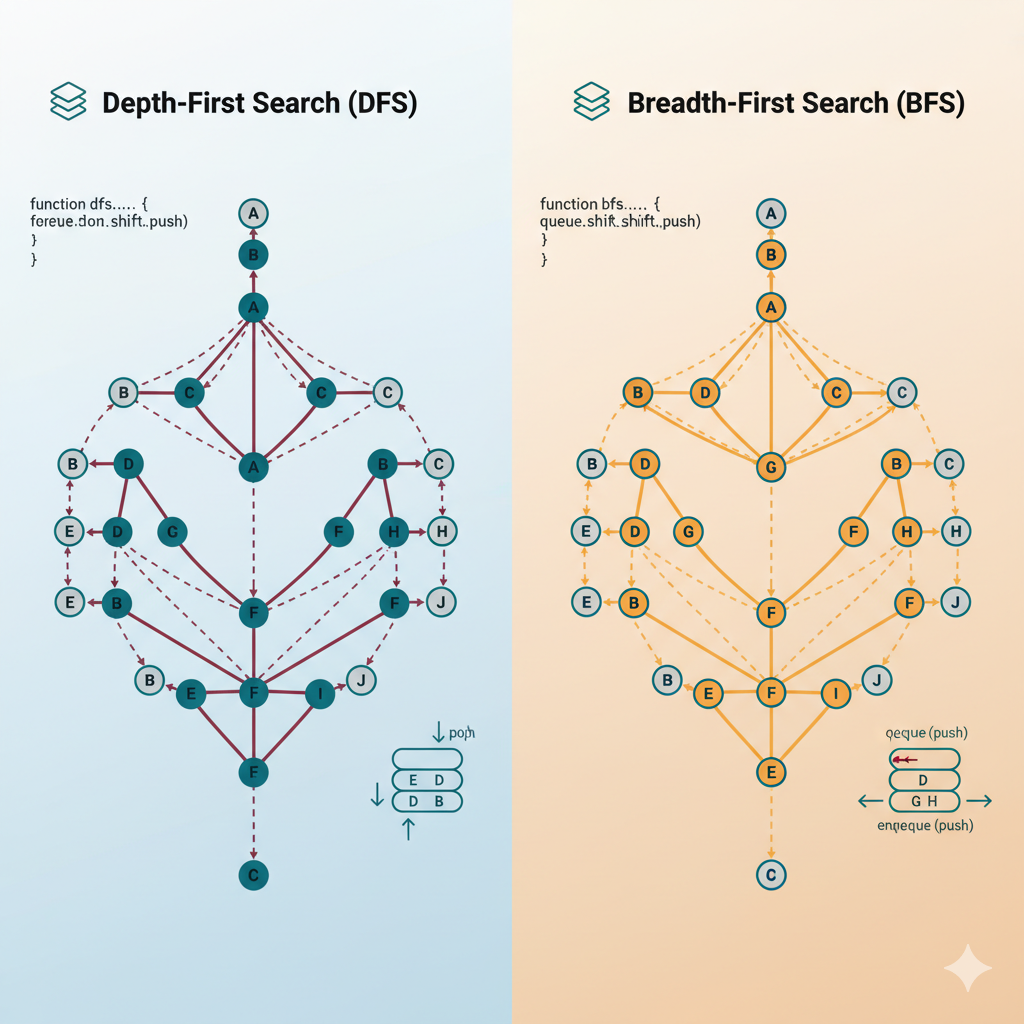
DFS와 BFS는 알고리즘의 기초이자 핵심이라고 할 수 있다.
1. DFS (Depth-First Search)
- DFS는 그래프 탐색 알고리즘 중 하나로, '깊이'를 우선으로 탐색한다.
- 다시 말해, 한 노드에서 시작하여 다음 분기로 넘어가기 전에 해당 분기를 완벽하게 탐색하는 방식이다.
- 동작 원리: 스택(Stack) 또는 재귀 함수를 이용
- 활용 예시: 미로 찾기, 모든 노드를 방문하는 경우, 사이클(Cycle) 판별 등
const graph = {
'A': ['B', 'C'],
'B': ['A', 'D'],
'C': ['A', 'G', 'H'],
'D': ['B', 'E', 'F'],
'E': ['D'],
'F': ['D'],
'G': ['C'],
'H': ['C', 'I'],
'I': ['H']
};
function dfs(graph, startNode, visited = new Set(), result = []) {
if (visited.has(startNode)) {
return;
}
visited.add(startNode);
result.push(startNode);
(graph[startNode] || []).forEach(neighbor => {
if (!visited.has(neighbor)) {
dfs(graph, neighbor, visited, result);
}
});
return result;
}
# 그래프 (인접 리스트) 예시
graph = {
'A': ['B', 'C'],
'B': ['A', 'D'],
'C': ['A', 'G', 'H'],
'D': ['B', 'E', 'F'],
'E': ['D'],
'F': ['D'],
'G': ['C'],
'H': ['C', 'I'],
'I': ['H']
}
# 방문한 노드를 저장할 집합(Set)
visited = set()
def dfs(graph, node):
if node not in visited:
visited.add(node)
for neighbor in graph.get(node, []):
dfs(graph, neighbor)2. BFS (Breadth-First Search)
- BFS는 그래프 탐색 알고리즘 중 하나로, '너비'를 우선으로 탐색.
- 시작 노드에서 가까운 노드들을 먼저 모두 탐색한 후, 점차 먼 노드로 이동하는 방식.
- 동작 원리: 큐(Queue) 자료구조를 이용
- 활용 예시: 최단 경로 찾기 (가중치가 없는 그래프에서), 미로 최단 경로, 최소 횟수 문제 등
function bfs(graph, startNode) {
const queue = [startNode];
const visited = new Set([startNode]);
const result = [];
while (queue.length > 0) {
const node = queue.shift();
result.push(node);
(graph[node] || []).forEach(neighbor => {
if (!visited.has(neighbor)) {
visited.add(neighbor);
queue.push(neighbor);
}
});
}
return result;
}from collections import deque
def bfs(graph, start_node):
queue = deque([start_node])
visited = {start_node}
result = []
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
result.append(node)
print(f"방문 노드: {node}")
for neighbor in graph.get(node, []):
if neighbor not in visited:
visited.add(neighbor)
# 방문하지 않은 노드는 큐의 맨 뒤에 추가합니다 (append).
queue.append(neighbor)
return result