📔설명
생활코딩님의 수업을 들으면서 정리하고, 공부해보도록 하자~
자바에서 예상하지 못한 여러가지 버그, 오류, 예외 ( Exception ) 라는 것을
다루는 방법을 배워보자.
숙명과 운명.
숙명은 내가 어찌할 수 없는 것이다.
운명은 내가 더 열심히하면 더 좋게 나를 바꿀 수 있고,
바뀔 수 있는 숙명이 운명이다.
Exception이 숙명과 운명이랑 관련이 있다.
자바에는 ERROR 와 EXCEPTION이 있다.
에러(error)는 숙명과 같은 것이라 내가 잘못한 것이 아니다.
예를 들면 메모리 부족, 운영체제 문제 등이다.
Exception은 파일 읽으려 했는데, 파일이 없거나
사용자가 예상하지 못한 값을 입력해서 예외적인 상황이 발생한 경우 등을 말한다.
💦예외 발생 1
public class ExceptionApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(1);
System.out.println(2/0); //
System.out.println(3);
}
}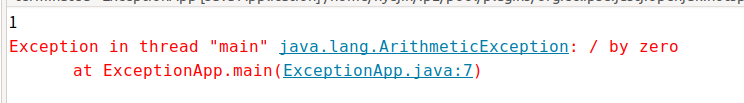
ArithmeticException이라는 Exception이 발생했다.
0으로 나눈다는 것은 자바에서 허용하지 않기 때문에, 프로그램이 멈추면서
어떤 예외가 발생했는지 알려준다.
그리고 예외가 발생한 다음의 프로그램은 출력되지 않는다.
🌊예외 처리 1
public class ExceptionApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(1);
try {
System.out.println(2/0); //
}catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("wrong calculation");
}
System.out.println(3);
}
}try-catch 구문을 사용하자!
try 안의 코드에서 catch 뒤의 예외가 발생했을 경우, catch구문 안의 문장을 실행시킨다!

그리고 3도 출력이 되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
💦예외 발생 2

배열은 0부터 2까지 있는데, 사용자가 scores[3]을 참조하려고 한다고 가정해보자.
그러면 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException이 발생한다.
아주 자주 본 친구다..
🌊예외 처리 2
public class ExceptionApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(1);
int[] scores= {10,20,30};
try {
System.out.println(scores[3]);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("No value");
}
try {
System.out.println(2/0); //
}catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("wrong calculation");
}
System.out.println(3);
}
}얘도 예외 처리를 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 으로 해주자.
🌊예외 처리 1+2
public class ExceptionApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(1);
int[] scores= {10,20,30};
try {
System.out.println(2);
System.out.println(scores[3]);
System.out.println(3);
System.out.println(2/0); //
System.out.println(4);
}catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("wrong calculation");
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("No value");
}
System.out.println(5);
}
}이렇게 코드를 합칠 수도 있다!
물론 같은 역할을 하는 코드는 아니다.
여기서 try의 두번째 줄에서 예외가 발생하기 때문에,
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException의 catch로 가게 되어
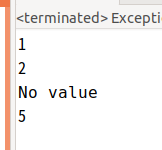
이렇게 출력되고 끝이난다.
wrong calculation은 출력도 안된다~
❓Exception의 자식과 우선순위
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/?java/lang/ArithmeticException.html
여기 들어가면 자바의 예외에 대해서 알 수 있다.

이렇게 코드를 작성하면, 밑의 catch문 두개는 실행될 일이 없다.
둘다 Exception의 자식이기 때문에 결국 다 Exception에 걸리게 되기 때문이다.
public class ExceptionApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(1);
int[] scores= {10,20,30};
try {
System.out.println(2);
System.out.println(scores[3]);
System.out.println(3);
System.out.println(2/0);
System.out.println(4);
}catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("Something Wrong.");
}
System.out.println(5);
}
}
보면, scores[3]에서 예외처리가 된 것을 알 수 있다.
