1. JavaScript
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// console.log('this is a debug message');
function solution(N) {
// write your code in JavaScript (Node.js 8.9.4)
const bin = N.toString(2);
const gap = bin.slice(bin.indexOf('1')+1, bin.lastIndexOf('1'));
const count = gap.split('1').map(zero => zero.length)
return count.length ? Math.max(...count) : 0;
}
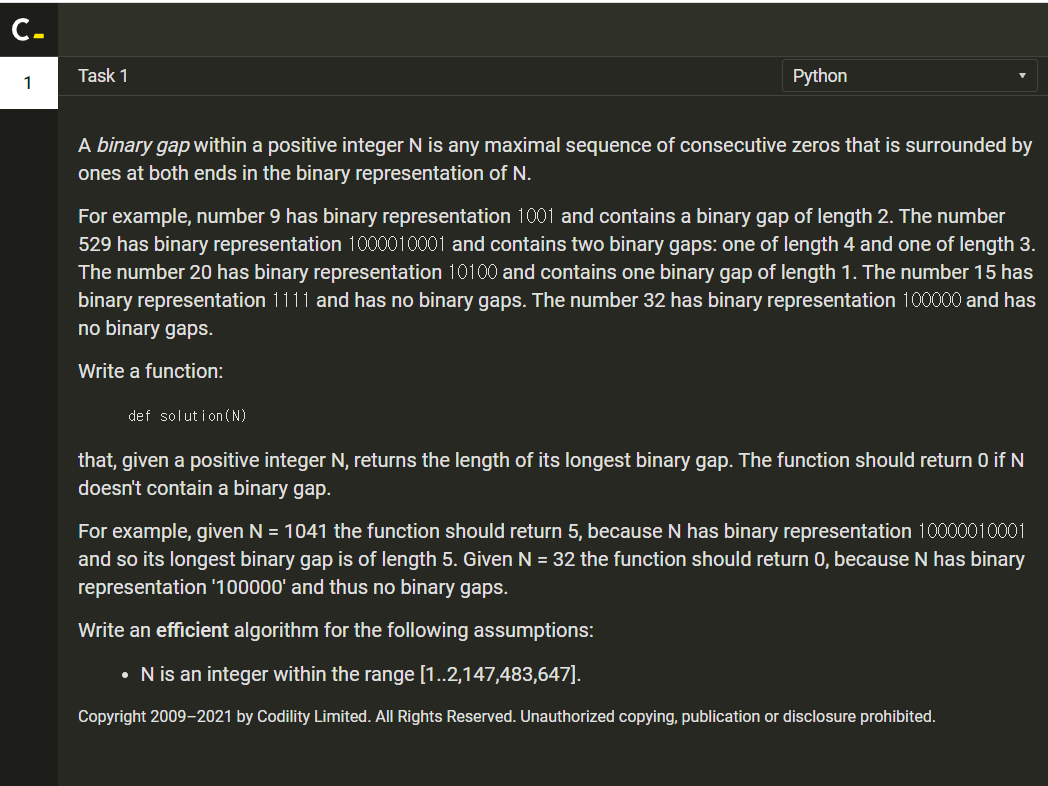
2. Python
def solution(N):
# write your code in Python 3.6
binary = bin(N)
binary = binary[2:]
if binary.count('1') == 1:
return 0
one_list = []
for i in range(len(binary)):
if binary[i] == '1':
one_list.append(i)
gap = []
for idx in range(len(one_list) - 1):
gap.append(one_list[idx + 1] - one_list[idx] - 1)
return max(gap)
print(solution(1041))
리스트 컴프리헨션
def solution(N):
return max([len(x) for x in format(N, 'b').strip('0').split('1')])
-
format(N, 'b')는 N을 2진수로 변환합니다. -
1 사이에 있는 0의 개수를 구하는 거라 양쪽 끝에 있는 0을 버립니다.
-
'1'로 split 하면 연속된 '0'으로 이루어진 문자열로 구성된 배열이 리턴됩니다.
-
[len(x) for x in arr]로 문자열들의 길이로 구성된 배열을 만듭니다. -
길이들 중 가장 큰 값을 리턴합니다.
