1. 객체 생성 방식
1. DI (Dependency Injection, 의존 주입)
- 외부에서 두 객체 간의 관계를 결정해주는 디자인 패턴으로, 인터페이스를 사이에 둬서 클래스 레벨에서는 의존관계가 고정되지 않도록 하고 런타임 시에 관계를 다이나믹하게 주입하여 유연성을 확보하고 결합도를 낮출 수 있게 해준다.
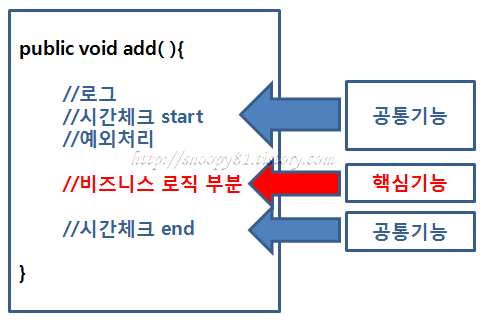
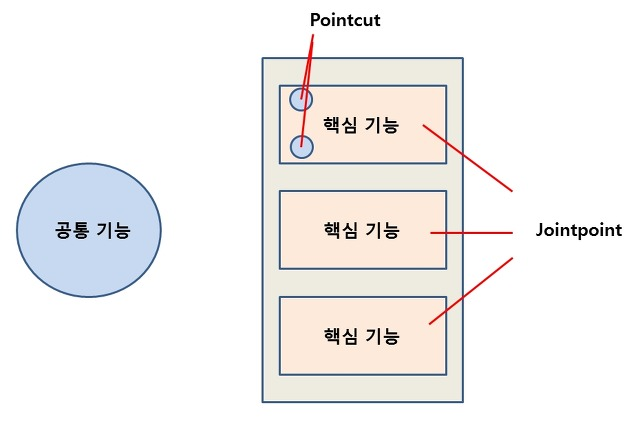
2. AOP (Aspect Oriented Programming, 관점 지향 프로그래밍)
- 기능별로 class를 분리했음에도 불구하고 생기는 중복코드의 단점을 해결하고자 나온 방식, 공통기능과 핵심부분을 분리하여, 필요할 때에만 공통기능을 핵심부위에 넣어주는 방식
3. IoC (Inversion of Control,제어의 역전)
-
제어의 역전은 의존성 주입의 상위 개념
-
스프링 컨테이너가 필요에 따라 개발자 대신 Bean들을 관리(제어)해주는 행위
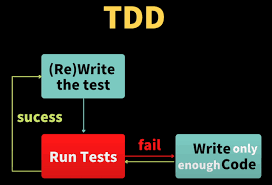
TDD (Test Driven Development, 테스트 주도 개발)
- 테스트 프로그램을 만드는 것
- 코드는 볼 수 없다
- 즉 프로그래머와 테스터는 분리된다.
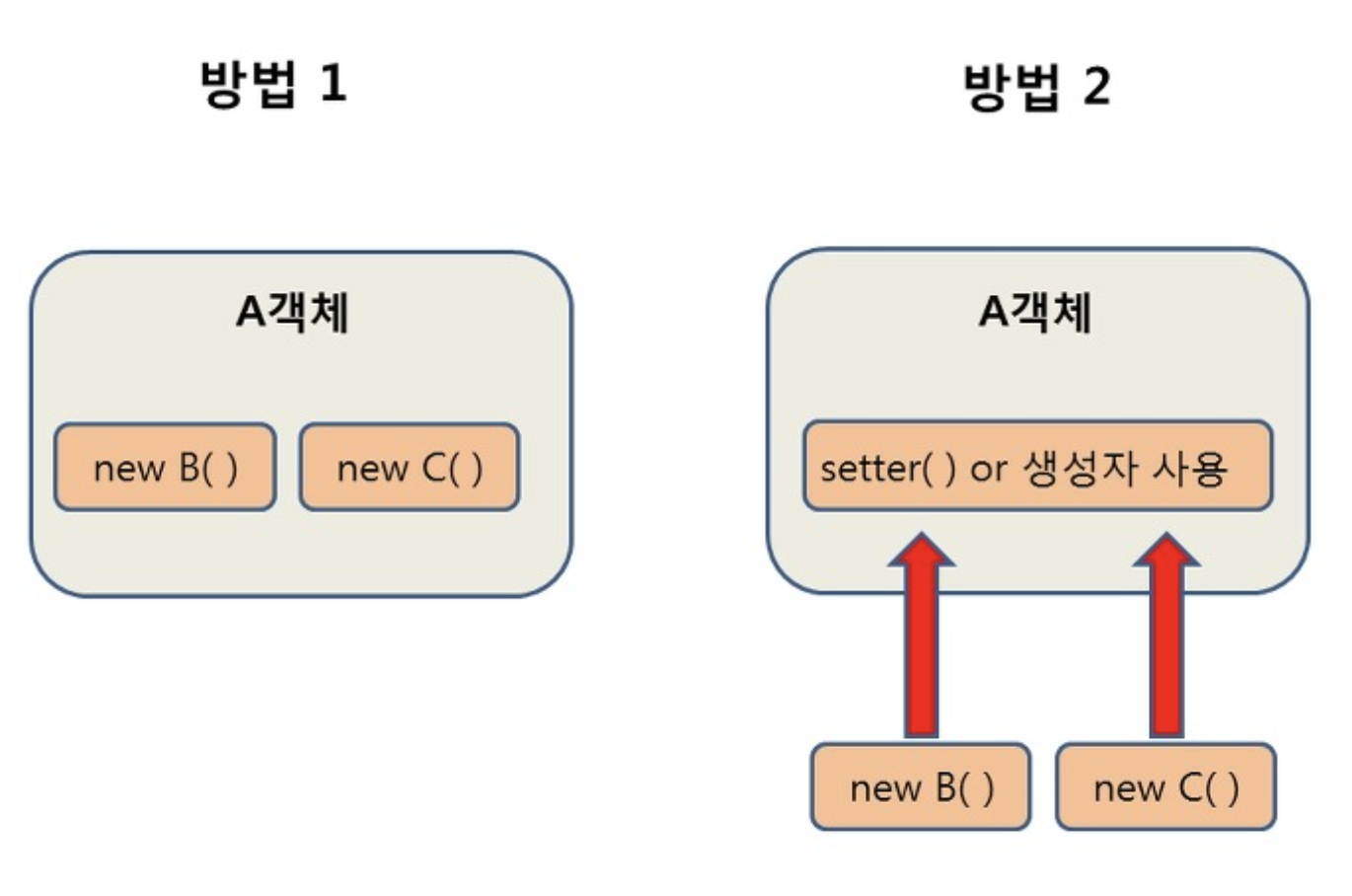
2. DI (Dependency Injection, 의존 주입)
-
주입 방식
-
생성자 주입
-
필드 주입 (@Autowired)
-
setter 주입
-
setter @Autowired 주입
-
스프링 X - 생성자 주입
//1. 스프링 없이 주입시키는 방법
// - 생성자 주입
class Apple{
void f1() { System.out.println("test"); }
}
class Orange{
Apple apple;
Orange(Apple apple){
this.apple = apple;
}
void f2() {
apple.f1();
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Orange orange = new Orange(new Apple());
orange.f2();
}
}
스프링 X - setter 주입
//2. 스프링 없이 주입시키는 방법
//- setter 주입
class Apple{
void f1() { System.out.println("test"); }
}
class Orange{
Apple apple;
void setApple(Apple apple) {
this.apple = apple;
}
void f2() {
apple.f1();
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Orange orange = new Orange();
orange.setApple(new Apple());
