<예시>
Person 클래스 생성
=============================코드=============================
public class Person {
// 멤버변수
String juminNo; // 주민번호
String name; // 이름
int age; // 나이
String job; // 직업
}Person 클래스를 상속 받을 Student 클래스 생성
=============================코드=============================
public class Student extends Person {
// String juminNo;
// String name;
// int age;
// String job;
String major; // 학과
public Student() {
super(); // 부모클래스
} // 기본 생성자
public Student(String juminNo, String name, int age, String job, String major) {
super();
this.juminNo = juminNo;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.job = job;
this.major = major;
} // 인자 생성자
void getStudentInfo() {
System.out.println("주민번호 >>> " + juminNo);
System.out.println("이 름 >>> " + name);
System.out.println("나 이 >>> " + age);
System.out.println("직 업 >>> " + job);
System.out.println("학 과 >>> " + major);
} // getStudentInfo() 메서드 end
}1. super( ) 키워드
: 자식클래스에서 부모클래스의 생성자를 호출하는 명령어
형식) super(인자); // 인자는 생략도 가능함
2. this( ) 키워드
: 현재(자식) 클래스에서 현재 클래스 안에 있는 다른 생성자를 호출하는 명령어
형식) this(인자);
★ 주의 : this( ) 키워드를 사용 시에는 반드시 생성자 첫 문장에 와야 함
Person 클래스를 상속 받을 Employee 클래스 생성
=============================코드=============================
public class Employee extends Person {
// String juminNo;
// String name;
// int age;
// String job;
int salary; // 급여
// 기본생성자
void getEmployeeInfo() {
System.out.println("주민번호 >>> " + juminNo);
System.out.println("이 름 >>> " + name);
System.out.println("나 이 >>> " + age);
System.out.println("직 업 >>> " + job);
System.out.println("급 여 >>> " + salary);
} // getEmployeeInfo() 메서드 end
}메인메서드로 받을 Person_03 클래스 생성
=============================코드=============================
// Student student = new Student();
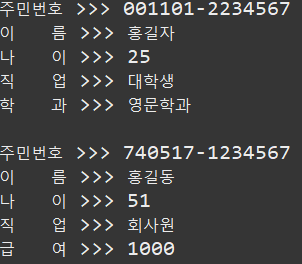
Student student = new Student("001101-2234567", "홍길자", 25, "대학생", "영문학과");
student.getStudentInfo();
System.out.println();
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.juminNo = "740517-1234567";
employee.name = "홍길동";
employee.age = 51;
employee.job = "회사원";
employee.salary = 1000;
employee.getEmployeeInfo();=============================실행=============================
<예시>
Point 클래스 생성
=============================코드=============================
public class Point {
int x;
int y;
public Point() { } // 기본 생성자
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
} // 인자 생성자
}Point 클래스를 상속받을 Point3D 클래스 생성
=============================코드=============================
public class Point3D extends Point {
// int x;
// int y;
int z;
public Point3D() {
super(); // 부모 클래스의 기본 생성자를 호출
} // 기본 생성자
public Point3D(int x, int y) {
super(x, y); // super이거나 this일 경우 꼭 상단에 먼저 호출해야 함!! (부모 클래스 생성자가 먼저 필요)
//this.x = x;
//this.y = y;
} // 인자 생성자
