Knowledge is Power
- Successful market planning depends upon informed decision making.
-Developing marketing objectives
-Selecting target markets
-Positioning products
-Developing 4 Ps strategies
- Information is the fuel that runs the marketing engine.
Marketing Research Ethics
- Marketing research ethics refers to taking an aboveboard approach in conducting market research that does no harm to the participant.
-Privacy issues
-Confidentiality issues
marketing info. system - 4개 구성요소
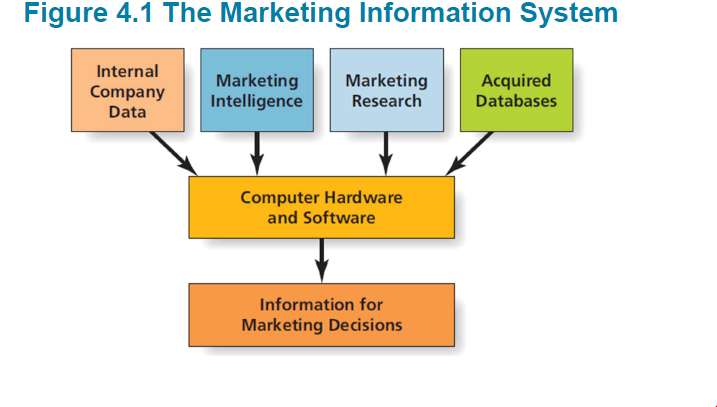
Internal Company Data
- Information generated from within the company
-Used to produce reports on sales and marketing activities
-Commonly accessed via secure intranets
Market Intelligence
-
마켓 인텔리전스: 급변하는 환경에 대응하기 위하여 기업에 적합한 정보만을 수집, 가공, 분석하여 기업의 비전과 목표에 맞게 전략 방향을 설정해주는 것
-
Gathered via monitoring of everyday data sources, observations, and discussions with sales representatives.
-
A market intelligence system is a method by which marketers get information about what’s
going on in the world that is relevant to their business -
Reverse engineering (역공학) is the process of physically deconstructing a competitor’s product to determine how it’s put together.
Market Research
- 한 상품이나 서비스가 어떻게 구입되며 사용되고 있는가, 그리고 어떤 평가를 받고 있는가 하는 시장에 관한 조사
- Refers to the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data about customers, rivals, and the business environment
-Syndicated research
-Custom research reports
(ex) Q-Scores, Nielsen Ratings
Acquired Databases
- Externally sourced databases can be used to collect various types of useful information (ex) 사용자 개인정보를 외부에서 얻어 기업체에서 사용
-Noncompeting businesses
-Government databases - Misuse of databases can be problematic and has led to “do-not-call” lists and anti-spamming laws
Marketing Decision Support System
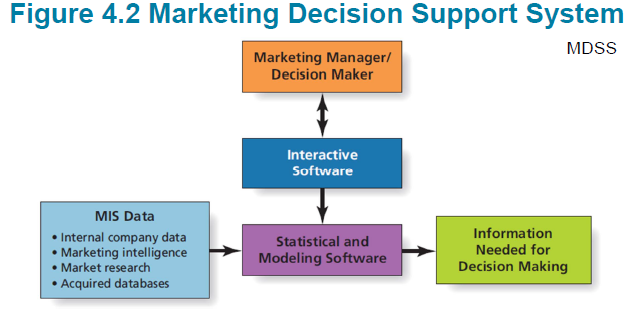
- 마케팅 의사 결정 지원 시스템 : 마케팅 활동을위한 의사 결정 지원 시스템. 과거 이벤트에서 이미 수집 된 데이터를 활용하여 기업이 다양한 시나리오를 탐색하는 데 사용
MIS, MDSS and Customer Insights
- To make good decisions, marketing managers need timely access to quality information!
