스택 (Stack)
스택의 구현
✏️ ADT를 다른 형태로 구현할 때,
논리적인 연산을 바꿀 필요는 없고, 구체적인 구현(코드)만 변경하면 된다.
- 배열 (Array)

- 스택의 최대 크기를 생성자의 파라미터로 받아서, 고정된 크기의 스택을 생성한다.
- 컴파일 시간에 메모리 정적 할당
→ 최대 크기에 제한이 있고, 낭비되는 메모리가 있을 수 있다.
- 연결 리스트 (Linked List)
- 스택에 요소를 삽입(push)할 때마다 동적으로 메모리를 할당한다.
- 스택에 요소를 삽입(push)할 때마다 동적으로 메모리를 할당한다.
연결 리스트로 구현된 스택
- 노드 (Node)
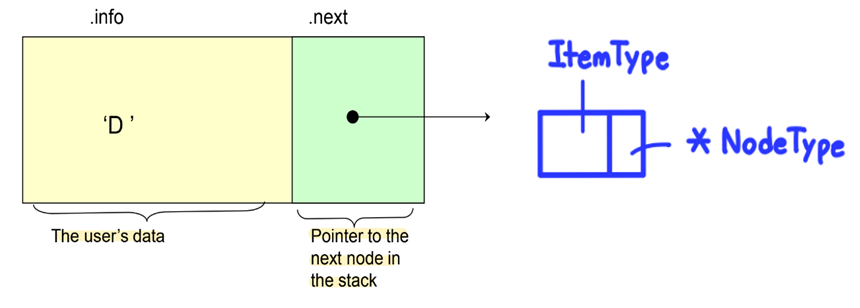
Struct NodeType { ItemType info; NodeType* next; }
StackType.hclass StackType { public: //Identical to previous implementation private: NodeType* topPtr; };
- 연산
- 생성자 및 소멸자
- StackType()
StackType::StackType() { topPtr = NULL; } - ~StackType()
: 지역 변수인topPtr은 함수가 종료될 때 자동으로 할당 해제되지만,topPtr이 가리키는 노드들은 할당 해제되지 않으므로 소멸자의 역할이 중요하다.Stacktype::~StackType() { //Post: stack is empty and all items have been deallocated. NodeType* tempPtr; // topPtr이 NULL이 아닐 때까지 pop의 원리 반복 while (topPtr != NULL) { tempPtr = topPtr; topPtr = topPtr->next; delete tempPtr; } }✏️
delete- 포인터가 현재 가리킨 오브젝트의 메모리 할당 해제 (deallocated)
- 포인터, unassinged로 가정
