다중 catch 문
- catch 문을 여러 개 사용하여 처리하는 방식
- catch 문은 순차적으로 위에서 아래로 실행이 됨
- 주의) 예외를 처리하는 가장 최상위의 Exception 클래스는 맨 마지막에 나와야 함 (만약 맨 첫 줄에 나오는 경우 error 발생)
<예시>
=============================코드=============================
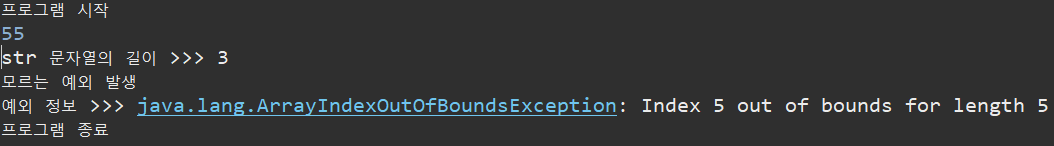
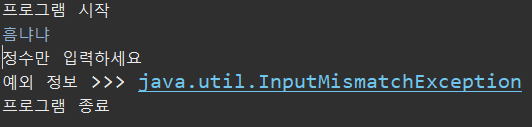
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("프로그램 시작");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = 0;
String str = "dfs";
int[] arr = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
try {
num = sc.nextInt(); // 예외 발생할 가능성이 있는 코드
System.out.println("str 문자열의 길이 >>> " + str.length());
arr[5] = 60;
}catch(InputMismatchException e) {
System.out.println("정수만 입력하세요");
System.out.println("예외 정보 >>> " + e);
}catch(NullPointerException e1) {
System.out.println("null 값이 들어왔어요");
System.out.println("예외 정보 >>> " + e1);
// 최상위 예외 클래스이기 때문에 맨 밑에 넣어줘야 함 -> Input~, Null~이 갖고 있는 예외를 Exception이 다 갖고 있음
}catch(Exception e2) {
System.out.println("모르는 예외 발생");
System.out.println("예외 정보 >>> " + e2);
}finally {
sc.close();
}
System.out.println("프로그램 종료");
}=============================실행=============================
printStackTrace( ) 란?
: 에러 메세지의 발생 근원을 찾아서 단계별로 에러를 출력해 주는 메서드
=============================코드=============================
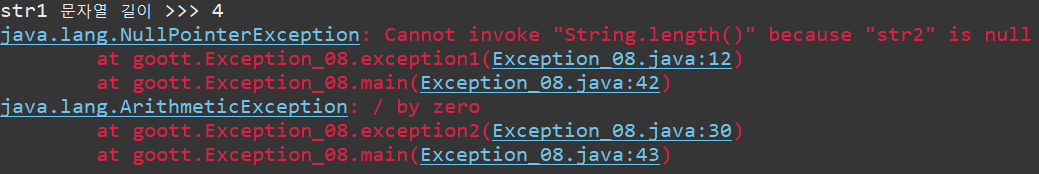
void exception1() {
String str1 = "java";
String str2 = null;
try {
System.out.println("str1 문자열 길이 >>> " + str1.length());
System.out.println("str2 문자열 길이 >>> " + str2.length());
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
/*
* printStackTrace()
* - 에러 메세지의 발생 근원을 찾아서
* 단계별로 에러를 출력해 주는 메서드
*/
}
void exception2() {
int num1 = 15, num2 = 0, result = 0;
try {
result = num1 / num2;
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Exception_08 exception = new Exception_08();
exception.exception1();
exception.exception2();
}=============================실행=============================
**어려웠던 점
-InputMismatchException 과 NullPointerException을 포함하는 예외처리가 Exception 이라는 것을 기억하자!!
