💻lesson4 - MaxCounters
1. 문제
You are given N counters, initially set to 0, and you have two possible operations on them:
increase(X) − counter X is increased by 1,
max counter − all counters are set to the maximum value of any counter.
A non-empty array A of M integers is given. This array represents consecutive operations:
if A[K] = X, such that 1 ≤ X ≤ N, then operation K is increase(X),
if A[K] = N + 1 then operation K is max counter.
For example, given integer N = 5 and array A such that:
A[0] = 3
A[1] = 4
A[2] = 4
A[3] = 6
A[4] = 1
A[5] = 4
A[6] = 4
the values of the counters after each consecutive operation will be:
(0, 0, 1, 0, 0)
(0, 0, 1, 1, 0)
(0, 0, 1, 2, 0)
(2, 2, 2, 2, 2)
(3, 2, 2, 2, 2)
(3, 2, 2, 3, 2)
(3, 2, 2, 4, 2)
The goal is to calculate the value of every counter after all operations.
Write a function:
def solution(N, A)
that, given an integer N and a non-empty array A consisting of M integers, returns a sequence of integers representing the values of the counters.
Result array should be returned as an array of integers.
For example, given:
A[0] = 3
A[1] = 4
A[2] = 4
A[3] = 6
A[4] = 1
A[5] = 4
A[6] = 4
the function should return [3, 2, 2, 4, 2], as explained above.
Write an efficient algorithm for the following assumptions:
N and M are integers within the range [1..100,000];
each element of array A is an integer within the range [1..N + 1].2. 문제 접근
문제 이해하는 것이 제일 어려웠다. 문제 중 operation을 배열로 이해해버려서 서치하고 나서 문제 이해했다...
