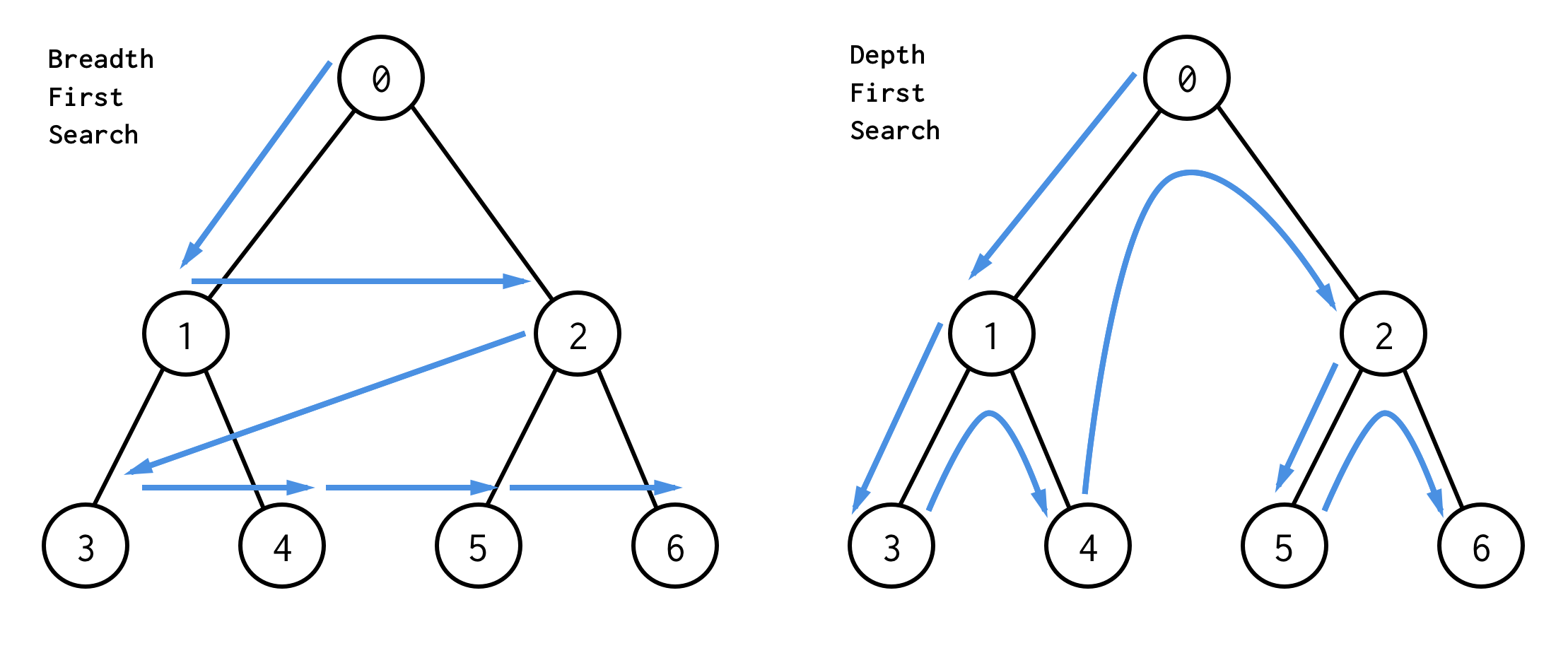
문제
임의의 tree를 구성하는 노드 중 하나의 Node 객체를 입력받아, 해당 노드를 시작으로 깊이 우선 탐색(DFS, Depth First Search)을 합니다. 이 때, 탐색되는 순서대로 노드의 값이 저장된 배열을 리턴해야 합니다.
주의사항
생성자 함수(Node)와 메소드(addChild)는 변경하지 않아야 합니다.
입출력 예시
let root = new Node(1);
let rootChild1 = root.addChild(new Node(2));
let rootChild2 = root.addChild(new Node(3));
let leaf1 = rootChild1.addChild(new Node(4));
let leaf2 = rootChild1.addChild(new Node(5));
let output = dfs(root);
console.log(output); // --> [1, 2, 4, 5, 3]
leaf1.addChild(new Node(6));
rootChild2.addChild(new Node(7));
output = dfs(root);
console.log(output); // --> [1, 2, 4, 6, 5, 3, 7]풀이
let dfs = function (node) {
// TODO: 여기에 코드를 작성합니다.
let result = [node.value];
node.children.forEach((el) => {
result = result.concat(dfs(el));
});
return result;
};
// 이 아래 코드는 변경하지 않아도 됩니다. 자유롭게 참고하세요.
let Node = function (value) {
this.value = value;
this.children = [];
};
// 위 Node 객체로 구성되는 트리는 매우 단순한 형태의 트리입니다.
// membership check(중복 확인)를 따로 하지 않습니다.
Node.prototype.addChild = function (child) {
this.children.push(child);
return child;
};재귀함수를 통해 자식노드를 하나씩 훑는다.
자식노드의 결과값을 concat하여 문제의 요구사항과 같이 출력할 수 있다.
자식노드가 없을 때 상위노드의 다른 자식노드를 탐색한다.
let dfs = function (node) {
// TODO: 여기에 코드를 작성합니다.
let values = [node.value];
for(let i = 0; i < node.children.length; i++){
values = values.concat(dfs(node.children[i]));
}
return values;
};
// 이 아래 코드는 변경하지 않아도 됩니다. 자유롭게 참고하세요.
let Node = function (value) {
this.value = value;
this.children = [];
};
// 위 Node 객체로 구성되는 트리는 매우 단순한 형태의 트리입니다.
// membership check(중복 확인)를 따로 하지 않습니다.
Node.prototype.addChild = function (child) {
this.children.push(child);
return child;
};개인적으로는 아래 작성한 코드를 더 선호한다.