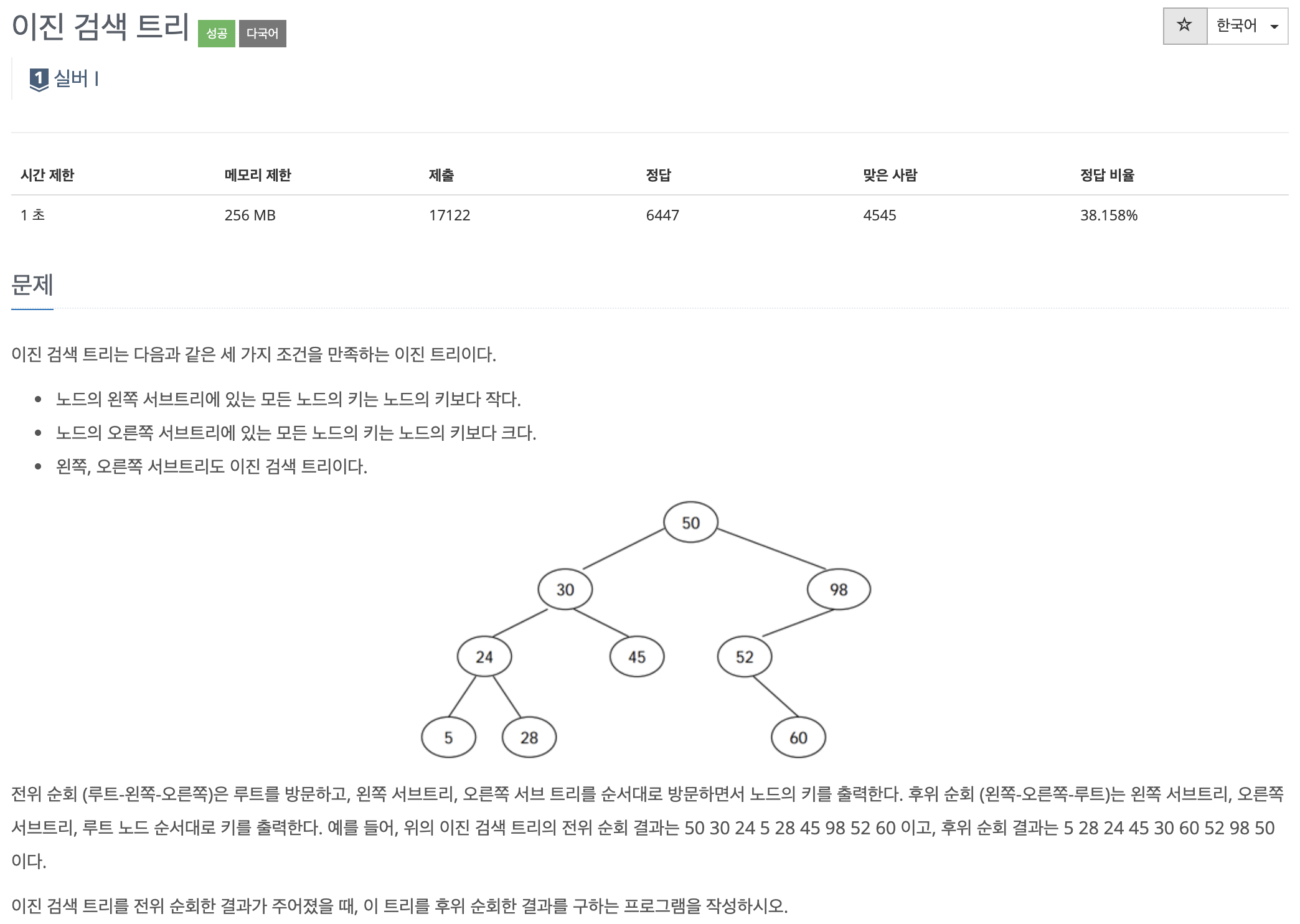
문제
 문제 바로가기> 백준 5639번: 이진 검색 트리
문제 바로가기> 백준 5639번: 이진 검색 트리
풀이
먼저 binary search tree를 구축하고, postorder(후위순회)를 진행한다.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node* leftchild;
Node* rightchild;
};
void postorder(Node* node) {
if (node->leftchild != NULL)
postorder(node->leftchild);
if (node->rightchild != NULL)
postorder(node->rightchild);
cout << node->data << '\n';
}
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
int data; cin >> data;
Node* root = new Node();
root->data = data; root->leftchild=NULL; root->rightchild=NULL;
while (cin>>data) {
if(data==EOF) break;
Node* node = new Node();
node->data = data; node->leftchild=NULL; node->rightchild = NULL;
Node* tmp = root;
while (1) {
if(data <= tmp->data){
if(tmp->leftchild == NULL) {
tmp->leftchild = node;
break;
}
else tmp = tmp->leftchild;
}
else{
if(tmp->rightchild == NULL) {
tmp->rightchild = node;
break;
}
else tmp = tmp->rightchild;
}
}
}
postorder(root);
}c++ 속도 향상
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); : ios_base::sync_with_stdio 구문은 c의 stdio와 c++의 iostream을 동기화시켜주는 역할을 하는데, 이 때 iostream과 stdio의 버퍼를 모두 사용하기 때문에 딜레이가 발생한다. 따라서 이 코드를 사용하여 c와 c++의 표준 stream의 동기화를 끊어주면, 사용하는 버퍼의 수가 줄어들었기 때문에 실행 속도가 빨라진다. 단, 이 코드를 사용할 경우 c++ stream들은 독립적인 버퍼를 갖게되므로 c의 표준 입출력(printf, scanf, getchar 등) 을 섞어쓰면 안된다. 또한 동기화가 비활성화됐기 때문에 멀티 쓰레드 환경에서는 출력 순서를 보장할 수 없다. 하지만 알고리즘 문제를 풀 때는 대부분 싱글 쓰레드 환경이기 때문에 해당 코드를 추가해도 문제가 발생하지 않을 확률이 높다.
cin.tie(NULL); : cin과 cout의 묶음을 풀어준다. stream을 tie 하면 다른 stream에서 입출력 요청 오기 전에 stream을 먼저 flush 시킨다.
