
case .left:
let leftChildIndex = poppedIndex * 2
heap.swapAt(poppedIndex, leftChildIndex)
poppedIndex = leftChildIndex
case .right:
let rightChildIndex = (poppedIndex * 2) + 1
heap.swapAt(poppedIndex, rightChildIndex)
poppedIndex = rightChildIndex
}
}
}
}