문제
n개의 정점을 갖는 이진 트리의 정점에 1부터 n까지의 번호가 중복 없이 매겨져 있다. 이와 같은 이진 트리의 인오더와 포스트오더가 주어졌을 때, 프리오더를 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
입력
첫째 줄에 n(1 ≤ n ≤ 100,000)이 주어진다. 다음 줄에는 인오더를 나타내는 n개의 자연수가 주어지고, 그 다음 줄에는 같은 식으로 포스트오더가 주어진다.
출력
첫째 줄에 프리오더를 출력한다.
예제 입력
3
1 2 3
1 3 2
예제 출력
2 1 3
해설
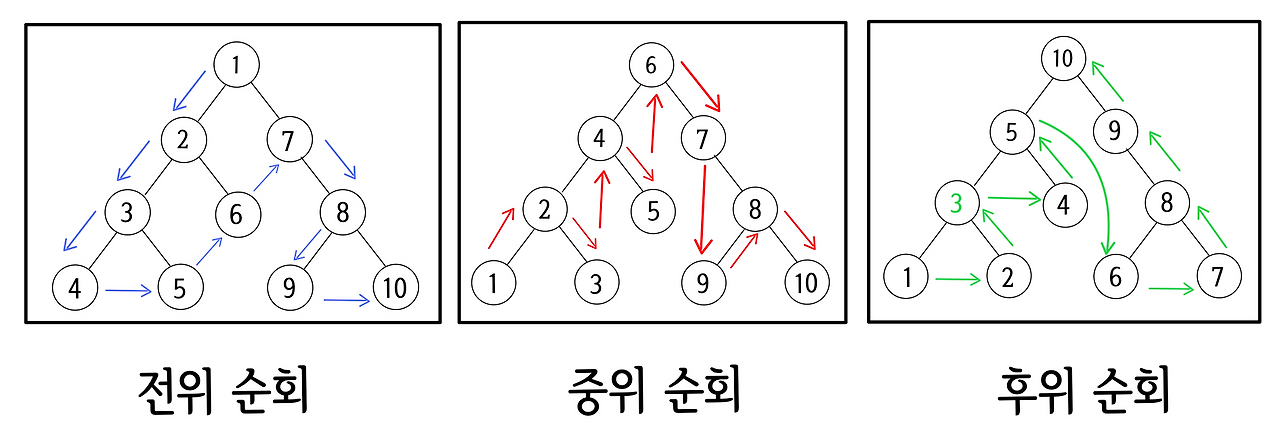
-
전위 순회 Preorder : Root - Left - Right
-
중위 순회 Inorder : Left - Root - Right
-
후위 순회 Postorder : Left - Right - Root
설계
- 후위 순회와 중위 순회가 주어졌을 때 전위 순회를 구해야 하는 상황
- 후위 순회의 가장 마지막 원소는 현재 트리의 루트
- 중위 순회에서는 후위 순위를 찾은 루트를 기준으로 왼쪽 서브트리 / 오른쪽 서브트리로 나뉨
- 첫번째 루트 ➡️ 가장 큰 분기점으로 왼쪽 서브트리 / 오른쪽 서브트리 나뉨
- 두번째 루트 ➡️ 두번째로 큰 분기점으로 첫번째 루트로 나뉜 서브트리들에서 1~2번 반복
- N번째 루트 ➡️ N번째로 큰 분기점으로 이전에 나뉜 서브트리들에서 모두 1~2번 반복
➡️ 재귀
파이썬 재귀 사용 주의점
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
def build(il, ir, pl, pr):
if il > ir:
return
root = postorder[pr]
ans.append(root)
idx = inorder.index(root, il, ir + 1)
ls = idx - il
build(il, idx - 1, pl, pl + ls - 1)
build(idx + 1, ir, pl + ls, pr - 1)
N = int(input())
inorder = list(map(int, input().split()))
postorder = list(map(int, input().split()))
ans = []
build(0, N - 1, 0, N - 1)
print(" ".join(map(str, ans)))
- 파이썬은 기본 재귀 횟수가 1000으로 제한
sys.setrecursionlimit(N)을 통해 횟수 제한을 늘려줘야함- 대부분 10^6 정도 사용하는 느낌...
