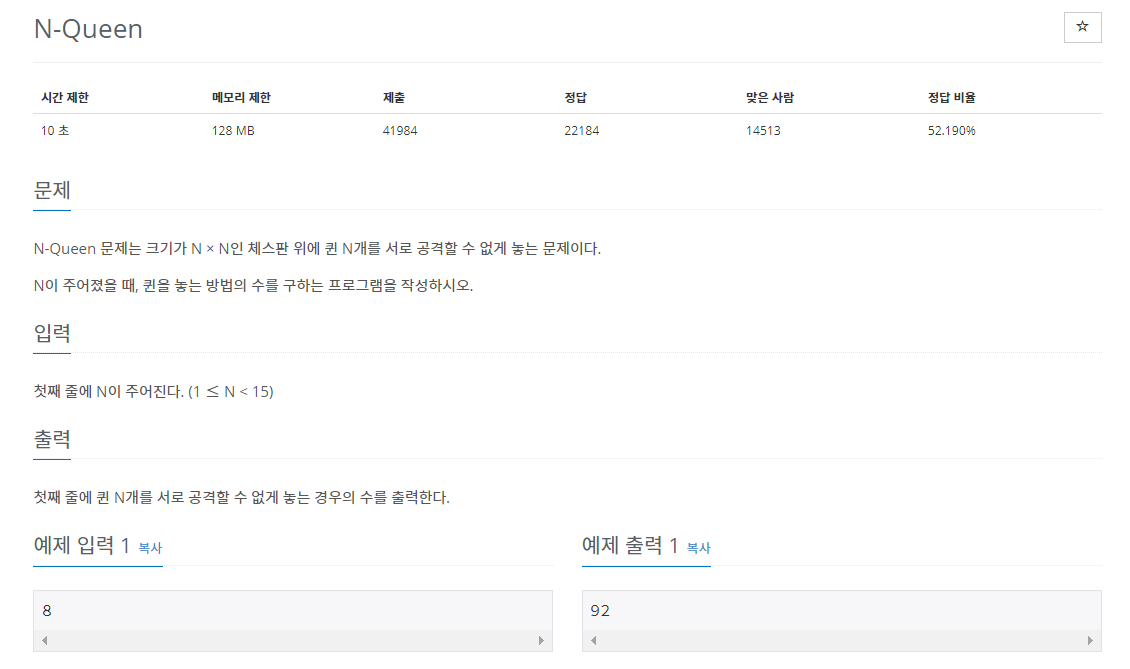
백준
1. Python
def check(n):
for i in range(n):
if row[n] == row[i] or abs(row[n]-row[i]) == n-i:
return 0
return 1
def dfs(n):
global res
if n == N:
res += 1
else:
for i in range(N):
row[n] = i
if check(n):
dfs(n+1)
N = int(input())
row = [0]*N
res = 0
dfs(0)
print(res)
출처: https://jinho-study.tistory.com/979
n = int(input())
def dfs(arr):
global ans
length = len(arr)
if length==n:
ans+=1
return
candidate = list(range(n))
for i in range(length):
if arr[i] in candidate:
candidate.remove(arr[i])
distance = length - i
if arr[i] + distance in candidate:
candidate.remove(arr[i] + distance)
if arr[i] - distance in candidate:
candidate.remove(arr[i] - distance)
if candidate:
for i in candidate:
arr.append(i)
dfs(arr)
arr.pop()
else:
return
ans = 0
for i in range(n):
dfs([i])
print(ans)
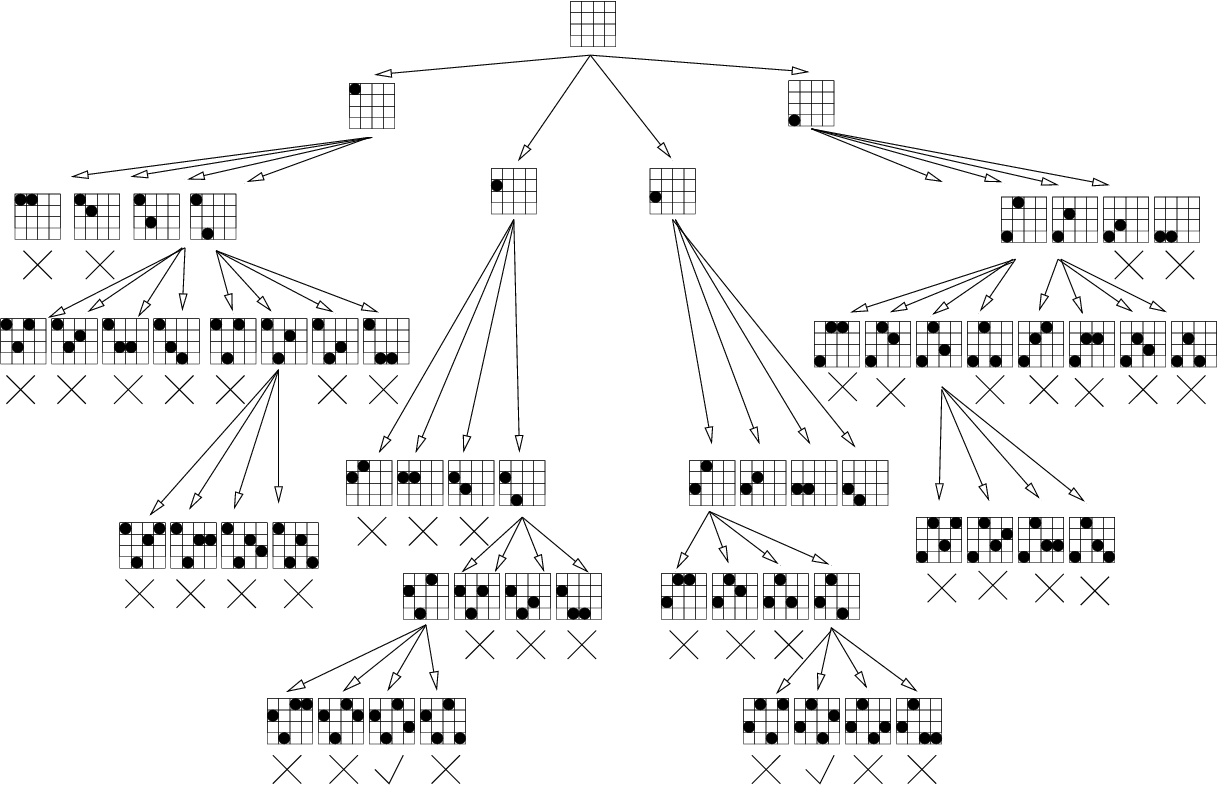

참고
2. C++
#include <cstdio>
int n, ans;
int chess[14][14];
void recur(int line) {
if (line == n) {
ans++;
return;
}
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {
