📌 배열 API
- Index
배열데이터 내부에 들어있는 특정한 데이터를 가르키는 숫자를 의미한다.- Indexing
fruites[2] 처럼 특정한 숫자를 기입해서 찾는 행위 - element (요소) = item
인덱스 안에 들어있는 각각의 데이터들 (Apple...)
- Indexing
const nubmers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry']
console.log(numbers[1]) // 2
console.log(fruites[2]) // Cherry📌 Properties
Array.prototype.length()
배열의 길이가 얼마인지 표시해준다. (갯수가 몇개인지)
const nubmers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry']
console.log(numbers.length) // 4
console.log([1, 2].length) // 2Array.prototype.find(), findIndex()
주어진 판별 함수를 만족하는 첫번째 요소 값을 반환한다.
예시 1번
const array1 = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44];
const found = array1.find(element => element > 10); // element에서 요소가 10보다 작으면 찾을때까지 반복
console.log(found);예시 2번
const nubmers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry']
const a = fruits.find(fruit => /^B/.test(fruit))//fruit에서 B로 시작되는 문자데이터 찾아줌
console.log(a) // Banana
const a = fruits.findIndex(fruit => /^C/.test(fruit))//fruit에서 C로 시작되는 문자데이터에 몇번째 배열에 있는지 찾아줌
console.log(a) // 2/^B/ : 정규표현식, 대문자B로 시작하는 문자데이터
매개변수
- callback
배열의 각 값에 대해 실행할 함수 (아래 세가지의 인자를 받아서 실행시킴)- element
처리할 현재 요소 - index
처리할 현재 요소의 인덱스 - array (선택적)
- element
- thisArg (선택적)
Array.prototype.concat()
두개의 배열데이터를 병합해서 새로운 배열 데이터를 그 자리에 반환해준다.
원본데이터는 손상시키지 않는다.
const nubmers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry']
console.log(numbers.concat(fruits)) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 'Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry']Array.prototype.forEach()
forEach가 붙어있는 배열데이터의 아이템 갯수만큼 인수로 사용된 콜백함수가 반복적으로 실행된다.
map 과 다르게 따로 반환되는 값이 존재하지 않는다 주의!
const nubmers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry']
fruits.forEach(function (element, index, array) { // frutes [] 속에 있는게 반복적으로 나타남(숫자가 늘어남)
console.log(element, index, array) // index 는 i 로만 적어도 가능
})Array.prototype.map()
인수로 사용하는 callback의 내부에서 반환(return) 하는 하나의 데이터를 가지고 그 데이터를 모아놓은 새로운 배열을 만들어서 반환한다.
const nubmers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry']
const a = fruits.forEach(function (fruit, index) {
console.log(`${fruit}-${index}`) // Apple-0 Banana-1 Cherry-2
})
console.log(a) // a 에 반환한 것이 없기 때문에 값이 undifined
const b = fruits.map(function (fruit, index) {
return {
id: index, // 0 ...
name: fruit // Apple ...
}
// return `${fruit}-${index}`
})
console.log(b) // return 을 const b에 반환을 해서 값이 존재함, (3) ["Apple-0"...]- return {} 의 값 (객체데이터)
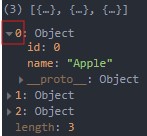
- return
${}-${}의 값

Array.prototype.filter()
배열 데이터 안에 들어있는 각각의 아이템들을 특정한 기준에 의해서 필터링를 해준다.
원본데이터를 유지한다.
const nubmers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry']
const a = number.map(number => number < 3) // 화살표함수 : 매개변수가 1개이면 소괄호 생략 가능
console.log(a) // (4) [true, true, false, fasle]
const b = numbers.filter(number => number < 3)
console.log(b) // (2) [1, 2]Array.prototype.includes()
includes 의 앞부분 (numbers) 부분에 인수로 사용된 특정한 데이터가 포함되어져있는지 확인해줌
const nubmers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry']
const a = numbers.includes (3)
console.log(a) // trueArray.prototype.push(), unshift()
원본이 수정될 수 있음!
- push
배열의 가장 뒤쪽에 특정한 인수의 내용을 밀어 넣는다(삽입한다). - unshift
배열의 가장 앞쪽에 특정한 인수의 내용을 밀어 넣는다(삽입한다).
const nubmers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry']
numbers.push(5) // (5) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
numbers.unshift(0) // (6) [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]Array.prototype.reverse()
원본이 수정될 수 있음!
기존 데이터들을 뒤집어서 출력시킴
const nubmers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry']
numbers.reverse() // (4) [4, 3, 2, 1]
fruits.reverse() // (3) ["Cherry" ...]Array.prototype.splice()
원본이 수정될 수 있음!
첫번째 값에 배열데이터의 인덱스 값을 집어넣는다.
두번째 값은 내가 정한 숫자(1)만큼 값을 지우라는 의미
새로운 아이템을 끼워넣을 수도 있다.
const nubmers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry']
numbers.splice(2, 1) // (3) [1, 2, 4] // 2번 위치 3을 지움
numbers.splice(2, 0, 999) // (5) [1, 2, 999, 3, 4] 새로운 번호를 2번 자리에 끼워넣고 나머지 뒤로 밀기

