💻lesson3 - FrogJmp
1. 문제
A small frog wants to get to the other side of the road. The frog is currently located at position X and wants to get to a position greater than or equal to Y. The small frog always jumps a fixed distance, D.
Count the minimal number of jumps that the small frog must perform to reach its target.
Write a function:
def solution(X, Y, D)that, given three integers X, Y and D, returns the minimal number of jumps from position X to a position equal to or greater than Y.
For example, given:
X = 10
Y = 85
D = 30the function should return 3, because the frog will be positioned as follows:
after the first jump, at position 10 + 30 = 40
after the second jump, at position 10 + 30 + 30 = 70
after the third jump, at position 10 + 30 + 30 + 30 = 100
Write an efficient algorithm for the following assumptions:
X, Y and D are integers within the range [1..1,000,000,000];
X ≤ Y.
2. 문제 접근
Y는 무조건 X보다 크거나 같고 개구리는 항상 D만큼 뛴다고 한다.
개구리가 있는 위치인 X에서 D * n만큼을 더해서 Y보다 같거나 더 크게 이동시키는 것이 이 문제의 해결방법인듯하다. 목적은 최소 n을 구하는 것.
처음에는 그냥 반복문을 사용하여 횟수를 구하면 되겠다고 생각했음. 그래도 0(n)정도만 나올거니깐 충분히 해결가능할 것이라고 생각했다.(안돼!!)
3. 첫번째 시도
def solution(X, Y, D):
cnt = 0
while(X<Y):
cnt += D
X = X + D
return cnt//D4. 첫번째 결과
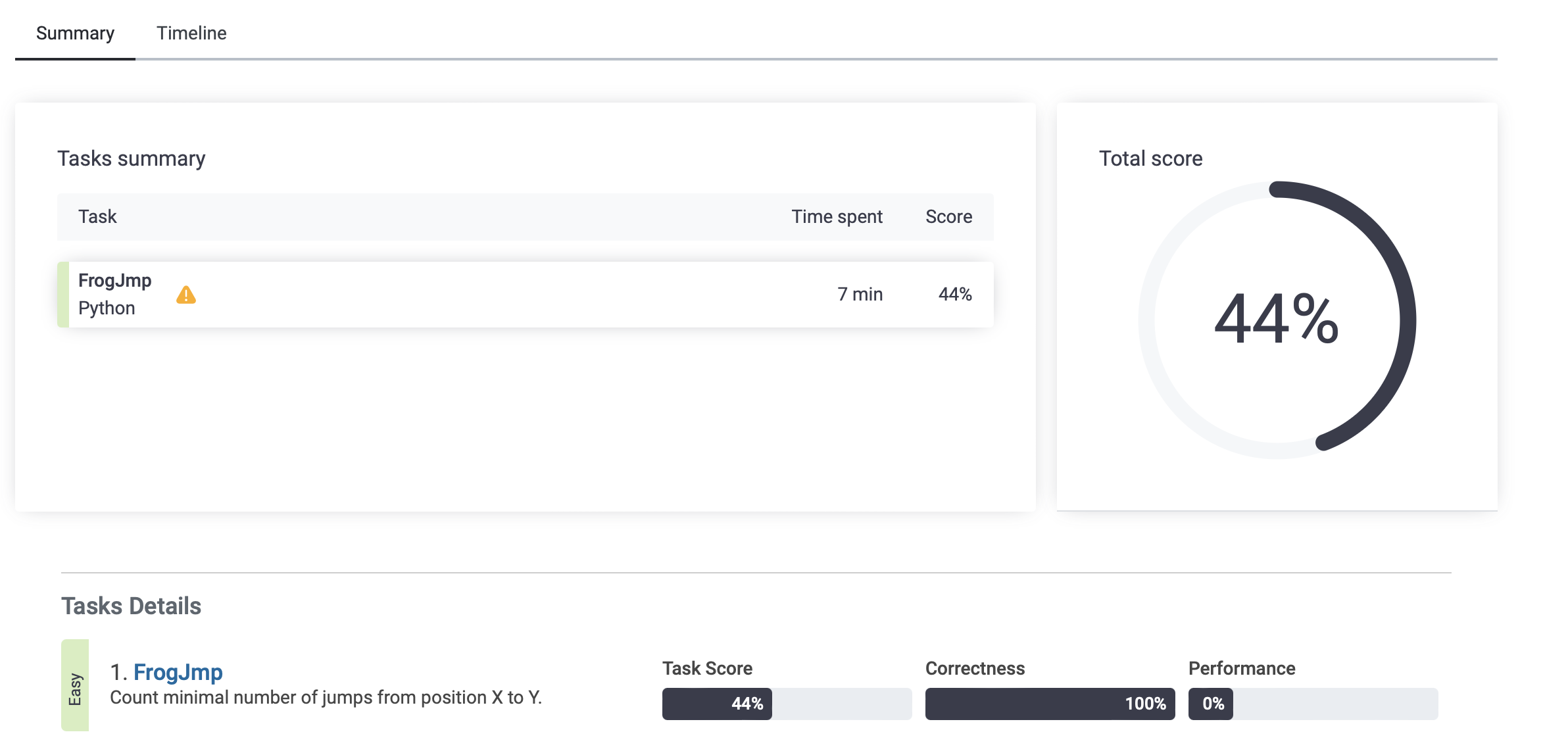
역시나 오늘도 역시다 역시... 44%라니 어디서 문제가 발생한 것일까.
