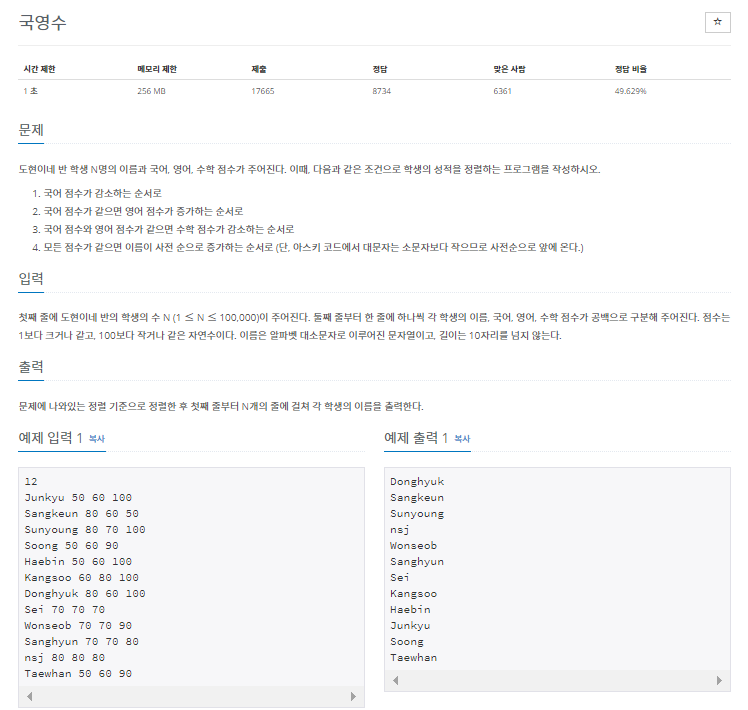
백준
1. Python
n = int(input())
data = []
for _ in range(n):
data.append(input().split())
data.sort(key=lambda x: (-int(x[1]), int(x[2]), -int(x[3]), x[0]))
for d in data:
print(d[0])
'''
1. 두번째 원소를 기준으로 내림차순 정렬
2. 두번째 원소가 같은 경우, 세번째 원소를 기준으로 오름차순 정렬
3. 세번째 원소가 같은 경우, 네번째 원소를 기준으로 내림차순 정렬
4. 네번째 원소가 같은 경우, 첫 번째 원소를 기준으로 오름차순 정렬
'''
'''
2. C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Student {
public:
string name;
int kor;
int eng;
int m;
Student(string name, int kor, int eng, int m) {
this->name = name;
this->kor = kor;
this->eng = eng;
this->m = m;
}
bool operator <(Student &other) {
if (this->kor == other.kor && this->eng == other.eng && this->m == other.m) {
return this->name < other.name;
}
if (this->kor == other.kor && this->eng == other.eng) {
return this->m > other.m;
}
if (this->kor == other.kor) {
return this->eng < other.eng;
}
return this->kor > other.kor;
}
};
int n;
vector<Student> v;
int main(void) {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
string name;
int kor;
int eng;
int m;
cin >> name >> kor >> eng >> m;
v.push_back(Student(name, kor, eng, m));
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << v[i].name << '\n';
}
}