if (chess[line][i] != -1) continue;
chess[line][i] = line;
for (int x = 0 ; x < n ; x++) {
if (chess[line][x] == -1) {
chess[line][x] = line;
}
}
for (int y = line ; y < n ; y++) {
if (chess[y][i] == -1) {
chess[y][i] = line;
}
}
for (int y = line, x = i ; y < n && 0 <= x ; y++, x--) {
if (chess[y][x] == -1) {
chess[y][x] = line;
}
}
for (int y = line, x = i ; y < n && x < n ; y++, x++) {
if (chess[y][x] == -1) {
chess[y][x] = line;
}
}
recur(line + 1);
for (int x = 0 ; x < n ; x++) {
if (chess[line][x] == line) {
chess[line][x] = -1;
}
}
for (int y = line ; y < n ; y++) {
if (chess[y][i] == line) {
chess[y][i] = -1;
}
}
for (int y = line, x = i ; y < n && 0 <= x ; y++, x--) {
if (chess[y][x] == line) {
chess[y][x] = -1;
}
}
for (int y = line, x = i ; y < n && x < n ; y++, x++) {
if (chess[y][x] == line) {
chess[y][x] = -1;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
for (int i = 0 ; i < 14 ; i++) {
for (int j = 0 ; j < 14 ; j++) {
chess[i][j] = -1;
}
}
scanf("%d", &n);
recur(0);
printf("%d", ans);
}
3. Java


