Union-Find
Disjoint set (서로 중복되지 않는 부분 집합들로 나눠진 원소 정보를 저장/조작하는 자료구조)을 표현할 때 사용하는 알고리즘으로, 두 node가 같은 집합에 속하는지 판별할 때 유용하게 사용할 수 있다!
구현
초기화
다음과 같이 모든 값이 자기 자신을 가리키도록 초기화해준다! 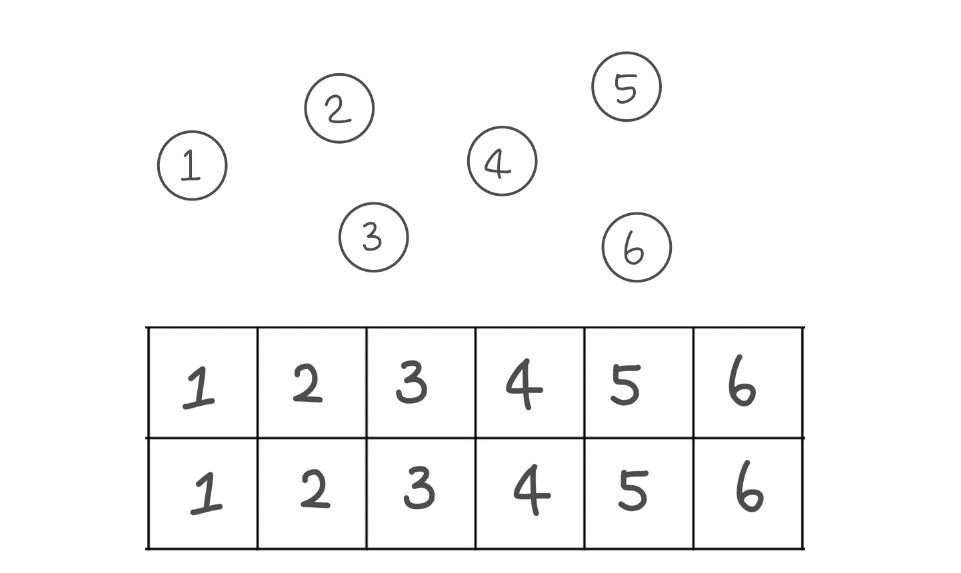
int root[1000001];
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) root[i] = i;find()
x의 root(집합의 부모? 집합을 대표하는 값?)를 찾는 함수이다. 만약 x와 y가 같은 집합에 속해 있다면 find(x) = find(y) 가 되는 것이다!
- 자신이 root인 경우 그 집합의 대표값이라고 할 수 있다!
- 그렇지 않은 경우 재귀적으로 타고 올라가서 집합의 대표값을 찾는다.
(이 때, 경로 단축을 통해 다음에 찾을 때 시간을 절약할 수 있다!)
int find(int x){
if(root[x]==x) return x; // 집합의 대표값 반환
return root[x] = find(root[x]); // 경로 단축
}union_()
find 함수를 통해 각 원소(노드)가 속한 root를 찾은 후, 합쳐 준다!
아래의 경우에는 x의 대표값이 y의 대표값의 하위 node로 들어가게 되어 두 집합(그래프)가 합쳐지는 것이다!
void union_(int x, int y){
root[find(x)] = find(y);
}최종 코드
union & find를 이용한 백준 1717번: 집합의 표현 문제 풀이이다!
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int root[1000001];
int find_(int x){
if(root[x]==x) return x;
return root[x] = find_(root[x]); // 경로 단축
}
void union_(int a, int b){
root[find_(a)] = find_(b);
}
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(NULL);
int n, m; cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=0; i<=n; i++) root[i] = i; // 초기화
for(int i=0; i<m; i++){
int oper, a, b; cin>>oper>>a>>b;
if(oper == 0) union_(a, b);
else if(find_(a)==find_(b)) cout << "YES\n";
else cout << "NO\n";
}
}