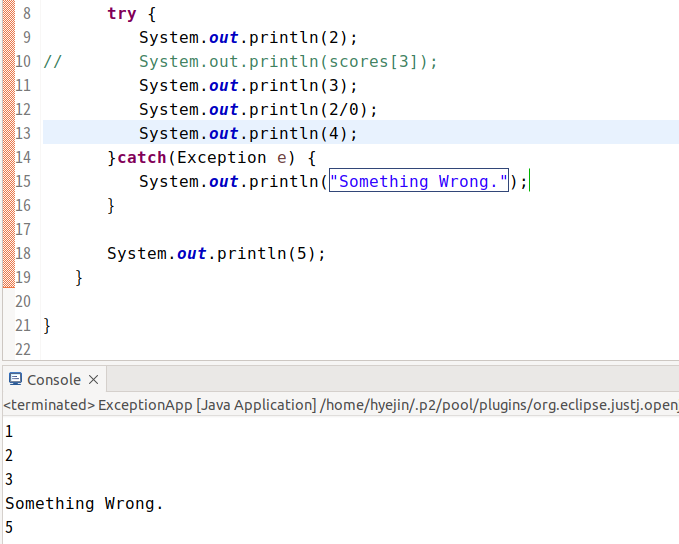
scores[3]을 주석처리하고,
2/0에서 예외가 걸리도록 해보면 해당 사진처럼 출력이 나온다.
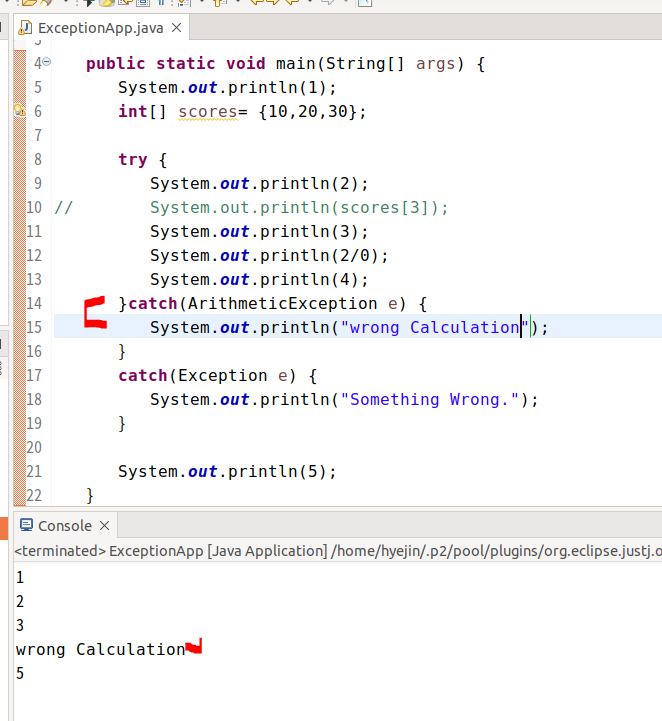
해당 소스코드처럼 변경해주면(2/0에서 예외 발생),
ArithmeticException이 발생하며 해당 catch구문이 실행되게 된다.
