💻lesson3 - TapeEquilibrium
1. 문제
A non-empty array A consisting of N integers is given. Array A represents numbers on a tape.
Any integer P, such that 0 < P < N, splits this tape into two non-empty parts: A[0], A[1], ..., A[P − 1] and A[P], A[P + 1], ..., A[N − 1].
The difference between the two parts is the value of: |(A[0] + A[1] + ... + A[P − 1]) − (A[P] + A[P + 1] + ... + A[N − 1])|In other words, it is the absolute difference between the sum of the first part and the sum of the second part.
For example, consider array A such that:
A[0] = 3
A[1] = 1
A[2] = 2
A[3] = 4
A[4] = 3We can split this tape in four places:
P = 1, difference = |3 − 10| = 7
P = 2, difference = |4 − 9| = 5
P = 3, difference = |6 − 7| = 1
P = 4, difference = |10 − 3| = 7Write a function:
def solution(A)that, given a non-empty array A of N integers, returns the minimal difference that can be achieved.
For example, given:
A[0] = 3
A[1] = 1
A[2] = 2
A[3] = 4
A[4] = 3the function should return 1, as explained above.
Write an efficient algorithm for the following assumptions:
N is an integer within the range [2..100,000];
each element of array A is an integer within the range [−1,000..1,000].
2. 문제 접근
시간복잡도를 어떻게 줄일 수 있을지 전혀 떠오르지 않는다.
중첩 반복문 밖에 생각이 안떠올라서 일단 이 문제를 해결하는 것에 초점을 맞추고 풀기로 한다.
그저 반복문으로 사용하면 쉬운 문제...시간 복잡도 생각으로 너무 시간을 많이 써버려서 제출을 해보기로 한다.
3. 첫번째 시도 - python
def solution(A):
lst = []
for P in range(1, len(A)):
fst = 0
for i in range(0, P):
fst += A[i]
snd = 0
for j in range(P, len(A)):
snd += A[j]
lst.append(abs(fst-snd))
return min(lst)4. 첫번째 결과
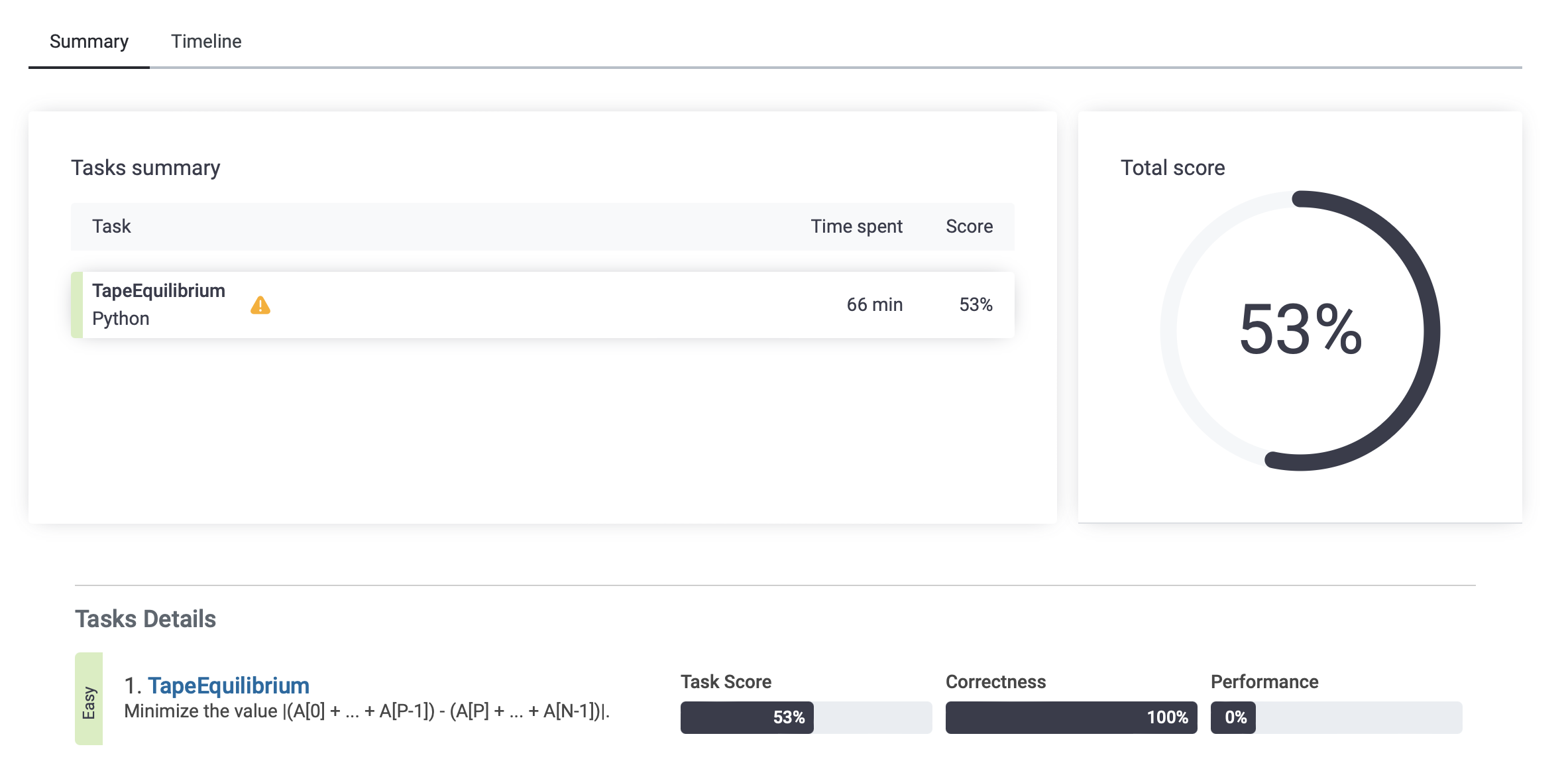

으악! 역시 O(N^2)가 나왔다.