- A firm’s MIS stores and analyses data from a variety of
sources - A firm’s MDSS makes it easier to access the MIS and find
answers to specific “what-if” questions
- A firm’s MIS stores and analyses data from a variety of
Customer Insights and Marketing
- Goal of the Marketing Insights function -transform data
into information- Data are raw unorganized facts
- Information is interpreted data
- More complicated than it sounds
- Massive amounts of data
- Much data is unstructured
- Functional silos
Marketing Research Process의 7단계
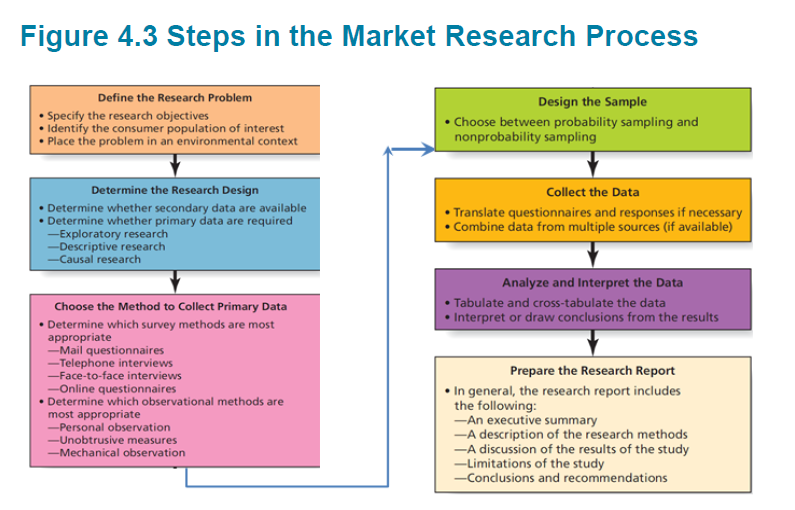
Step 1: Define the Research Problem
- Specify the research objectives (research objectives : the questions that the research will answer)
- Identify the consumer population of interest
- Place the problem in an environmental context
Step 2: Determine the Research Design
- Once the problem is isolated, the next step is to determine a ‘plan of attack’
-A research design is a plan that specifies what information marketers will collect and what type of study they will do
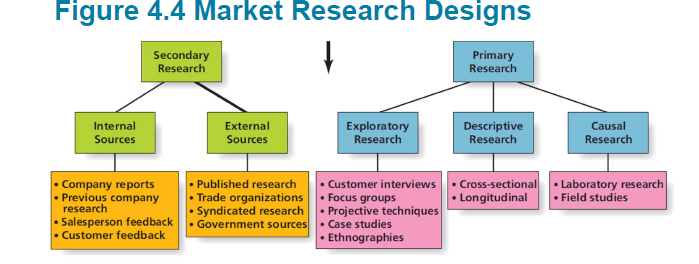
- Research designs fall into two categories:
-Secondary data(2차 자료): Secondary data can save time and money/ 이미 수집된 자료
-Primary data(1차 자료):
refers to data collected by the firm to address a specific question (when make a specific decision)/ 문제를 해결하기 위해 조사자가 처음으로 만든 자료
primary data research에 필요한 조사들: Exploratory, descriptive, and causal research
- Exploratory Research (탐색적 연구) :
해결해야 할 문제의 정확한 특성을 명확히 하기위한 예비 연구. 구체적인 연구 계획의 시작점에 가장 적합
Identifying new opportunities -
Focus groups(포커스 그룹) consist of 5–9 individuals who typically share certain characteristics, and who have agreed to participate in an in-depth discussion of the product or service in question. (ex: IKEA) / 소수의 사람들이 참여하는 그룹 인터뷰. 특정 연구원이 제기 한 질문에 대한 그들의 반응을 연구한다.
- Descriptive Research(기술적 연구) : Systematically investigate marketing problem/ 미리 계획되고 구성되어 수집된 정보가 한 인구집단에서 통계적으로 추론될 수 있도록 함. 주어진 주제에 대해 사람들의 의견을 잘 정리할 수 있음.(ex) 설문조사: 객관식 질문
-Cross-sectional designs(횡단연구) systematically use instruments such as questionnaires to systematically collect information / 정보를 얻기 위해 특정한 시점에 조사하는 연구
-Longitudinal studies(종단연구) attempt to track changes over time, by collecting data from the same set of consumers at multiple points in time./ 여러 시점에 걸쳐서 반복 조사하는 연구
-Causal Research(인과적 연구) : Attempts to identify cause-and effect/ 현상의 원인과 결과를 조사함. (ex) 맥주와 기저귀 판매량의 상관관계?