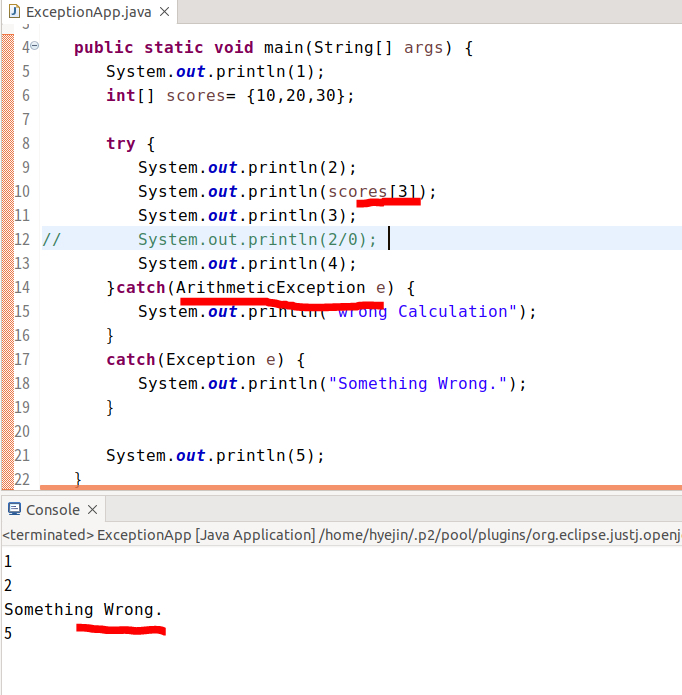
하지만, 이렇게 소스코드를 수정해주면(scores[3]에 예외 발생),
catch(Exception e) 쪽의 catch문이 처리를 해주게 된다.
Exception은 자식 Exception을 다 포괄해주고,
catch 문의 위치에 따라서 우선순위가 달라진다는 것을 알 수 있다!
💻변수 e
catch문 뒤의 e는 변수명이다! 그래서 사실 맘대로 아무거나 지정해도 된다.
하지만, 앞의 Exception 등은 데이터 타입으로 마음대로 하면 안된다.
public class ExceptionApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(1);
int[] scores= {10,20,30};
try {
System.out.println(2);
// System.out.println(scores[3]);
System.out.println(3);
System.out.println(2/0);
System.out.println(4);
}catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("wrong Calculation");
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("Something Wrong.");
}
System.out.println(5);
}
}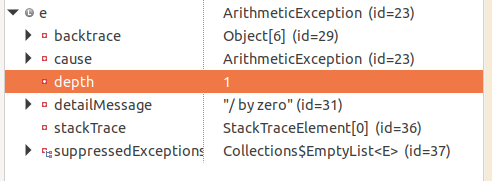
해당 소스코드에 ArithmeticException안의 sysout 문에 breakpoint를 걸고,
디버깅을 해보자. 그러면 e안의 값에는 해당 사진처럼 값이 들어가있다.
detail message안에 있는 것을 통해 왜 예외가 발생했는지 알 수 있다.
public class ExceptionApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(1);
int[] scores= {10,20,30};
try {
System.out.println(2);
// System.out.println(scores[3]);
System.out.println(3);
System.out.println(2/0);
System.out.println(4);
}catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("wrong Calculation"+e.getMessage());
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("Something Wrong.");
}
System.out.println(5);
}
}wrong calcultaion 뒤에 e.getMessage()를 통해
detail Message의 값을 받아올 수 있다
직접 접근이 안되니까 getMessage()를 쓰자.
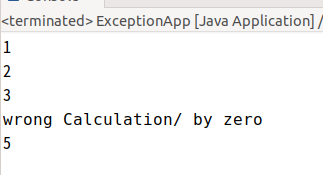
해당 사진처럼 출력이 된다.
만약, 예외 발생시 나왔던 빨간색 그 문장도 출력하고 싶을땐
e.printStackTrace()를 사용하자.
public class ExceptionApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(1);
int[] scores= {10,20,30};
try {
System.out.println(2);
// System.out.println(scores[3]);
System.out.println(3);
System.out.println(2/0);
System.out.println(4);
}catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("wrong Calculation"+e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("Something Wrong.");
}
System.out.println(5);
}
}
몇번째 줄에서 예외가 발생하는지 알려준다.
사실 정보보안 공부를 했다면,
이렇게 예외 발생하는 것을 절대 사용자에게 보여주면 안된다는 것을 안다..
이런 사소한 것 하나 조차 보안에 위협이 되는 단서가 될 수 있기 때문!