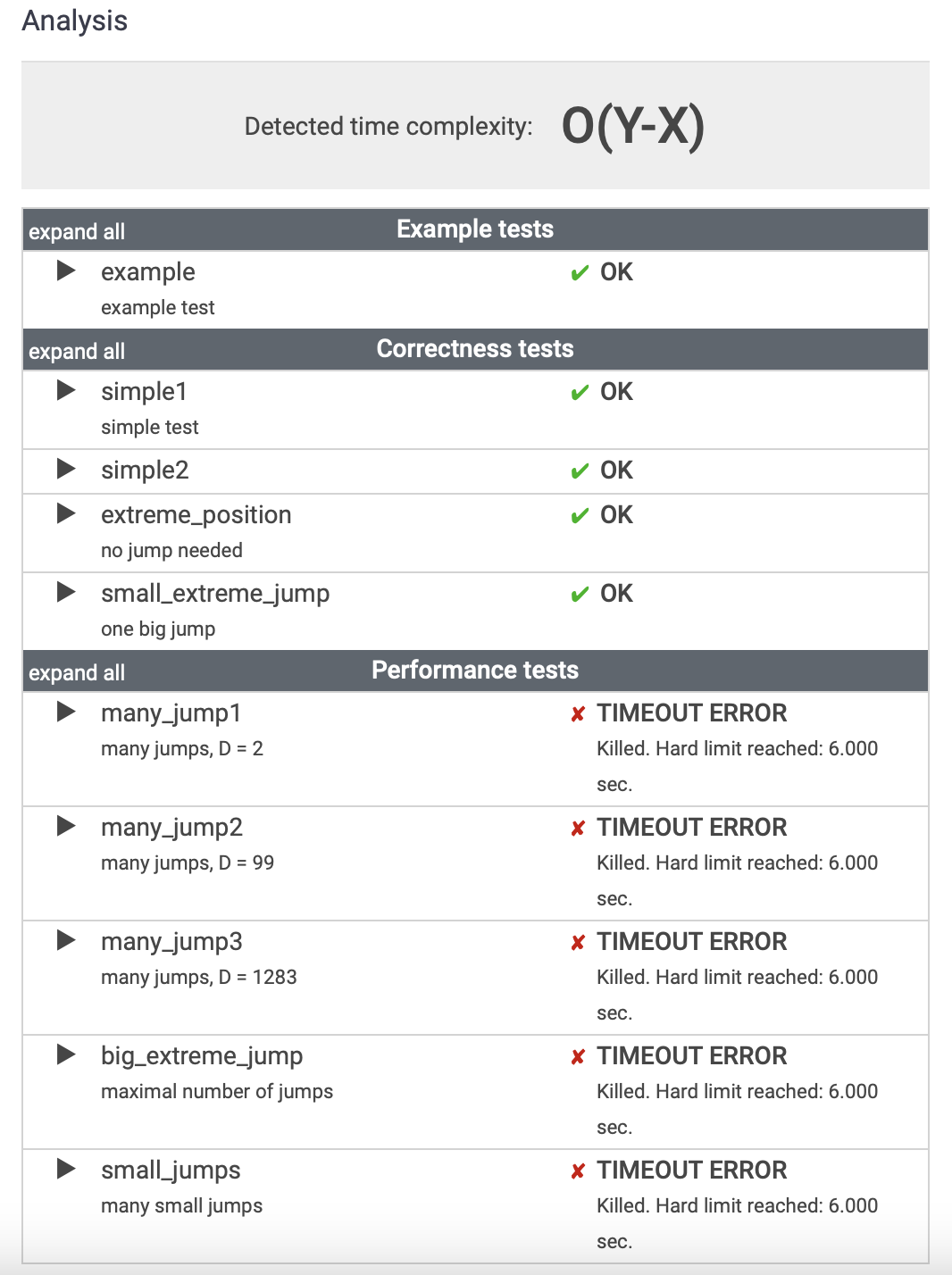
또또...타임에러...