시간 초과 해결
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
sys.setrecursionlimit(10**6)
def build(il, ir, pl, pr):
if il > ir:
return
root = postorder[pr]
ans.append(root)
idx = inorder.index(root, il, ir + 1)
ls = idx - il
build(il, idx - 1, pl, pl + ls - 1)
build(idx + 1, ir, pl + ls, pr - 1)
N = int(input())
inorder = list(map(int, input().split()))
postorder = list(map(int, input().split()))
ans = []
build(0, N - 1, 0, N - 1)
print(" ".join(map(str, ans)))
- 재귀 해결하고 이번엔 시간 초과 발생
- root를 찾기 위해 사용한 파이썬의 arr.index()가 문제라 생각
- 직접 돌리면 빠르려나???
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
sys.setrecursionlimit(10**6)
def build(il, ir, pl, pr):
if il > ir:
return
root = postorder[pr]
ans.append(root)
idx = -1
for k in range(il, ir + 1):
if inorder[k] == root:
idx = k
break
ls = idx - il
build(il, idx - 1, pl, pl + ls - 1)
build(idx + 1, ir, pl + ls, pr - 1)
N = int(input())
inorder = list(map(int, input().split()))
postorder = list(map(int, input().split()))
ans = []
build(0, N - 1, 0, N - 1)
print(" ".join(map(str, ans)))- 똑 같 다 !
- .indx()를 사용한 이유 : 트리의 순회 문제에서는 값이 모두 다르기 때문에 가장 빠른 배열값의 인덱스를 리턴해도 괜찮다고 생각함
| 연산 | 시간 복잡도 | 설명 |
|---|---|---|
len(a) | O(1) | 전체 요소의 개수를 리턴 |
a[i] | O(1) | 인덱스 i의 요소 |
a[i:j] | O(k) | i부터 j-1까지 슬라이싱으로 길이만큼 k개의 요소 |
elem in a | O(n) | elem 요소가 존재하는지 확인 / 순차 탐색 -> n만큼 시간이 소요 |
a.count(elem) | O(n) | elem 요소의 개수 리턴 |
a.index(elem) | O(n) | elem 요소의 인덱스 리턴 |
a.append(elem) | O(1) | 리스트 마지막에 elem 추가 |
a.pop() | O(1) | 리스트 마지막 요소를 추출 |
a.pop(0) | O(n) | 리스트 첫번째 요소 추출 / 전체 복사 -> O(n) / Deque 사용 권장 |
del a[i] | O(n) | 최악이 O(n) / 순차 탐색 |
a.sort() | O(n log n) | Tim Sort |
min(a), max(a) | O(n) | 전체 선형 탐색 |
index()가 선형 탐색으로 O(n)- O(1)로 해결해야 시간 초과 안난다 생각
정답 코드
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
sys.setrecursionlimit(10**6)
def build(il, ir, pl, pr):
if il > ir:
return
root = postorder[pr]
ans.append(root)
idx = pos[root]
ls = idx - il
build(il, idx - 1, pl, pl + ls - 1)
build(idx + 1, ir, pl + ls, pr - 1)
N = int(input())
inorder = list(map(int, input().split()))
postorder = list(map(int, input().split()))
pos = {v: i for i, v in enumerate(inorder)}
ans = []
build(0, N - 1, 0, N - 1)
print(" ".join(map(str, ans)))pos = {v: i for i, v in enumerate(inorder)}inorder리스트를 처음부터 끝까지 보면서 각 값v가 중위 순회에서 몇 번째 인덱스에 있는지를 저장- ex)
inorder = [4, 2, 5, 1, 6, 3, 7]
➡️pos = {4: 0, 2: 1, 5: 2, 1: 3, 6: 4, 3: 5, 7:6}
- 배열 한번 돌고 인덱스 찾을 때는 O(1)