orange.f2();
}
}
ex1) 생성자 주입①
package Pack;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
class Apple{
void f1() {
System.out.println("test");
}
}
class Orange{
Apple apple;
Orange(Apple apple){
this.apple = apple;
}
void f2() {
apple.f1();
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
//Bean객체의 이름을 변경할 수 있다
//@Bean(name="appleMange")
@Bean
Apple apple() {
return new Apple();
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
//얘네들이 관리하는 객체의 수
System.out.println(ctx.getBeanDefinitionCount());
Orange orange = new Orange(new Apple());
orange.f2();
ctx.close();
}
}
ex2) 생성자 주입②
package Pack;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
class Apple{
void f1() {
System.out.println("test");
}
}
class Orange{
Apple apple;
//생성자 주입
Orange(Apple apple){
this.apple = apple;
}
void f2() {
apple.f1();
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
//Bean객체의 이름을 변경할 수 있다
//@Bean(name="appleMange")
@Bean
Apple apple() {
return new Apple();
}
//결국 apple은 싱글톤으로 같은 객체이다
@Bean
Orange orange() {
return new Orange(apple());
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
// //얘네들이 관리하는 객체의 수
// System.out.println(ctx.getBeanDefinitionCount());
// Orange orange = new Orange(new Apple());
// orange.f2();
//
Orange orange = ctx.getBean("orange", Orange.class);
orange.f2();
ctx.close();
}
}
ex3) 필드 주입 - @Autowired
- 사용하지 말라고 권장된다. - 스프링 제작진
- 서로 호출하면서 의존관계에 빠진다라는 주장
- 하지만 어차피 처음부터 이렇게 짜면 안된다.
- 실전에서 사용을 많이 한다.