Step 3: Choose the Method to Collect Primary Data
-
Primary data collection falls into two broad categories
-Survey
-Observation:Personal observation(개인적 조사: 소비자의 행동 관찰),
Unobtrusive measures(눈에 거슬리지 않는 조사: 소비자의 남아있는 증거의 흔적을 찾음. ex. 소비자의 쓰레기를 조사),
Mechanical forms of observation (기계를 이용한 조사: 관찰을 저렴, 정확하게 할 수 있음) (ex) records-Online Research : 온라인 서핑/소스 (쿠키/해시태그)에서 정보 수집
Predictive technology(예측 기술) : uses shopping patterns of large numbers of people to determine which products are likely to be purchased if others are /많은 사람들의 쇼핑 패턴을 이용-> 다른 사람들이 구매할 가능성 있는 제품을 특정
- 새로운 기술 도입: Neuro-marketing(ex: fMRI, virtual stores)
-Bounce Rate(이탈률) : a measure of how many visitors come to a page on a website and leave without viewing any other pages./ 웹 사이트의 페이지를 방문 후, 다른 페이지를 보지 않고 떠난 방문자 수

-Data and Measurement Quality Issues(데이터 및 측정 품질 문제): 쓰레기 출입 조사를 통한 조사
• Three key considerations:
-Validity (유효성) : the extent to which the research actually measures what it was intended to measure./ 실제로 측정하고자하는 것을 측정하는 정도
-Reliability (신뢰성) : the extent to which research measurement techniques are free of errors. /오류가 없는 정도
-Representativeness (대표성) : the extent to which consumers in the study are similar to a larger group in which the organization has an interest. Self-selection bias is a threat to representativeness in online and offline research designs /연구에서 관심을 갖고 있는 그룹과 유사한 정도. 자기 선택 편향은 온라인 및 오프라인 연구 설계의 대표성에 위협이 됨.
Step 4: Design the Sample
- Probability sampling (추출 확률)
-Each member of the population has some known chance of being included (example: action films vs. “chick flicks”) / 각 구성원들은 모두 포함될 가능성이 있음.
-Simple random sample(간단 무작위 추출) : 모집단의 모든 구성원이 동일 확률 갖음. (ex) 모자에서 이름을 꺼내는 것
-Systematic sampling procedure(체계적인 추출) : 연구자가 구성원에 번호를 매김 (간격을 정해서 샘플의 다음 구성원을 간격별로 선택)
-Stratified sample(층화추출) : 조사집단을 분할하고자 할 때 사용.
-Nonprobability sampling (비확률적 샘플링) : 응답자를 선택하기 위해 개인적 판단을 사용하는 추출법. (ex) Convenience sample(그 시간과 장소에 참석자가 있다는 이유만으로 표본으로 선택)/ Quota sample
Step 5: Collect the Data
- The quality of research conclusions is only as good as the data used to generate them
- Challenges to gathering data in foreign countries/ 해외 데이터 수집의 어려움
-Cultural issues/ Language issues (문화적 문제 / 언어 문제)
->Major differences exist in the sophistication of research operations (연구 결과의 정교함의 차이) / Infrastructure differences(인프라의 차이) /Local customs and cultural differences (현지 관습과 문화적 차이) / Language translation difficulties(번역의 어려움)
Step 6: Analyze and Interpret the Data
• Tabulation (표)
-Arranging data in a table or other summary form to get a broad picture of overall response
• Cross-tabulation (교차표)
-Exploring data by sub-groups in order to see how results vary across categories / 카테고리별로 결과가 어떻게 다른지 확인. 하위그룹별로 데이터 탐색
Step 7: Prepare the Research Report
• Research reports typically include the following sections
-Executive summary (요약)
-Description of research methods (연구 방법 설명)
-Discussion of study results (연구 결과 논의)
-Limitations of study (연구의 한계)
-Conclusions and recommendations (결론 및 권고)