public Point3D(int x, int y, int z) {
//this.x = x;
//this.y = y;
this(x, y); // 위에 있는 멤버 호출 (자식 생성자 호출)
this.z = z;
} // 인자 생성자(오버로딩)
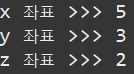
void output() {
System.out.println("x 좌표 >>> " + x);
System.out.println("y 좌표 >>> " + y);
System.out.println("z 좌표 >>> " + z);
} // output() 메서드 end
}메인메서드로 받을 Point_04 클래스 생성
=============================코드=============================
public class Point_04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point3D point = new Point3D(5, 3, 2);
point.output();
}
}=============================실행=============================
<예시>
Volume 클래스 생성 (getter, setter 생성)
=============================코드=============================
public class Volume {
int volume = 1;
public void setVolume(int volume) {
this.volume = volume;
}
public int getVolume() {
return volume;
}
// 볼륨을 올리는 메서드
void volumeUp() {
volume++;
if(volume > 15) {
volume = 15;
}
} // volumeUp() 메서드 end
// 볼륨을 내리는 메서드
void volumeDown() {
volume--;
if(volume < 1) {
volume = 1;
}
} // volumeDown() 메서드 end
}Volume 클래스를 상속받을 TV, Audio, Computer 클래스 생성 (3개 각자 생성)
=============================코드=============================
///////// TV 클래스
public class TV extends Volume {
}
///////// Audio 클래스
public class Audio extends Volume {
}
///////// Computer 클래스
public class Computer extends Volume {
}메인메서드로 출력할 Volume_05 클래스 생성
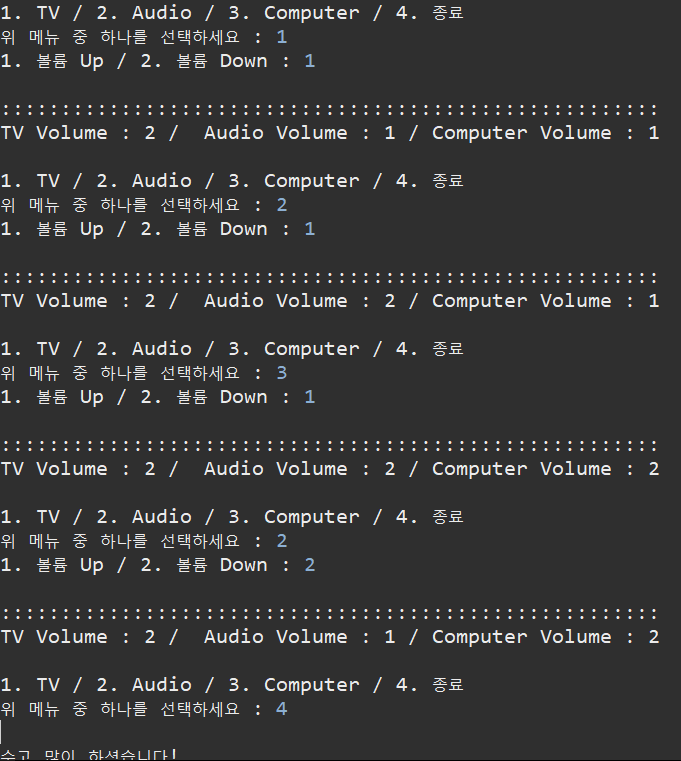
=============================코드=============================
public static void main(String[] args) {
TV tv = new TV();
Audio audio = new Audio();
Computer computer = new Computer();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
System.out.println();
System.out.println("1. TV / 2. Audio / 3. Computer / 4. 종료");
System.out.print("위 메뉴 중 하나를 선택하세요 : ");
int menu = sc.nextInt();
if(menu == 4) {
break;
}
System.out.print("1. 볼륨 Up / 2. 볼륨 Down : ");
int volume = sc.nextInt();
switch(menu) {
case 1 : // TV 메뉴를 선택한 경우
if(volume == 1) {
tv.volumeUp();
}else {
tv.volumeDown();
}
break;
case 2 : // Audio 메뉴를 선택한 경우
if(volume == 1) {
audio.volumeUp();
}else {
audio.volumeDown();
}
break;
case 3 : // Computer 메뉴를 선택한 경우
if(volume == 1) {
computer.volumeUp();
}else {
computer.volumeDown();
}
break;
} // switch ~ case 조건문 end
System.out.println();
System.out.println(":::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::");
System.out.println("TV Volume : " + tv.getVolume() + " / Audio Volume : " + audio.getVolume() +
" / Computer Volume : " + computer.getVolume());
} // while 반복문 end
System.out.println();
System.out.println("수고 많이 하셨습니다!");
sc.close();
}=============================실행=============================
**기억할 점!
-super는 부모클래스의 생성자를 가져오는 것!
-super나 this를 사용할 경우 꼭 상단에 먼저 사용하는 것이 원칙이다!