package Pack;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
class Apple{
void f1() {
System.out.println("test");
}
}
class Orange{
@Autowired //아래와 동일한 생성자코드를 만들어준다. + 아래의 Orange(apple())
Apple apple;
// Orange(Apple apple){
// this.apple = apple;
// }
void f2() {
apple.f1();
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
//Bean객체의 이름을 변경할 수 있다
//@Bean(name="appleMange")
@Bean
Apple apple() {
return new Apple();
}
//결국 apple은 싱글톤으로 같은 객체이다
@Bean
Orange orange() {
return new Orange();
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
// //얘네들이 관리하는 객체의 수
// System.out.println(ctx.getBeanDefinitionCount());
// Orange orange = new Orange(new Apple());
// orange.f2();
//
Orange orange = ctx.getBean("orange", Orange.class);
orange.f2();
ctx.close();
}
}
ex4) setter 주입 (수정자 주입)
객체 수가 많을 때는 보이기 위해 주로 setter함수를 사용
- 객체가 적으면 생성자 주입을 주로 사용
package Pack;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
class Apple{
void f1() {
System.out.println("test");
}
}
class Orange{
Apple apple;
//setter 주입 - 수정자 주입
void setApple(Apple apple) {
this.apple = apple;
}
void f2() {
apple.f1();
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
@Bean
Apple apple() {
return new Apple();
}
// //결국 apple은 싱글톤으로 같은 객체이다
// @Bean
// Orange orange() {
// return new Orange();
// }
//spring용 setter 주입
@Bean
Orange orange() {
Orange o = new Orange();
o.setApple(apple());
return o;
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
// //setter 주입
// Orange o = new Orange();
// o.setApple(new Apple());
// o.f2();
Orange orange = ctx.getBean("orange", Orange.class);
orange.f2();
ctx.close();
}
}
ex5) setter 주입 (수정자 주입) - @Autowired
package Pack;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
class Apple{
void f1() {
System.out.println("test");
}
}
class Orange{
Apple apple;
//setter 주입 - 수정자 주입
@Autowired
void setApple(Apple apple) {
this.apple = apple;
}
void f2() {
apple.f1();
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
@Bean
Apple apple() {
return new Apple();
}
// //결국 apple은 싱글톤으로 같은 객체이다
// @Bean
// Orange orange() {
// return new Orange();
// }
//spring용 setter 주입
@Bean
Orange orange() {
// Orange o = new Orange();
// o.setApple(apple());
// return o;
//@Autowired 사용할 시 이렇게만
return new Orange();
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
// //setter 주입
// Orange o = new Orange();
// o.setApple(new Apple());
// o.f2();
Orange orange = ctx.getBean("orange", Orange.class);
orange.f2();
ctx.close();
}
}
불변의 원칙
- 생성자 주입
package Pack;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
class Apple{
void f1() {
System.out.println("test");
}
}
class Orange{
//한번만 받도록
//한 번 주입이 일어나면 이후는 불변의 원칙
final Apple apple;
Orange(Apple apple){
this.apple = apple;
}
void f2() {
apple.f1();
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
@Bean
Apple apple() {
return new Apple();
}
//spring용 setter 주입
@Bean
Orange orange() {
return new Orange(apple());
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Orange orange = ctx.getBean("orange", Orange.class);
orange.f2();
ctx.close();
}
}
@Nullable
-
객체가 없을 때, @Nullable은 setter 함수 호출은 시켜준 다음 터진다.
- 따라서 제어코드 작성이 가능해진다.
package Pack;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
class Apple{
void f1() {
System.out.println("----헤드라인----");
}
}
class Orange{
Apple apple;
@Autowired
//void setApple(Apple apple) {
//Apple 객체가 없을 때, @Nullable은 호출은 시켜준다음 터진다
void setApple(@Nullable Apple apple) {
System.out.println("호출");
//@Nullable이 있기에 제어코드 작성이 가능해진다.
if(apple != null) {
this.apple = apple;
}
}
void f2() {
if(apple != null) {
apple.f1();
}
System.out.println("대선 D-1");
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
// @Bean
// Apple apple() {
// return new Apple();
// }
//spring용 setter 주입
@Bean
Orange orange() {
return new Orange();
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Orange orange = ctx.getBean("orange", Orange.class);
orange.f2();
ctx.close();
}
}
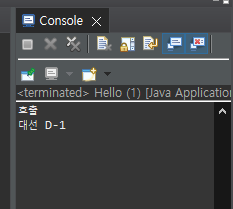
- 객체가 있는 경우
package Pack;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
class Apple{
void f1() {
System.out.println("----헤드라인----");
}
}
class Orange{
Apple apple;
@Autowired
//void setApple(Apple apple) {
//Apple 객체가 없을 때, @Nullable은 호출은 시켜준다음 터진다
void setApple(@Nullable Apple apple) {
System.out.println("호출");
//@Nullable이 있기에 제어코드 작성이 가능해진다.
