코드
const tree = {
root: {
value: 5,
left: {
value: 3,
left: {
value: 1,
left: null,
right: null,
},
right: {
value: 4,
left: null,
right: null
}
},
right: {
value: 8,
left: {
value: 6,
left: null,
right: null,
},
right: {
value: 9,
left: null,
right: null
}
}
}
}
class Node {
constructor(data){
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
class Tree {
constructor(data){
let init = new Node(data);
this.root = init;
this.데이터수 = 0;
}
length() {
return this.데이터수;
}
insert(data){
let 새로운노드 = new Node(data);
let 순회용현재노드 = this.root;
while(순회용현재노드){
if(data === 순회용현재노드.data){
return;
}
if(data < 순회용현재노드.data){
if(!순회용현재노드.left){
순회용현재노드.left = 새로운노드;
this.data += 1;
return;
}
순회용현재노드 = 순회용현재노드.left;
}
if(data > 순회용현재노드.data){
if(!순회용현재노드.right){
순회용현재노드.right = 새로운노드;
this.data += 1;
return;
}
순회용현재노드 = 순회용현재노드.right;
}
}
}
DFS() {
let 결과값 = [];
let 스택 = [this.root];
// 스택의 길이가 0이 될 때까지 계속해서 꺼낸다.
while(스택.length !== 0){
let current = 스택.pop();
// 만약 current.right가 존재한다면 스택에 넣어둬라.
// 예를들어 0 다음 1을 순회한다.
// 0은 끝난 상태에서 1로 가야하고, current.left가 존재한다면 1을 스택 = [this.root]에 넣어라.
if(current.right){
스택.push(current.right);
}
if(current.left){
스택.push(current.left);
}
결과값.push(current.data);
}
return 결과값;
}
BFS() {
let 결과값 = [];
let 큐 = [this.root];
// 큐의 길이가 0이 될 때까지 계속해서 꺼낸다.
while(큐.length !== 0){
let current = 큐.shift();
// DFS에서 바뀐점은 스택이 큐로 바뀌고,
// let current에서 pop()을 shift()로 바꿨다.
// BFS에서 shift()를 사용하는 이유는 마지막을 꺼내는게 아니라 첫번째를 꺼낸다.
if(current.left){
큐.push(current.left);
}
if(current.right){
큐.push(current.right);
}
결과값.push(current.data);
}
return 결과값;
}
}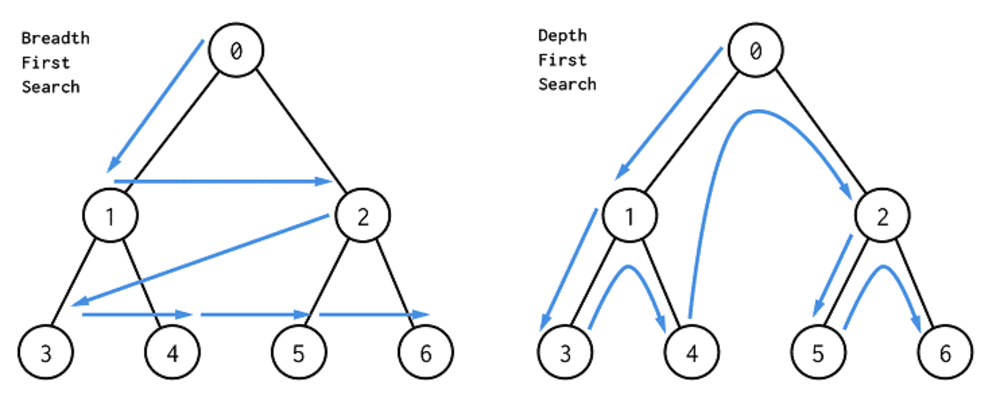
BFS (Breath-First-Search, 너비우선탐색)
Queue를 활용한다.
DFS (Depth-First-Search, 깊이우선탐색)
Stack을 활용한다.
