문제
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order, and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
예시
Input
l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]output
[7,0,8]Input
l1 = [0], l2 = [0]output
[0]Input
l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]output
[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]제약조건
- The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range
[1, 100]. 0 <= Node.val <= 9- It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.
Follow-up
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
* /문제 분석하기
두 개의 ListNode 를 입력 받아, 각각의 리스트가 표현하는 숫자를 역순으로 저장하고 있다.
두 개의 리스트를 해석하여 더한 다음, 그 결과를 다시 역순으로 ListNode 형태로 반환해야 한다.
- 각 노드는 한 자리 숫자를 포함한다.
- 두 리스트의 노드를 순서대로 더하여 새로운 리스트를 만들어야한다. -> 자릿수 올림 처리 생각하기
처리방법
-
l1 와 l2 를 동시에 순회하며 각 노드의 값을 더한다.
-
자릿수를 올려야 할 상황이 생기면 처리한다.
- 10 이상이면 10으로 나눈 나머지를 현재값으로 사용하고 몫을 다음자리에 넘겨야한다.
-
두 리스트의 길이가 다르수도 있으므로, 한 리스트가 끝난 후에도 다른 리스트의 나머지 값을 계속 더해야 한다.
-
모든 계산을 마치고도 올림값이 남았을 경우, 리스트에 추가해 줘야 한다.
손으로 풀어보기
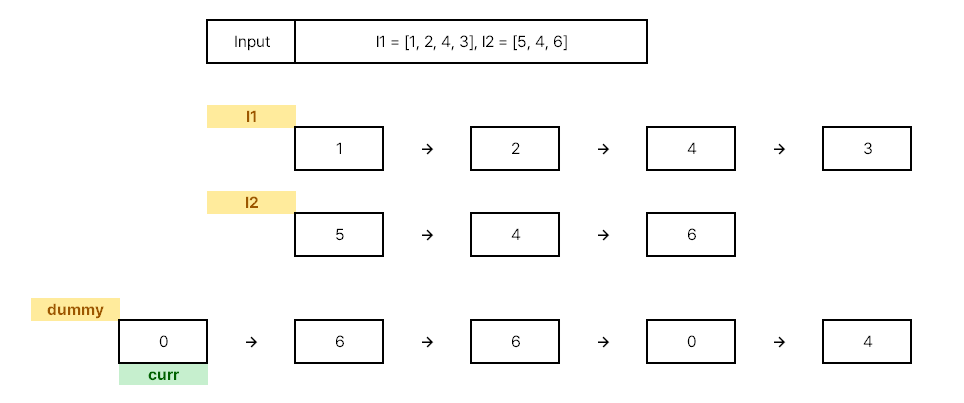
아래와 같은 입력이 주어진다고 가정했을 때를 보자
두 리스트의 노드들의 합을 저장할 리스트(dummy) 을 생성한 후 포인터(curr) 를 설정해 준다.
0 으로 초기화 시킨 이유는 엣지 케이스 처리를 위해...
두 리스트의 노드들의 합계를 구할 때에는 l1 + l2 + carry(자릿수) 를 신경써야한다.
curr = sum % 10
carry = sum / 10
- Step. 1
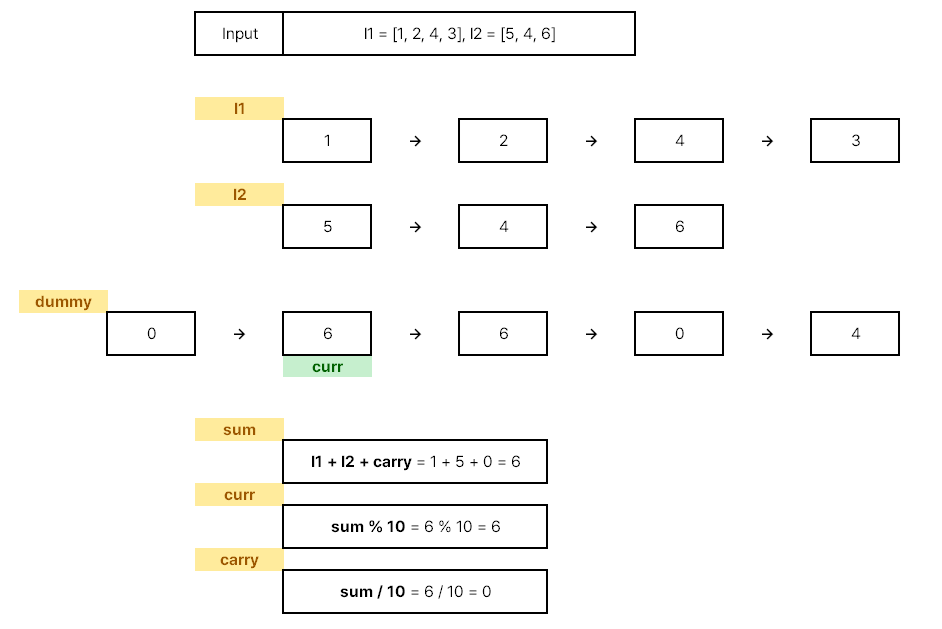
- Step. 2

- Step. 3
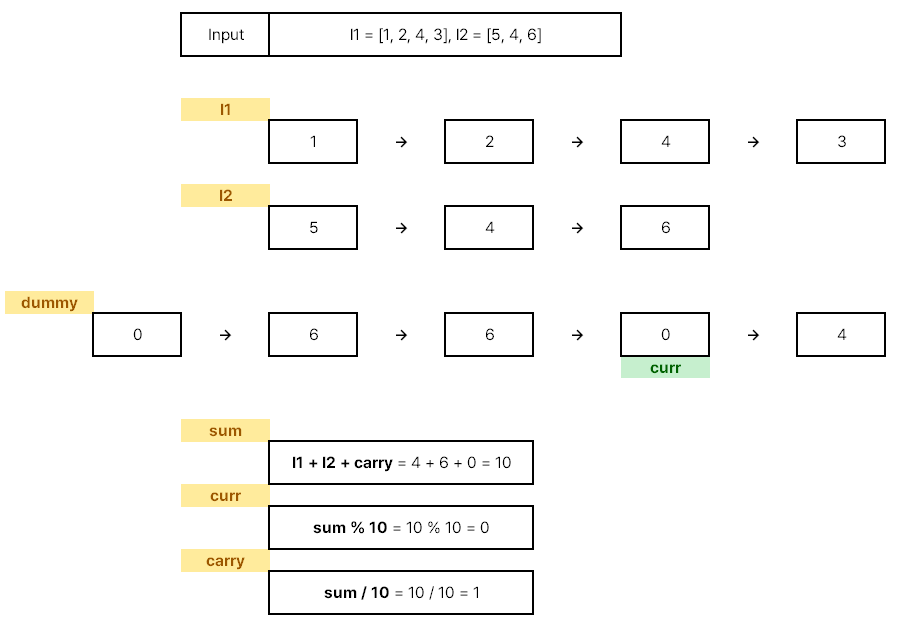
- Step. 4
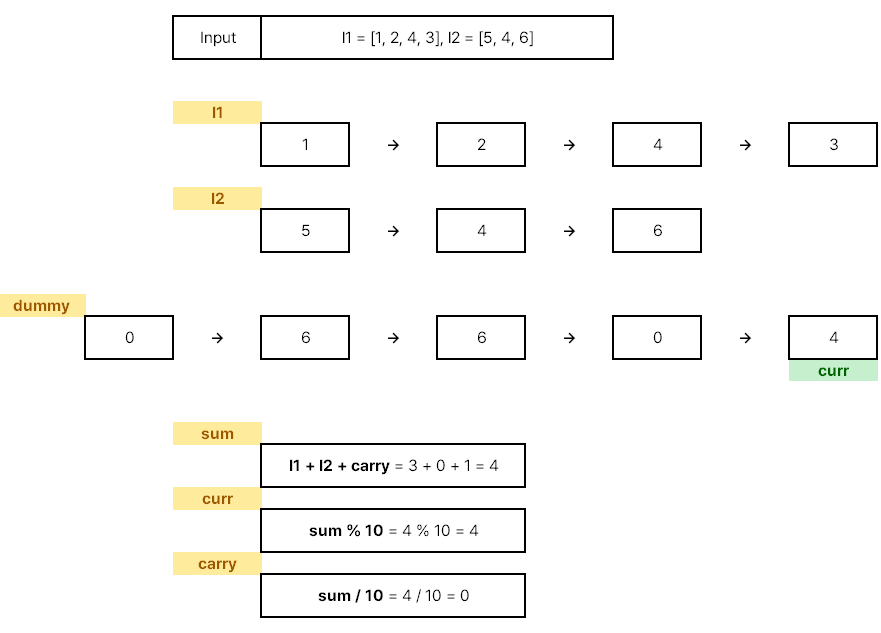
슈도코드 작성하기
// 사전의 정의된 ListNode 클래스 작성
...
// 더비 헤드 노드를 0값으로 초기화 해서 에지 케이스 처리를 간소화 한다.
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0) 으로 초기화
ListNode curr = dummyHead // 현재값으로 위 초기화된 ListNode 대입