if(apple != null) {
this.apple = apple;
}
}
void f2() {
if(apple != null) {
apple.f1();
}
System.out.println("대선 D-1");
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
@Bean
Apple apple() {
return new Apple();
}
//spring용 setter 주입
@Bean
Orange orange() {
return new Orange();
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Orange orange = ctx.getBean("orange", Orange.class);
orange.f2();
ctx.close();
}
}
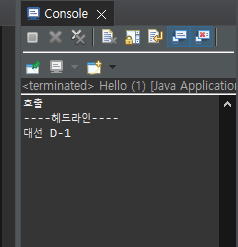
Optional
- 객체가 있는지 없는지를 물어 사용하는 방법
- 객체 존재 X
package Pack;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
class Apple{
void f1() {
System.out.println("----헤드라인----");
}
}
class Orange{
Apple apple;
@Autowired
//void setApple(Apple apple) {
//Apple 객체가 없을 때, @Nullable은 호출은 시켜준다음 터진다
//void setApple(@Nullable Apple apple) {
void setApple(Optional<Apple> apple) {
if(apple.isPresent()) {
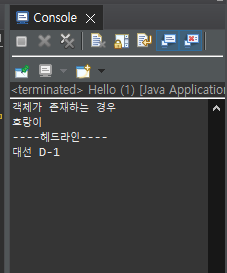
System.out.println("객체가 존재하는 경우");
this.apple = apple.get();
}else {
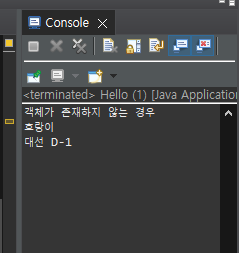
System.out.println("객체가 존재하지 않는 경우");
}
System.out.println("호랑이");
}
void f2() {
if(apple != null) {
apple.f1();
}
System.out.println("대선 D-1");
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
// @Bean
// Apple apple() {
// return new Apple();
// }
//spring용 setter 주입
@Bean
Orange orange() {
return new Orange();
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Orange orange = ctx.getBean("orange", Orange.class);
orange.f2();
ctx.close();
}
}
- 객체 존재 X
package Pack;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
class Apple{
void f1() {
System.out.println("----헤드라인----");
}
}
class Orange{
Apple apple;
@Autowired
//void setApple(Apple apple) {
//Apple 객체가 없을 때, @Nullable은 호출은 시켜준다음 터진다
//void setApple(@Nullable Apple apple) {
void setApple(Optional<Apple> apple) {
if(apple.isPresent()) {
System.out.println("객체가 존재하는 경우");
this.apple = apple.get();
}else {
System.out.println("객체가 존재하지 않는 경우");
}
System.out.println("호랑이");
}
void f2() {
if(apple != null) {
apple.f1();
}
System.out.println("대선 D-1");
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
@Bean
Apple apple() {
return new Apple();
}
//spring용 setter 주입
@Bean
Orange orange() {
return new Orange();
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Orange orange = ctx.getBean("orange", Orange.class);
orange.f2();
ctx.close();
}
}
문제가 발생하는 경우 - @Autowired
-
객체 생성자가 2개가 있는 경우
-
싱글톤에서는 문제가 발생하지 않는다.
-
하지만, AutoWired 잡으면 누구를 적용시켜야할지 모른다.
-
package Pack;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
class Apple{
void f1() {
System.out.println("----헤드라인----");
}
}
class Orange{
@Autowired
Apple apple;
void f2() {
if(apple != null) {
apple.f1();
}
System.out.println("대선 D-1");
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
@Bean
Apple apple01() {
return new Apple();
}
@Bean
Apple apple02() {
return new Apple();
}
//spring용 setter 주입
@Bean
Orange orange() {
return new Orange();
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Orange orange = ctx.getBean("orange", Orange.class);
orange.f2();
ctx.close();
}
}
@Qualifier
-
한정자: 사용 범위를 조건이나 제한을 걸 때 사용되는 예약어
- Default 값이기 때문에 생략이 가능하다
package Pack;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
class Apple{
void f1() {
System.out.println("----헤드라인----");
}
}
class Orange{
@Autowired
Apple apple;
void f2() {
if(apple != null) {
apple.f1();
}
System.out.println("대선 D-1");
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
@Bean
