What is MVC?
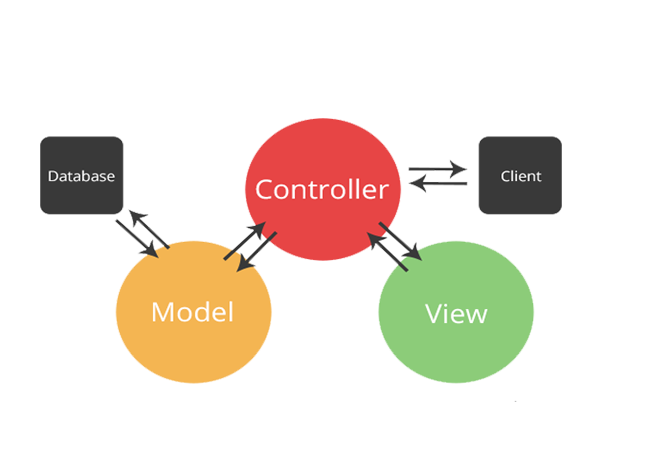
Model - View - Controller
architectural pattern that separates an application into three main logical components. Each of these components are built to handle specific development aspects of an application.
Model
Model component corresponds to all the data-related logic that the user work with. This can represent either the data that is being transferred between view and controller components.
-
Model is connected to the database and can bring data.
-
Model requested by the controller, and the Model returns a value to the controller.
View
View component is used for all the UI logic of the application. User can see screen all the UI components such as text boxes, dropdowns, etc..
Controller
Controllers act as an interface between Model and View components to process all the business logic and incoming request. Manipulate data using the Model component and interact with the Views to render the final output. handle all the interactions and inputs from the User View and update the database using the Model.
Why we use MVC?
Code management becomes easier and readability is improved. It is also very helpful for collaboration.
ORM
Object Relational Mapping
The technique of accessing a relational database using an object-oriented programming language. ORM is a way for javascript programs to manage database data by mapping.
ORM can be seen as an interpreter for communication between relational databases and Javascript objects.
Why we use ORM
ORM allows you to access the database without using SQL syntax. It is convenient to be able to access the database using the object type of Javascript.
Sequelize (Node.js ORM)
Support RDBS
- Postgres
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- SQLite
- MS SQL Server
Association (One-To-One, One-To-Many, Many-To-Many)
- HasOne Association
- BelongsTo Association
- HasMany Association
- BelongsToMany Association
ex) One To Many
Team.hasMany(Player);
Player.belongsTo(Team);ex) Many To Many
Movie.belongsToMany(Actor, { through: 'ActorMovies' });
Actor.belongsToMany(Movie, { through: 'ActorMovies' });four types of associations, will follow up to explain how to combine those to define the three standard association types.
ex)
const A = sequelize.define('A', /* ... */);
const B = sequelize.define('B', /* ... */);
A.hasOne(B); // A HasOne B
A.belongsTo(B); // A BelongsTo B
A.hasMany(B); // A HasMany B
A.belongsToMany(B, { through: 'C' }); // A BelongsToMany B through the junction table CTransaction (Unmanaged Transactions, Managed Transactions)
-
Unmanaged Transactions
Committing and rolling back the transaction should be done manually by the user. -
Managed Transactions
Sequelize will automatically rollback the transaction if any error is thrown, or commit the transaction otherwise. If Continuacation is enabled, all queries
ex) A situation where a user called sender has an api request to deposit $5 to receiver
-
Check that the sender and receiver are valid users.
-
If it is a valid user, continue, if the user cannot be found, make error and rollback.
-
minus $5 from the sender's balance after save, add $5 to the receiver's balance and save.
-
It records that the function has been performed and stores the value in the transfer table.
Getting Started Sequelize
Install Sequelize & Sequelize-cli
npm install --save sequelizenpm install --save-dev sequelize-cliSetting ORM
Installed sequelize-cli after, need to project bootstrapping.
(To create an empty project you will need to execute init command)
# using npm
npx sequelize-cli initThis will create following folders
- config, contains config file, which tells CLI how to connect with database
- models, contains all models for your project
- migrations, contains all migration files
- seeders, contains all seed files
Creating the first Model (and Migration)
Need to create the model used by cli.
Model component corresponds to all the data-related logic that the user works with. This can represent either the data that is being transferred between the View and Controller components or any other business logic-related data.
My Opinion
Model is a form of expressing an entity as an Object. Describes a data structure and collection of commands that can be performed on data.
If Model created incorrectly, delete after modify model, and run the command again.
Migration
If schema changed, need run migration again.
Create Controller and Connect Routes
Routes are endpoints that help you get into the Controller. You need to associate a Controller with Routes.
For example, if you send a GET or POST request to the /links URL, you can make the links Controller's method run.