그래도 퍼센트는 완전 극초반의 숫자일 줄 알았는데 생각보다 반타작은 쳐서 놀랍다.
다시 시간복잡도를 줄일 수 있는 방법을 생각해보자...
5. 두번째 시도
def solution(A):
sum_A = sum(A)
sum_B = 0
lst = []
for i in range(0, len(A)):
sum_A -= A[i]
sum_B += A[i]
lst.append(abs(sum_A-sum_B))
return min(lst)6. 두번째 결과
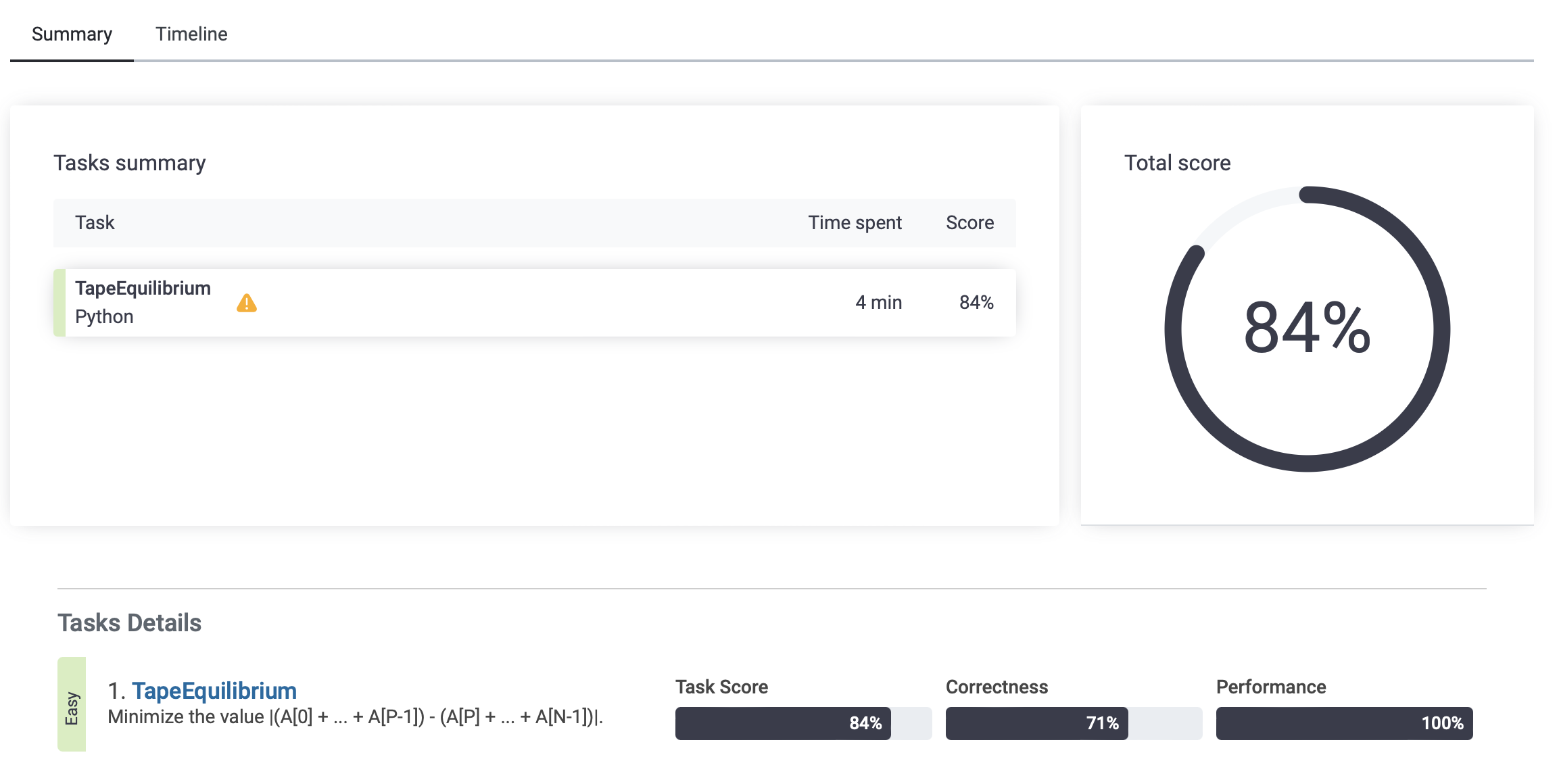
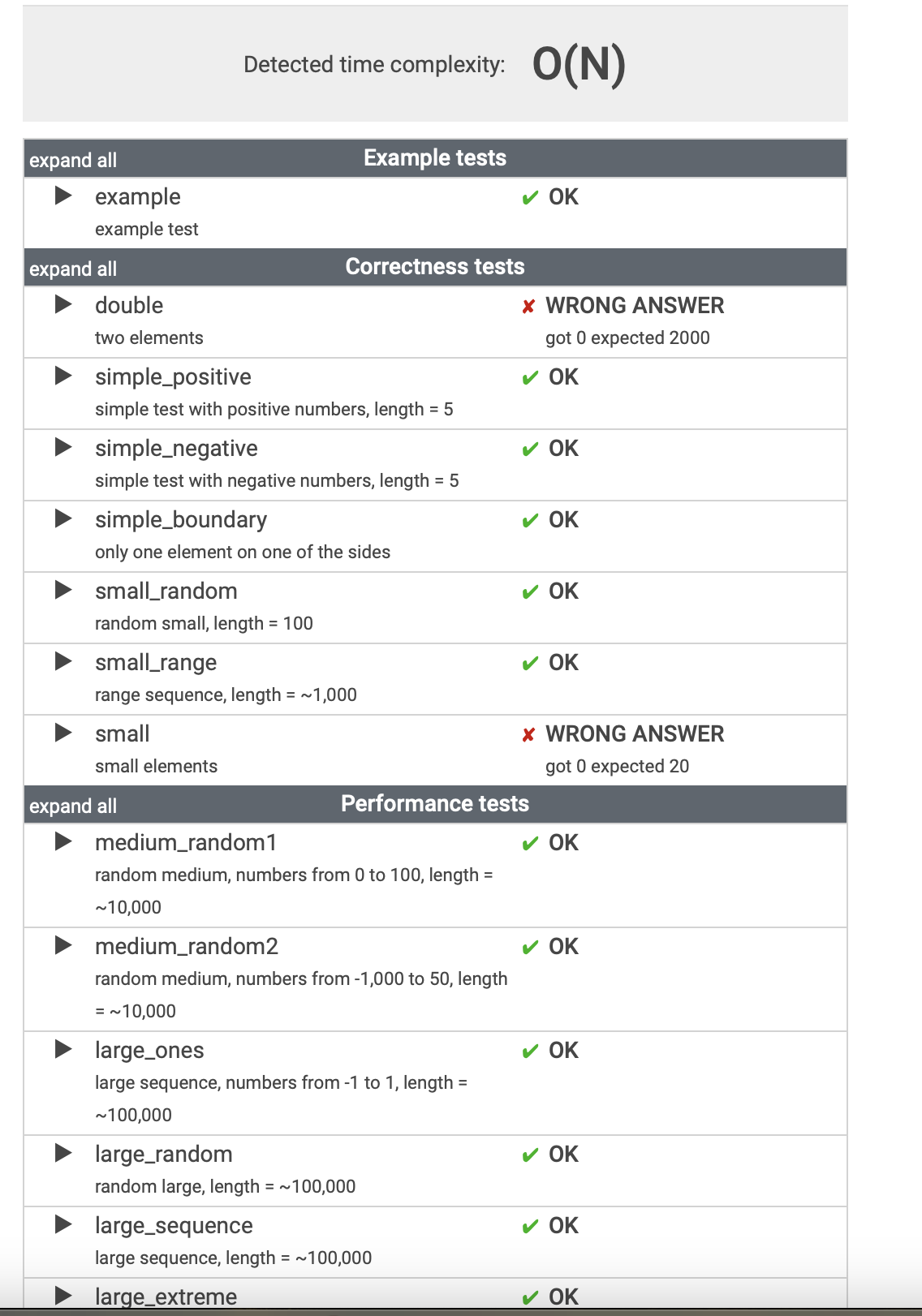
런타임 에러는 해결했는데 오답을 출력했나보다.
원소가 두개거나 작은 원소를 가지는 배열일때 오답이 있었다고 한다.
7. 마무리
반복문에 절여져서 안좋은 습관이 너무 많이 들었다.
시간복잡도 줄일 수 있으면 최대한 안쓰는 방향으로 습관을 바꿔나가자!

