
Introduction
분산락 (Distributed Lock) 을 사용하는 이유?
- 분산 환경에서 공유 자원에 관한 상호 배제(mutual exclusion) 을 보장하기 위해 사용한다.
- 공유 자원의 임계 영역을 접근하는 가능 여부를 확인하여 분산 환경의 원자성(atomic) 을 보장할 수 있다.
분산락을 Tx commit 이후 해제해야 하는 이유
동시성 환경에서 데이터 정합성을 위함이다. 락을 먼저 해제할 경우, 선행 트랜잭션의 내용이 반영되지 않고 후행 트랜잭션 내용만 반영되는 second lost updates problem 문제가 발생할 수 있다.
테스트 해보자
1. 도메인 구성
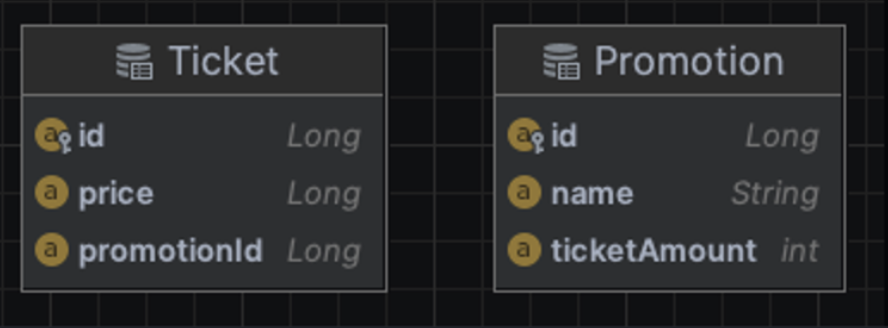
Promotion
@Entity
@Getter
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
public class Promotion {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(length = 20)
private Long id;
@Getter
@Column(length = 100, nullable = false)
private String name;
@Column(length = 20, nullable = false)
private int ticketAmount; // shared resources (warning race condition!)
public Promotion(final String name, final int ticketAmount) {
this.name = name;
this.ticketAmount = ticketAmount;
}
public void decreaseTicketAmount() {
this.ticketAmount -= 1;
}
public boolean soldOut() {
return ticketAmount <= 0;
}
public int remainingTickets() {
return this.ticketAmount;
}
}Ticker
@Entity
@NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
public class Ticket {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(length = 15, nullable = false)
private Long price;
@Column(length = 20, nullable = false)
private Long promotionId;
public Ticket(final Long price, final Long promotionId) {
this.price = price;
this.promotionId = promotionId;
}
}- 연관관계를 사용하는 경우
- 장점
-
매번 티켓 수를 조회하기 위한 조회 쿼리를 동작하므로
race condition에 관해 할 필요가 없다.다만, 여러 트랜잭션이 insert 하는 시점에 따라 티켓 사이즈가 정확히 일치하는 않는 이슈가 발생할 수 있다.
-
Promotion 안에 Ticket 을 관리하는 형태로
로직을 응집화할 수 있는 장점이 있다.
-
- 단점
- 생성된 티켓 수를 확인하기 위한 조회 쿼리가 필요하다.
- Ticket 테이블의 데이터양이 증가함에 따라 인덱스의 데이터 추가와 DB 부하를 줄 수 있다.
- 생성된 티켓 수를 확인하기 위한 조회 쿼리가 필요하다.
- 장점
- 연관 관계를 사용하지 않는 경우(티켓 잔여량을 관리하는 컬럼 활용하는 경우)
- 장점
- 티켓 사이즈를 확인하는 부수적 쿼리를 발생하지 않아
index row insert,query 수행에 관한 DB 부하를 줄일 수 있는 장점이 있다.
- 티켓 사이즈를 확인하는 부수적 쿼리를 발생하지 않아
- 단점
- 잔여 티켓 데이터의
race condition을 고려해야 한다. 동시 접근할 경우, 데이터 정합성이 깨질 수 있다.
- 잔여 티켓 데이터의
- 장점
2. JMeter 를 이용한 테스트
| index | api | explanation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | /api/v1/promotions/{promotionId}/ticket | @Transactional |
| 2 | /api/v2/promotions/{promotionId}/ticket | rLock.unlock()-> @Transactional commit |
| 3 | /api/v3/promotions/{promotionId}/ticket | @Transactional commit -> rLock.unlock() |
(1) ticketAmount, user 100개 동일하게 세팅
(1) thread condition
(2) 100개 HTTP Requests
| type | 잔여 티켓 수 | 실제 생성 티켓 | 데이터 정합성 유지 |
|---|---|---|---|
| @Transactional | 45 / 100 | 100 | X |
| rLock.unlock()→ @Transactional commit | 38 / 100 | 100 | X |
| @Transactional commit → rLock.unlock() | 0 / 100 | 100 | O |