int carry = 자릿수 저장할 변수 선언 및 초기화
while(l1 와 l2 의 노드들이 모두 소진되고 남은 자릿수가 없을 때 까지) {
int n1 = l1의 노드 값이 저장 될 변수 = n1 이 비어있지 않으면 n1.val; 비어있으면 0
int n2 = l2의 노드 값이 저장 될 변수 = n2 가 비어있지 않으면 n2.val; 비어있으면 0
int sum = n1 의 노드 값 + n2 의 노드 값 + 자릿수
자릿수 저장할 변수 = sum / 10;
sum 으로 새 노드를 생성하고 현재 노드와 연결
현재값을 다음 노드로 이동
l1 이 null 이 아니면 다음 노드로 이동
l2 이 null 이 아니면 다음 노드로 이동
}
return 위 0으로 초기화된 더비 헤드 다음 노드 부터 리턴코드 구현하기
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode curr = dummyHead;
int carry = 0;
while (l1 != null || l2 != null || carry != 0) {
int n1 = l1 != null ? l1.val : 0;
int n2 = l2 != null ? l2.val : 0;
int sum = n1 + n2 + carry;
carry = sum / 10;
curr.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
curr = curr.next;
if (l1 != null)
l1 = l1.next;
if (l2 != null)
l2 = l2.next;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}다른 접근법
위 접근법과 같이 dummyHeadNode(더미헤드노드) 를 사용하는 방법 외에 Stack(스택)기반 접근 방식 을 살펴보도록 하자.
public static ListNode solution(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
Stack<Integer> s1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> s2 = new Stack<>();
while (l1 != null) {
s1.push(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
}
while (l2 != null) {
s2.push(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
}
int carry = 0;
ListNode result = new ListNode();
while (!s1.empty() || !s2.empty() || carry != 0) {
int sum = carry;
if (!s1.empty())
sum += s1.pop();
if (!s2.empty())
sum += s2.pop();
ListNode resultNode = new ListNode(sum % 10);
resultNode.next = result;
result = resultNode;
carry = sum / 10;
}
return result;
}