이번에도 시간복잡도를 신경을 안쓴거 같다.
이번 레슨이 시간복잡도인만큼 얼마나 시간이 걸렸는지 알려주는데 O(Y-X)라니!
이 문제의 목표 시간복잡도는 O(1)인가보다.
그럼 우선 시간복잡도가 O(N)이게 되는 반복문은 사용하지 말고 간단한 연산을 사용하여서 코드를 만들어보기로 하자.
5. 두번째 시도
def solution(X, Y, D):
if((Y-X)%D>0):
return (Y-X)//D+1
elif((Y-X)%D==0):
return (Y-X)//D나누기, 뺄셈으로만 해결했다.
과연 결과는...!
6. 두번째 결과
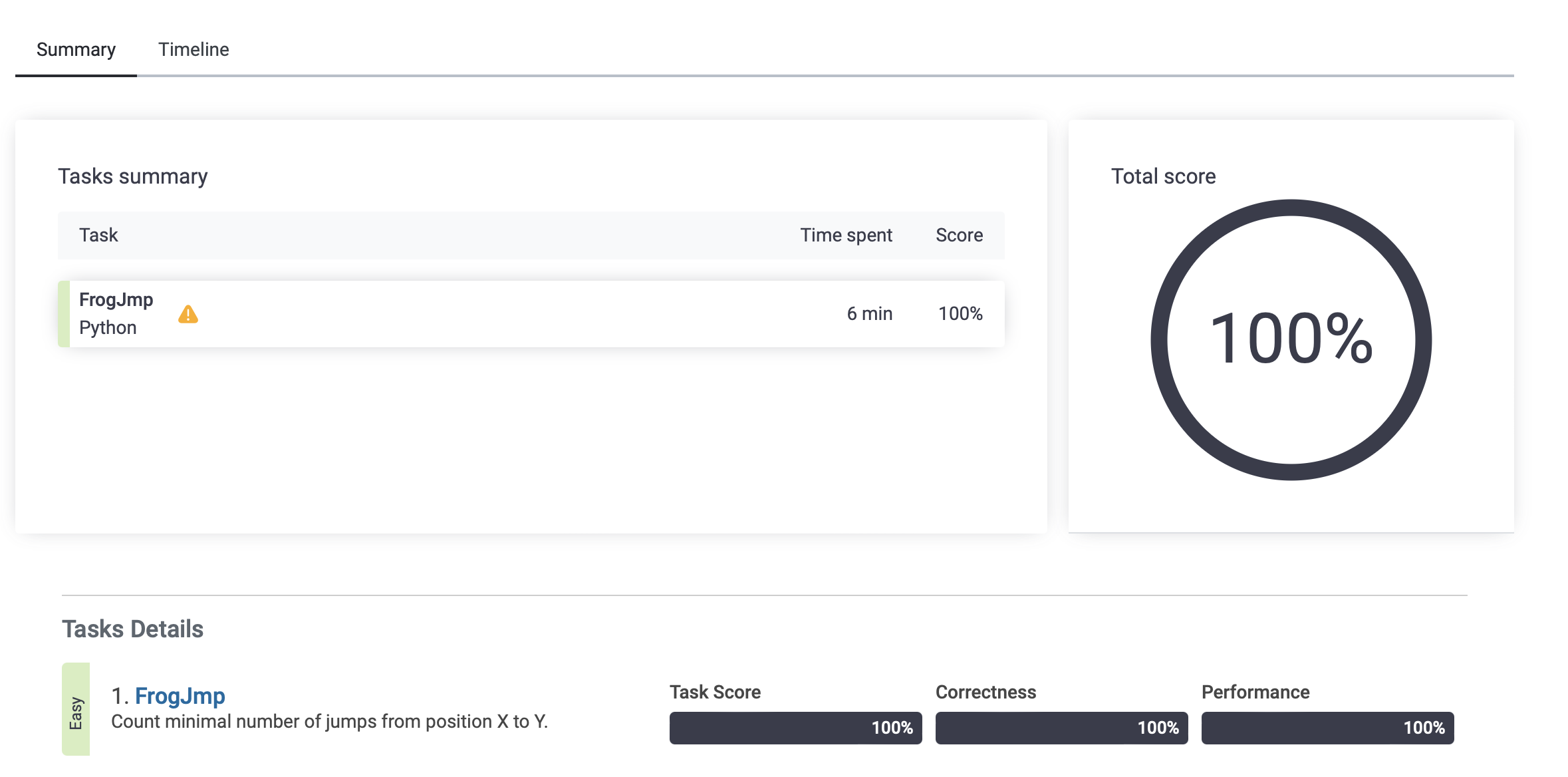
야호~~
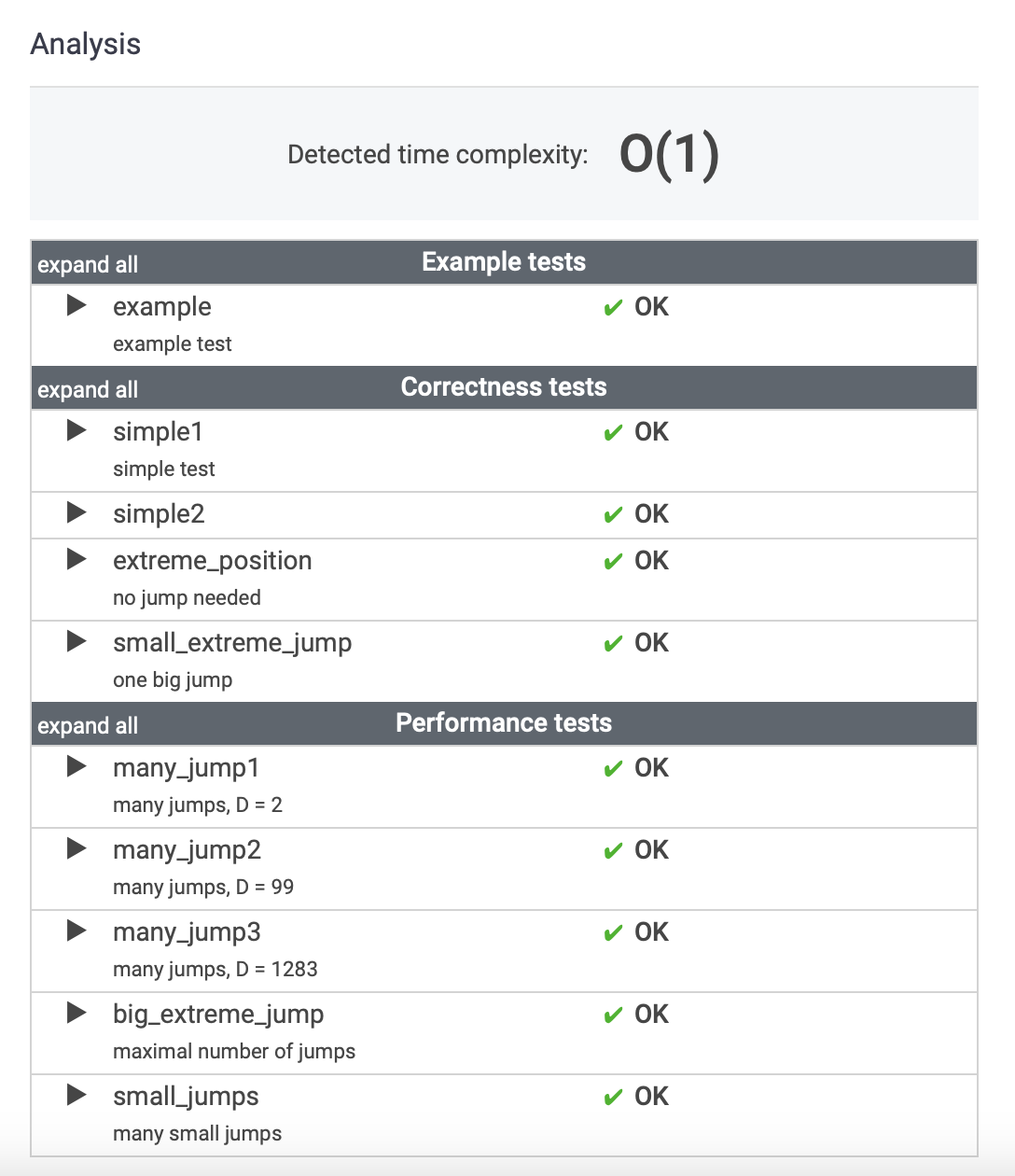
오늘도 한건 해냈다리~
7. 마무리
항상 문제를 풀때 되지도 않는 반복문 투척으로 인해 런타임 에러가 나기 부지기수였다. 제발! 앞으로 문제 풀때 시간복잡도 신경써서 풀어보자고!
다음 문제도 실수 없이!