@Qualifier("apple01")
Apple apple01() {
return new Apple();
}
@Bean
@Qualifier("apple02")
Apple apple02() {
return new Apple();
}
//spring용 setter 주입
@Bean
Orange orange() {
return new Orange();
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Orange orange = ctx.getBean("orange", Orange.class);
orange.f2();
ctx.close();
}
}
- 상속에서의 Qualifier
package Pack;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
class Apple{
void f1() {
System.out.println("사과");
}
}
class Orange extends Apple{
@Override
void f1() {
System.out.println("오렌지");
}
}
class Kiwi{
Apple a1 = new Apple();
Apple a2 = new Orange();
@Autowired
Apple apple; //Apple //Orange
void f2() {
apple.f1();
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
@Bean
Apple apple() {
return new Apple();
}
@Bean
Orange orange() {
return new Orange();
}
@Bean
Kiwi kiwi() {
return new Kiwi();
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Kiwi kiwi = ctx.getBean("kiwi", Kiwi.class);
kiwi.f2();
ctx.close();
}
}
package Pack;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
class Apple{
void f1() {
System.out.println("사과");
}
}
class Orange extends Apple{
@Override
void f1() {
System.out.println("오렌지");
}
}
class Kiwi{
Apple a1 = new Apple();
Apple a2 = new Orange();
@Autowired
@Qualifier("orange")
Apple apple; //Apple //Orange
void f2() {
apple.f1();
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
@Bean
Apple apple() {
return new Apple();
}
@Bean
Orange orange() {
return new Orange();
}
@Bean
Kiwi kiwi() {
return new Kiwi();
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Kiwi kiwi = ctx.getBean("kiwi", Kiwi.class);
kiwi.f2();
ctx.close();
}
}
예제
package Pack;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
//의존 관계 (Airplane-Water)
class Airplane{
Water water;
Airplane(Water water){
this.water = water;
}
void fly() {
this.water.use();
System.out.print(" 날아간다.");
}
}
class Water{
void use() {
System.out.print("물을 사용해서");
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Airplane airplane = new Airplane(new Water());
airplane.fly();
}
}
- 스프링 연결
package Pack;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
//의존 관계 (Airplane-Water)
class Airplane{
Water water;
Airplane(Water water){
this.water = water;
}
void fly() {
this.water.use();
System.out.print(" 날아간다.");
}
}
class Water{
void use() {
System.out.print("물을 사용해서");
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
@Bean
Water water() {
return new Water();
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Water water = ctx.getBean("water", Water.class);
Airplane airplane = new Airplane(water);
airplane.fly();
ctx.close();
}
}
- 자동 생성
package Pack;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
//의존 관계 (Airplane-Water)
class Airplane{
Water water;
Airplane(Water water){
this.water = water;
}
void fly() {
this.water.use();
System.out.print(" 날아간다.");
}
}
class Water{
void use() {
System.out.print("물을 사용해서");
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
@Bean
Water water() {
return new Water();
}
@Bean
Airplane airplane() {
return new Airplane(water());
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
//Water water = ctx.getBean("water", Water.class);
Airplane airplane = ctx.getBean("airplane", Airplane.class);
airplane.fly();
ctx.close();
}
}
- @Autowired
package Pack;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
//의존 관계 (Airplane-Water)
class Airplane{
@Autowired
Water water;
