상속연습1
-class MobilePhone : 전화걸기, 전화받기, 무선 기지국 연결, 배터리 충전하기
-class MusicPhone : 전화걸기, 전화받기, 무선기지국 연결, 배터리 충전하기, 음악다운받기, 음악재생하기
1) 공통 되는 부분은(MobilePhone) 부모로 만들어 공유하기
public class MobilePhone {
void 전화걸기() { System.out.println("전화걸기"); }
void 전화받기() { System.out.println("전화받기"); }
void 무선기지국연결() { System.out.println("무선 기지국 연결"); }
void 배터리충전하기() { System.out.println("배터리 충전하기"); }
}2) 공통부분 부모로 받고, 추가로 필요한 부분(MusicPhone) 만들기
public class MusicPhone extends MobilePhone{
void 음악다운받기() { System.out.println("음악 다운 받기"); }
void 음약재생하기() { System.out.println("음악 재생 하기"); }
}3) 출력해보기
public class business {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 자식 생성자 객체 생성
MusicPhone mp = new MusicPhone();
mp.전화걸기();
mp.전화받기();
mp.무선기지국연결();
mp.배터리충전하기();
mp.음악다운받기();
mp.음약재생하기();
// 부모생성자 객체 생성하여서 부모 클래스 메소드 다 써보기
System.out.println("-----------여기부터 부모 생성자 부분-----------");
MobilePhone mp1 = new MobilePhone();
mp1.전화걸기();
mp1.전화받기();
mp1.무선기지국연결();
mp1.배터리충전하기();
}
}실행결과
: 부모 클래스에서 만든 메소드를 자식 클래스에서 불러오기 가능
상속연습2
x,y의 한점을 표현하는 Point클래스와 이를 상속 받아 점을 추가한 ColorPoint클래스를 만들어라.
-class Point : 한점을 구성하는 x,y좌표, 점을 출력하는 메소드
-class ColorPoint : 한점을 구성하는 x,y좌표, 점을 출력하는 메소드, 점의 색깔, 컬러 점의 좌표 출력하는 메소드
실행결과 모습
(1,2)
red(3,4)
1) Point 클래스.
ColorPoint 클래스보다 작은 공통부분이라 부모 클래스로 작성했다.
//class Point : 한점을 구성하는 x,y좌표, 점을 출력하는 메소드
public class Point {
// 점 좌표 받을 x, y 필드값으로 작성
int x;
int y;
// 순서2. 받아서 필드값으로 저장된 x, y를
// (x, y)의 형태로 출력해줄 메소드
void pointPrint() {
System.out.println("( " + x + " , " + y + ")");
}
// 순서 1. 이 메소드로 들어온 x, y가 필드 값으로 올라간다.
Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
// 기본 생성자도 작성해준다
Point() { }
}- ColorPoint 클래스
point 에서 설정하지 않았던, 고유 부분 작성
// class ColorPoint
// : 한점을 구성하는 x,y좌표, 점의 색깔, 점을 출력하는 메소드, 컬러 점의 좌표 출력하는 메소드
public class ColorPoint extends Point {
// 부모 클래스에서 작성해주지 않은
// Coloer 필드 값으로 설정
String color;
// 받아와 필드값으로 저장된 값들을
// 색(x, y) 형태로 츨력해줄 메소드 설정
void printColor() {
System.out.println(color + "( " + x + " , " + y + " )");
}
// x, y를 필드값으로 설정하지 않았지만
// 부모 클래스에 있으니 사용 가능하다.
ColorPoint(int x, int y, String color) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.color = color;
}
// 기본 생성자도 작성해준다
ColorPoint() { }
}- PointBusiness
-Point클래스와 ColorPoint클래스 생성하고 제어 하는 부분
public class PointBusiness {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 부모 클래스 객체 생성
// (1,2) 있는 것만 먼저 출력
Point point = new Point(1, 2);
point.pointPrint();
// 자식 클래스 객체 생성
// red(3,4)호출
ColorPoint cp = new ColorPoint(3, 4, "red");
cp.printColor();
}
}실행결과
: 부모 클래스도 객체 생성 후 따로 사용 가능
상속연습 3
요구사항
A클래스 : 1~10까지의 합, 차(합-10)
B클래스 : 1~100까지의 합,
C클래스 : 1~ 200까지의 합, 차(합-200), 곱(1~20까지)
D클래스 : 전체 출력
// B클래스 : 1~100까지의 합
// 가장 상위 클래스
public class B {
int result = 0;
// 1 ~ num 까지의 합
// 메인에서 던져주는 num 까지 누적합이 result에 저장된다
int hap(int num) {
for(int i=0; i<=num; i++) {
result += i;
}
return result;
}
}
--------------------------------------------------------------
// A클래스 : 1~10까지의 합을 구하고 차(합-10)
// B의 자식 클래스
public class A extends B {
// 1~10 까지 합을 구한 다음 -num 을 하면 된다
int sub(int num) {
// 합을 구하는 메소드 호출
for(int i=0; i<=num; i++) {
result += i;
}
return result - 10;
}
}
--------------------------------------------------------------
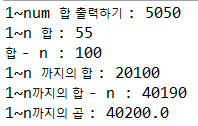
public class D {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1~100 합 출력하기
B b = new B();
int result = b.hap(100);
System.out.println("1~num 합 출력하기 : " + result);
// 1~10 합, 합-10
A a = new A();
int reuslt1 = a.hap(10);
System.out.println("1~n 합 : " + reuslt1);
// 잘못된 값 출력
//왜?
int result2 = a.sub(10);
System.out.println("합 - n : " + result2);
// 1~ 200까지의 합, 차(합-200), 곱(1~20까지)
C c = new C();
int resutl3 = c.hap(200);
System.out.println("1~n 까지의 합 : " + resutl3);
int result4 = c.sub(200);
System.out.println("1~n까지의 합 - n : " + result4);
double result5 = c.mul(200);
System.out.println("1~n까지의 곱 : " + result5);
}
}
실행결과