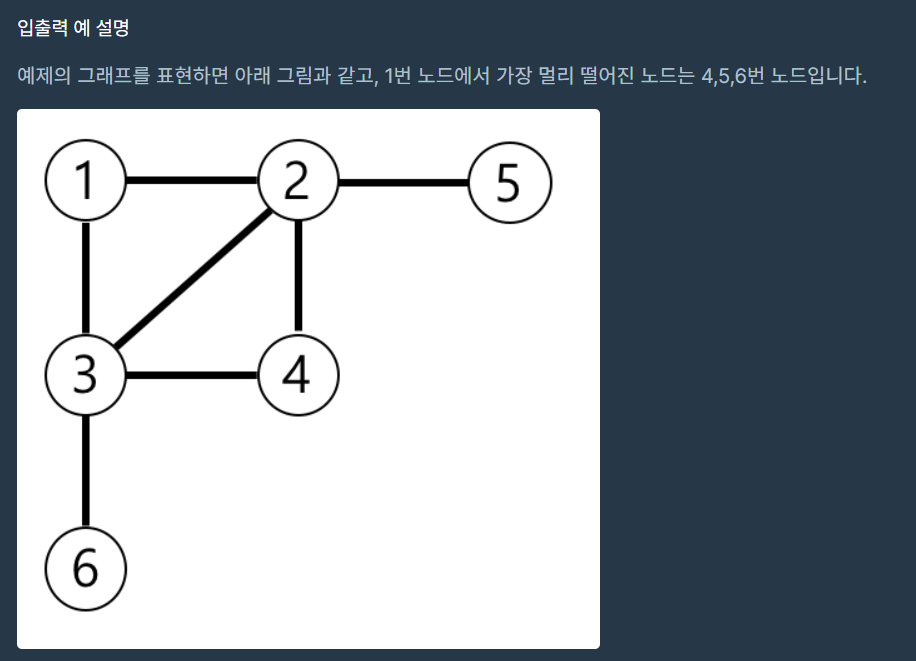
1. Python
from collections import deque, defaultdict
def bfs(v, visit, dict):
count = 0
q = deque([[v, count]])
while q:
v, count = q.popleft()
if visit[v] == -1:
visit[v] = count
count += 1
for e in dict[v]:
q.append([e, count])
def solution(n, edge):
answer = 0
dict = defaultdict(list)
visit = [-1] * (n + 1)
for a, b in edge:
dict[a].append(b)
dict[b].append(a)
bfs(1, visit, dict)
for value in visit:
if value == max(visit):
answer += 1
return answer
2. C++
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int d[20001][20001];
bool visit[20001];
int dist[20001];
int solution(int n, vector<vector<int>> edge) {
int max = 0;
int answer = 0;
for(int i=0;i<edge.size();i++)
{
d[edge[i][0]][edge[i][1]]=1;
d[edge[i][1]][edge[i][0]]=1;
}
queue<int> q;
visit[1] = true;
q.push(1);
dist[1] = 0;
while(!q.empty()){
int first = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 2;i <= n;i++){
if(d[first][i] == 1 && !visit[i]){
q.push(i);
visit[i]=true;
dist[i]=dist[first]+1;
if(max < dist[i]){
max = dist[i];
}
}
}
}
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++){
if(max == dist[i]){
answer++;
}
}
return answer;
}
3. JavaScript
function solution(n, edge) {
const adj = [];
const inq = new Array(n + 1).fill(-1);
const q = [];
const cost = new Array(n + 1).fill(Infinity);
edge.map(v => {
(adj[v[0]] || (adj[v[0]] = [])).push(v[1]);
(adj[v[1]] || (adj[v[1]] = [])).push(v[0]);
})
cost[1] = 1;
q.push(1);
while(q.length) {
const curr = q.shift();
adj[curr].map(next => {
if(cost[curr] + 1 < cost[next]) {
cost[next] = cost[curr] + 1;
if(inq[next] === -1) {
inq[next] = 1;
q.push(next);
}
}
})
}
let maxDist = cost.reduce((max, v) => v === Infinity ? 0 : Math.max(max, v), 0);
return cost.reduce((acc, n) => n === maxDist ? ++acc : acc, 0);
}