void fly() {
this.water.use();
System.out.print(" 날아간다.");
}
}
class Water{
void use() {
System.out.print("물을 사용해서");
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
@Bean
Water water() {
return new Water();
}
@Bean
Airplane airplane() {
return new Airplane(water());
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Airplane airplane = ctx.getBean("airplane", Airplane.class);
airplane.fly();
ctx.close();
}
}
- setter @Autowired
package Pack;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
//의존 관계 (Airplane-Water)
class Airplane{
Water water;
@Autowired
void setWater(Water water) {
this.water = water;
}
void fly() {
this.water.use();
System.out.print(" 날아간다.");
}
}
class Water{
void use() {
System.out.print("물을 사용해서");
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
@Bean
Water water() {
return new Water();
}
@Bean
Airplane airplane() {
return new Airplane();
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Airplane airplane = ctx.getBean("airplane", Airplane.class);
airplane.fly();
ctx.close();
}
}
- 객체가 없는 경우
package Pack;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
//의존 관계 (Airplane-Water)
class Airplane{
Water water;
@Autowired
void setWater(Water water) {
this.water = water;
}
void fly() {
this.water.use();
System.out.print(" 날아간다.");
}
}
class Water{
void use() {
System.out.print("물을 사용해서");
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
@Bean
Water water() {
return new Water();
}
// @Bean
// Airplane airplane() {
// return new Airplane();
// }
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Airplane airplane = ctx.getBean("airplane", Airplane.class);
airplane.fly();
ctx.close();
}
}
@Component & @ComponentScan
-
객체가 없는 경우 자동적으로 생성시켜버린다.
- 클래스 명을 소문자로해서
-
@ComponentScan-
스프링 3.1부터 도입된 Annotation이며 스캔 위치를 설정하고,
-
어떤 Annotation을 스캔할지 또는 하지 않을지 결정하는 Filter 기능을 가지고있다.
-
-
@Component-
컴포넌트 스캔이 스캐닝하는 기준
-
@Component를 들고있는 클래스들이 스캐닝되고, Bean으로 등록된다.
-
package Pack;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
//의존 관계 (Airplane-Water)
class Airplane{
Water water;
@Autowired
void setWater(Water water) {
this.water = water;
}
void fly() {
this.water.use();
System.out.print(" 날아간다.");
}
}
class Water{
void use() {
System.out.print("물을 사용해서");
}
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan
class AppConfig{
@Bean
Water water() {
return new Water();
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Airplane airplane = ctx.getBean("airplane", Airplane.class);
airplane.fly();
ctx.close();
}
}
3. XML
스프링 컨테이너는 다양한 형식의 설정 정보(Config)를 받을 수 있다.
ex) 자바코드, XML, Groovy 등
- 권장사항: XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
</beans>
<button></button>
//컴파일시
Button button = new Button();4. DAO, DTO, VO, Entity
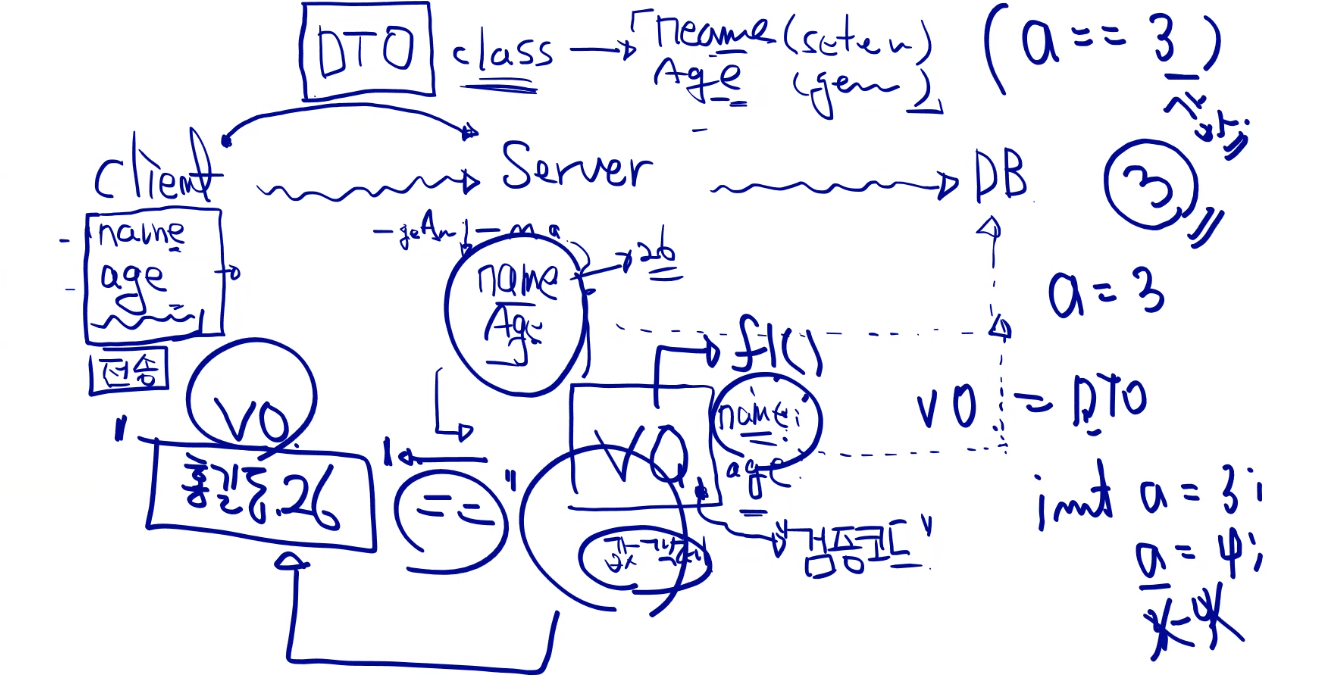
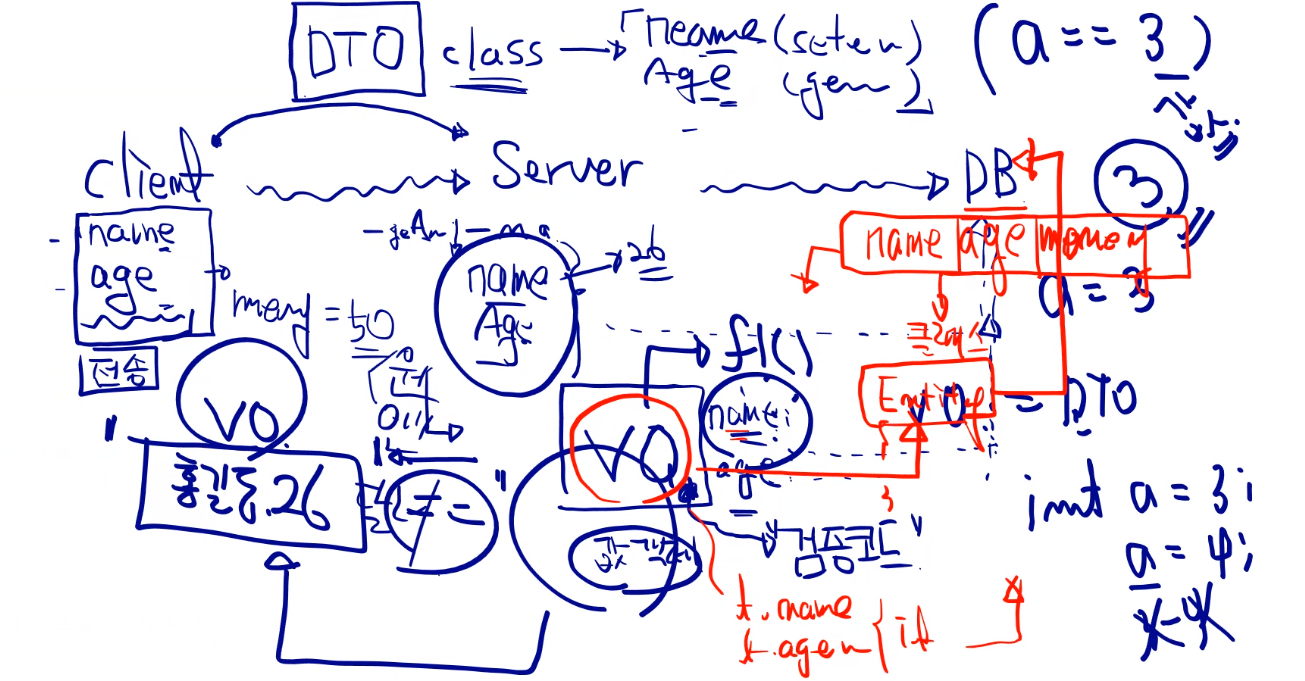
DAO (Data Access Object), DTO(Data Transfer Object), VO(Value Object), Entity
-
클래스 구성
-
Member: Entity 클래스의 역할
-
MemberDao: CRUD 담당
CRUD는 CRUD만 해야한다. 즉 다른 예외처리 등을 해서는 안된다.
-
RegisterRequest: VO 클래스의 역할
-
MemberRegisterService: MemberDao를 서포트해주는 역할
- 즉 DAO에서 일어난 CRUD에 대해 예외처리와 return 값을 이용하는 곳
-
ex1) VO class
package Pack;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
class FormDTO{
String name;
FormDTO(){
}
}
//VO class
class RegisterRequest{
String name;
RegisterRequest(String name){
this.name = name;
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 클라이언트에서 데이터를 전송
//2. 서버에서는 DTO 클래스로 값을 얻게 된다.