그러니깐
1. 원소가 N보다 같거나 작으면 배열 원소에 해당하는 위치에 +1
2. 원소가 N보다 크면 배열에 전부 max counter
여기서 max counter는 만들어가는 배열에서 가장 높은 숫자...
라고 이해하고 문제를 풀어가기 시작했다.
3. 첫번째 시도 - python
def solution(N, A):
max_counter = 0
result_array = [0]*N #크기 N만큼의 리스트
for i in A:
if(i>N): #N보다 A의 원소가 크면 배열에 맥스카운더
result_array = [max_counter]*N
else: # 아니면 그냥 해당하는 부분에 1더하고 맥스 카운터 계산
result_array[i-1] += 1
max_counter = max(result_array)
return result_array4. 첫번째 결과
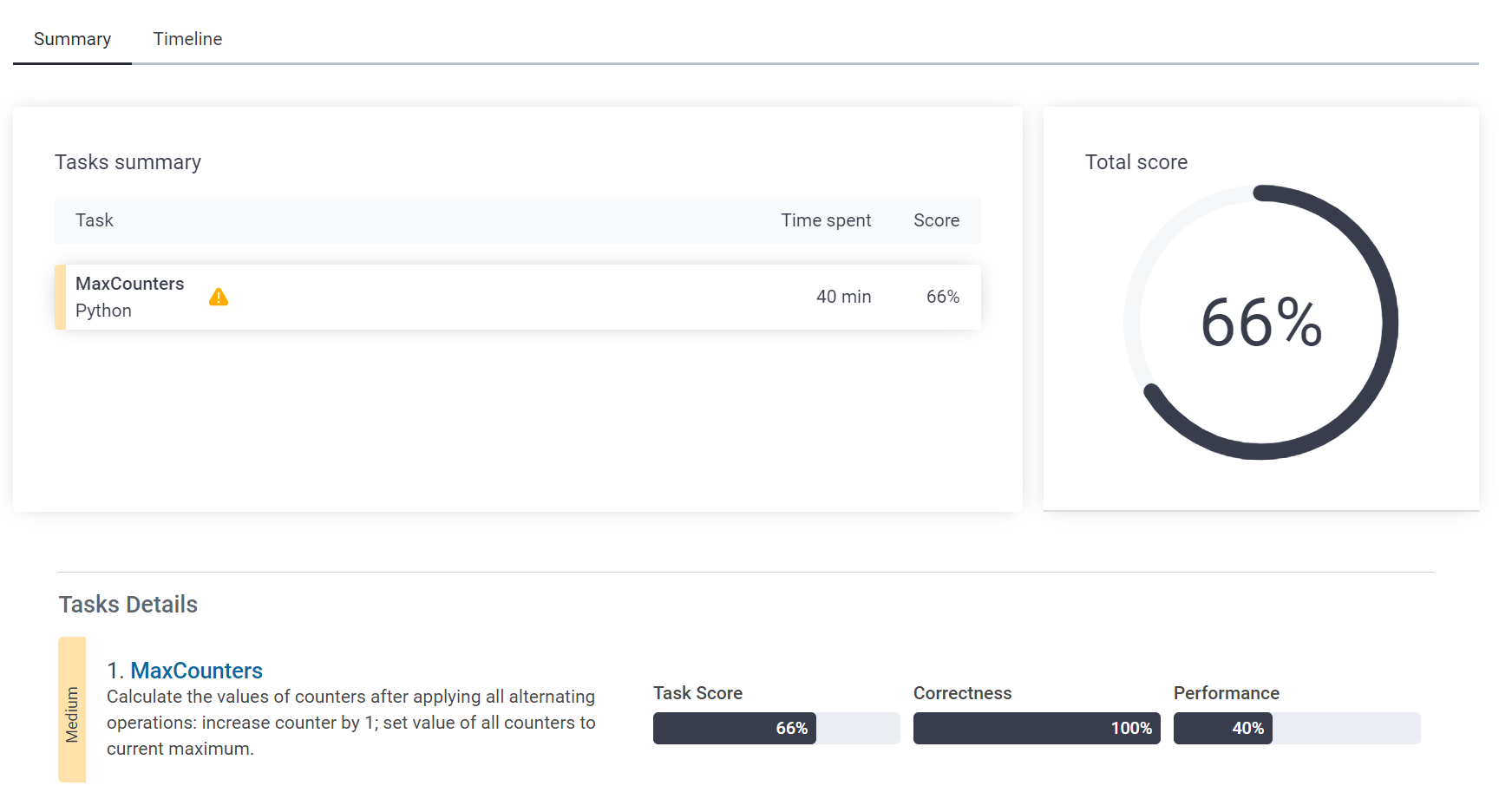
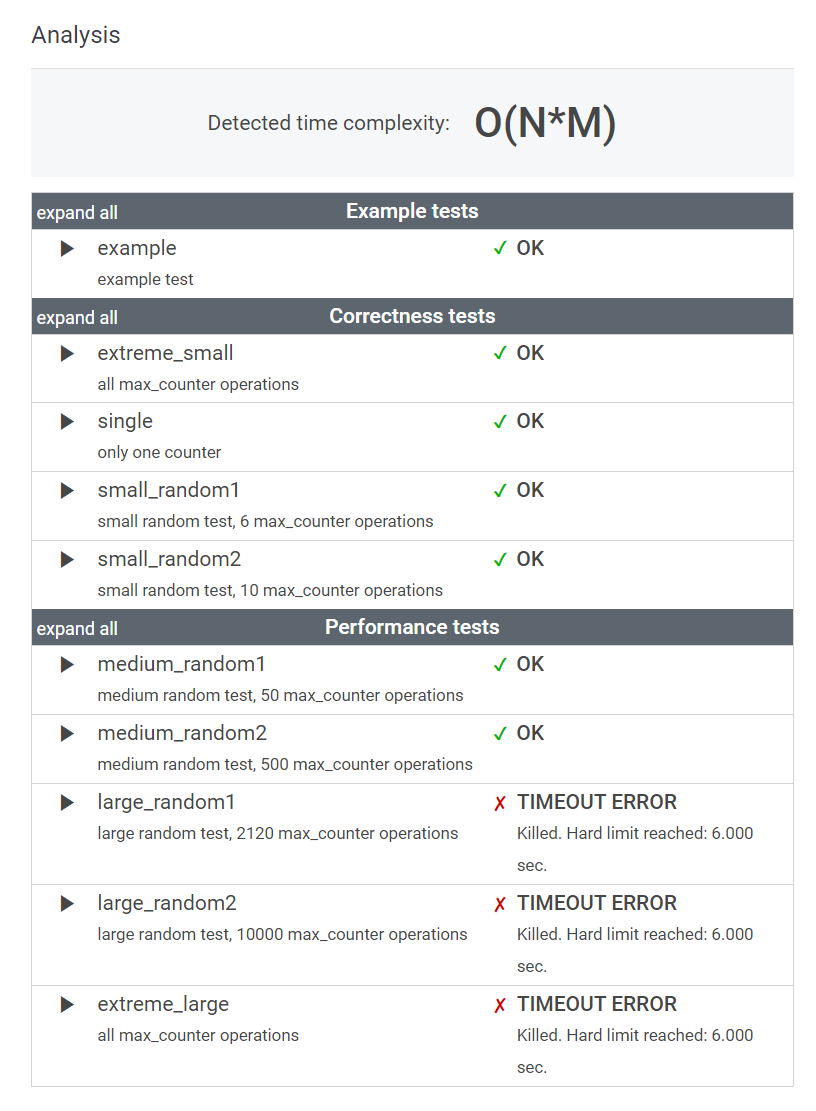
늦게 이해한것 치고는 답은 얼추 맞았나보다. 그런데 시간복잡도가 엄청나게 크게 나왔다.아무래도 무분별한 함수사용과 반복문 사용이 원인인듯하다.
시간복잡도 줄일 수 있는 부분에선 전부 고쳐봐야할 것 같다.
5. 두번째 시도
def solution(N, A):
max_counter = 0
result_array = [0]*N #크기 N만큼의 리스트
array = [0]*N
for i in A:
if(i>N): #N보다 A의 원소가 크면 배열에 맥스카운더
result_array = list(array)
else: # 아니면 그냥 해당하는 부분에 1더하고 맥스 카운터 계산
if(i==0):
continue
else:
result_array[i-1] += 1
max_counter = max(result_array)
for i in range(len(result_array)):
result_array[i] += max_counter
return result_array- 두번째 결과
ㅋㅋ...망했다
- 참고
def solution(N, A):
answer = [0]*N
max_counter = N+1
cache = 0
maximum = 0
for num in A:
if num < max_counter:
if answer[num-1] < cache:
answer[num-1] = cache + 1
else:
answer[num-1] += 1
if answer[num-1] > maximum:
maximum = answer[num-1]
else:
cache = maximum
for idx in range(N):
if answer[idx] < cache:
answer[idx] = cache
return answer도저히 100%를 만들 수 없을 것 같아서 찾아보았다.
너무 어려워...ㅜㅜ