//3. String name = DTO객체.name;
//4. 키보드에서 input을 받는다. (input이 DTO 데이터이다.)
String inputName = "홍길동";
RegisterRequest rr = new RegisterRequest(inputName);
// GenericXmlApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("classpath:Context.xml");
// ctx.close();
}
}ex2) Entity class
package Pack;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
class FormDTO{
String name;
FormDTO(){
}
}
//VO class
class RegisterRequest{
String name;
RegisterRequest(String name){
//데이터 검증 코드가 상당부분 생략되었다.
this.name = name + "독수리"; //가공
}
}
//Entity class
//class Entity{
// int id;
//}
//class Member extends Entity{
class Member{
int id;
String name;
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 클라이언트에서 데이터를 전송
//2. 서버에서는 DTO 클래스로 값을 얻게 된다.
//3. String name = DTO객체.name;
//4. 키보드에서 input을 받는다. (input이 DTO 데이터이다.)
String inputName = "홍길동";
RegisterRequest rr = new RegisterRequest(inputName);
//Entitiy에 정보 입력
Member member = new Member();
member.id = 1000;
member.name = rr.name;
//member -> DB에 저장(Map Collection 사용)
// GenericXmlApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("classpath:Context.xml");
// ctx.close();
}
}
ex3) DAO class
package Pack;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
class FormDTO{
String name;
FormDTO(){
}
}
//VO class
class RegisterRequest{
String name;
RegisterRequest(String name){
//데이터 검증 코드가 상당부분 생략되었다.
this.name = name + "독수리"; //가공
}
}
//Entity class
//class Entity{
// int id;
//}
//class Member extends Entity{
class Member{
int id;
String name;
}
//DAO class
class MemberDao{
void insert(Member member) {
//쿼리 문장을 사용하는 코드이지만
System.out.println(member.name + "DB에 저장하였습니다.");
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 클라이언트에서 데이터를 전송
//2. 서버에서는 DTO 클래스로 값을 얻게 된다.
//3. String name = DTO객체.name;
//4. 키보드에서 input을 받는다. (input이 DTO 데이터이다.)
String inputName = "홍길동";
RegisterRequest rr = new RegisterRequest(inputName);
//Entitiy에 정보 입력
Member member = new Member();
member.id = 1000;
member.name = rr.name;
//member -> DB에 저장(Map Collection 사용)
MemberDao memberDao = new MemberDao();
memberDao.insert(member);
// GenericXmlApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("classpath:Context.xml");
// ctx.close();
}
}
ex4) Service 클래스
Dao와의 차이점은 리턴값을 받아서 어떠한 판단을하게 된다.
package Pack;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
class FormDTO{
String name;
FormDTO(){
}
}
//VO class
class RegisterRequest{
String name;
RegisterRequest(String name){
//데이터 검증 코드가 상당부분 생략되었다.
this.name = name + "독수리"; //가공
}
}
//Entity class
//class Entity{
// int id;
//}
//class Member extends Entity{
class Member{
int id;
String name;
}
//DAO class
class MemberDao{
void insert(Member member) {
//쿼리 문장을 사용하는 코드이지만
System.out.println(member.name + "DB에 저장하였습니다.");
}
}
class MemberRegisterService{
MemberDao memberDao;
MemberRegisterService(MemberDao memberDao){
this.memberDao = memberDao;
}
void register(Member member) {
memberDao.insert(member);
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 클라이언트에서 데이터를 전송
//2. 서버에서는 DTO 클래스로 값을 얻게 된다.
//3. String name = DTO객체.name;
//4. 키보드에서 input을 받는다. (input이 DTO 데이터이다.)
String inputName = "홍길동";
RegisterRequest rr = new RegisterRequest(inputName);
//Entitiy에 정보 입력
Member member = new Member();
member.id = 1000;
member.name = rr.name;
MemberRegisterService mrs = new MemberRegisterService(new MemberDao());
//member -> DB에 저장(Map Collection 사용)
MemberDao memberDao = new MemberDao();
memberDao.insert(member);
// GenericXmlApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("classpath:Context.xml");
// ctx.close();
}
}
ex5) register 함수 변경
package Pack;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
class FormDTO{
String name;
FormDTO(){
}
}
//VO class
class RegisterRequest{
String name;
RegisterRequest(String name){
//데이터 검증 코드가 상당부분 생략되었다.
this.name = name + "독수리"; //가공
}
}
//Entity class
//class Entity{
// int id;
//}
//class Member extends Entity{
class Member{
int id;
String name;
}
//DAO class
class MemberDao{
boolean insert(Member member) {
//쿼리 문장을 사용하는 코드이지만
System.out.println(member.name + "DB에 저장하였습니다.");
return true;
}
}
class MemberRegisterService{
MemberDao memberDao;
public MemberRegisterService(MemberDao memberDao){
this.memberDao = memberDao;
}
void register(RegisterRequest rr) {
//Entitiy에 정보 입력
Member member = new Member();
member.id = 1000;
member.name = rr.name;
if(memberDao.insert(member) == true) {
System.out.println("모든 작업이 정상입니다.");
}
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 클라이언트에서 데이터를 전송
//2. 서버에서는 DTO 클래스로 값을 얻게 된다.
//3. String name = DTO객체.name;
//4. 키보드에서 input을 받는다. (input이 DTO 데이터이다.)
String inputName = "홍길동";
RegisterRequest rr = new RegisterRequest(inputName);
MemberRegisterService mrs = new MemberRegisterService(new MemberDao());
mrs.register(rr);
//member -> DB에 저장(Map Collection 사용)
// MemberDao memberDao = new MemberDao();
// memberDao.insert(rr);
// GenericXmlApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("classpath:Context.xml");
// ctx.close();
}
}
ex6) Spring으로 변경
package Pack;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
class FormDTO{
String name;
FormDTO(){
}
}
//VO class
class RegisterRequest{
String name;
RegisterRequest(String name){
//데이터 검증 코드가 상당부분 생략되었다.
this.name = name + "독수리"; //가공
}
}
//Entity class
//class Entity{
// int id;
//}
//class Member extends Entity{
class Member{
int id;
String name;
}
//DAO class
class MemberDao{
boolean insert(Member member) {
//쿼리 문장을 사용하는 코드이지만
System.out.println(member.name + "DB에 저장하였습니다.");
return true;
}
}
class MemberRegisterService{
@Autowired
MemberDao memberDao;
// public MemberRegisterService(MemberDao memberDao){
// this.memberDao = memberDao;
// }
//
void register(RegisterRequest rr) {
//Entitiy에 정보 입력
Member member = new Member();
member.id = 1000;
member.name = rr.name;
if(memberDao.insert(member) == true) {
System.out.println("모든 작업이 정상입니다.");
}
}
}
@Configuration
class AppConfig{
@Bean
MemberDao memberDao() {
return new MemberDao();
}
@Bean
MemberRegisterService memberRegisterService() {
//return new MemberRegisterService(memberDao());
return new MemberRegisterService();
}
}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 클라이언트에서 데이터를 전송
//2. 서버에서는 DTO 클래스로 값을 얻게 된다.
//3. String name = DTO객체.name;
//4. 키보드에서 input을 받는다. (input이 DTO 데이터이다.)
// String inputName = "홍길동";
// RegisterRequest rr = new RegisterRequest(inputName);
//
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
MemberRegisterService mrs = ctx.getBean("memberRegisterService", MemberRegisterService.class);
mrs.register(new RegisterRequest("홍길동"));
ctx.close();
// MemberRegisterService mrs = new MemberRegisterService(new MemberDao());
// mrs.register(rr);
//member -> DB에 저장(Map Collection 사용)
// MemberDao memberDao = new MemberDao();
// memberDao.insert(rr);
}
}
ex6) Spring 아닐 때 Config
package Pack;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
class FormDTO{
String name;
FormDTO(){
}
}
//VO class
class RegisterRequest{
String name;
RegisterRequest(String name){
//데이터 검증 코드가 상당부분 생략되었다.
this.name = name + "독수리"; //가공
}
}
//Entity class
//class Entity{
// int id;
//}
//class Member extends Entity{
class Member{
int id;
String name;
}
//DAO class
class MemberDao{
boolean insert(Member member) {
//쿼리 문장을 사용하는 코드이지만
System.out.println(member.name + "DB에 저장하였습니다.");
return true;
}
}
class MemberRegisterService{
MemberRegisterService(MemberDao memberDao){
this.memberDao = memberDao;
}
MemberDao memberDao;
// public MemberRegisterService(MemberDao memberDao){
// this.memberDao = memberDao;
// }
//
void register(RegisterRequest rr) {
//Entitiy에 정보 입력
Member member = new Member();
member.id = 1000;
member.name = rr.name;
if(memberDao.insert(member) == true) {
System.out.println("모든 작업이 정상입니다.");
}
}
}
//config
class Assemble{
MemberRegisterService f1() {
MemberRegisterService mrs = new MemberRegisterService(new MemberDao());
mrs.register(new RegisterRequest("홍길동"));
return mrs;
}
}
//@Configuration
//class AppConfig{
// @Bean
// MemberDao memberDao() {
// return new MemberDao();
// }
// @Bean
// MemberRegisterService memberRegisterService() {
// //return new MemberRegisterService(memberDao());
// return new MemberRegisterService(new MemberDao());
// }
//
//}
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 클라이언트에서 데이터를 전송
//2. 서버에서는 DTO 클래스로 값을 얻게 된다.
//3. String name = DTO객체.name;
//4. 키보드에서 input을 받는다. (input이 DTO 데이터이다.)
Assemble a = new Assemble();
MemberRegisterService msr = a.f1();
msr.register(new RegisterRequest("홍길동"));
// String inputName = "홍길동";
// RegisterRequest rr = new RegisterRequest(inputName);
// MemberRegisterService mrs = new MemberRegisterService(new MemberDao());
// mrs.register(rr);
//
// AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
// MemberRegisterService mrs = ctx.getBean("memberRegisterService", MemberRegisterService.class);
// mrs.register(new RegisterRequest("홍길동"));
// ctx.close();
//member -> DB에 저장(Map Collection 사용)
// MemberDao memberDao = new MemberDao();
// memberDao.insert(rr);
}
}
이제는 선택
- CRUD를 클래스로 분리시키기
- 현재코드에 구현하기