- 메모리, free store로 반환
- StackType()
- 변환자
- Push
void StackType::Push(ItemType newItem) { if (isFull()) throw FullStack(); NodeType* location; //1️⃣ 메모리의 stack 영역 location = new NodeType<ItemType>; //2️⃣ 메모리의 heap 영역 location->info = newItem; //3️⃣ location->next = topPtr; //4️⃣ topPtr = location; //5️⃣ } - Pop
void StackType::Pop() { if (isFull()) throw EmptyStack(); NodeType* tempPtr; //1️⃣ tempPtr = topPtr; //2️⃣ topPtr = topPtr->next; //3️⃣ delete tempPtr; //4️⃣ }
- Push
- 관찰자
- Top
ItemType StackType::Top() { if (isEmpty()) throw EmptyStack(); return topPtr->info; } - IsEmpty
bool StackType::IsEmpty() const { return (topPtr == NULL); } - IsFull
: 연결 리스트의 형태로 스택 구현시, 동적 할당을 하기 때문에 크기(size)에 제한을 받지 않는다. 따라서 더이상 메모리 확보가 불가능한 상태이면 full이다.bool StackType::IsFull() const { NodeType* location; try { location = new NodeType; delete location; return false; } catch (std::bad_alloc exception) { return true; } }
- Top
- 생성자 및 소멸자
스택 연산의 비교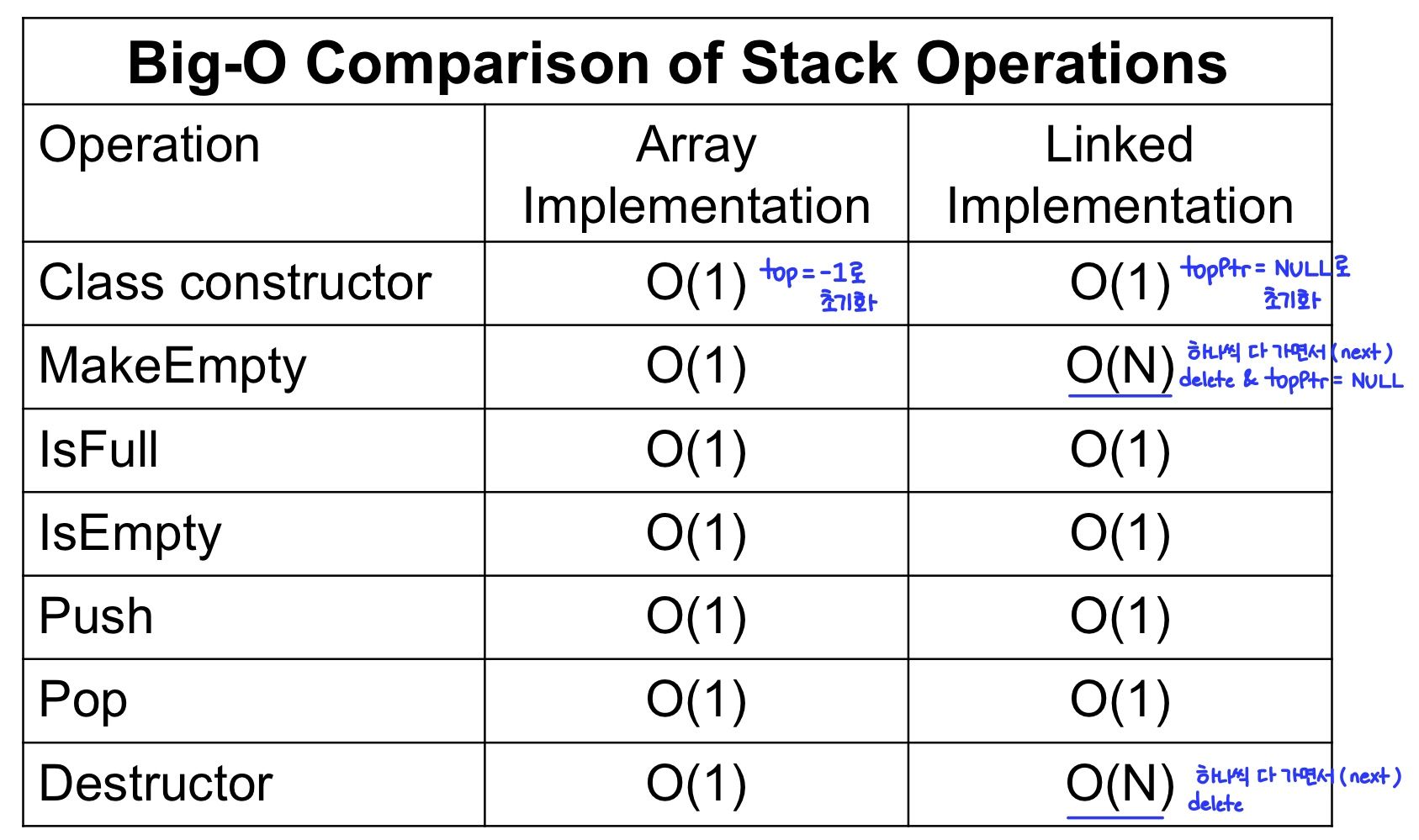
큐 (Queue)
큐의 구현
- 배열 (Array)
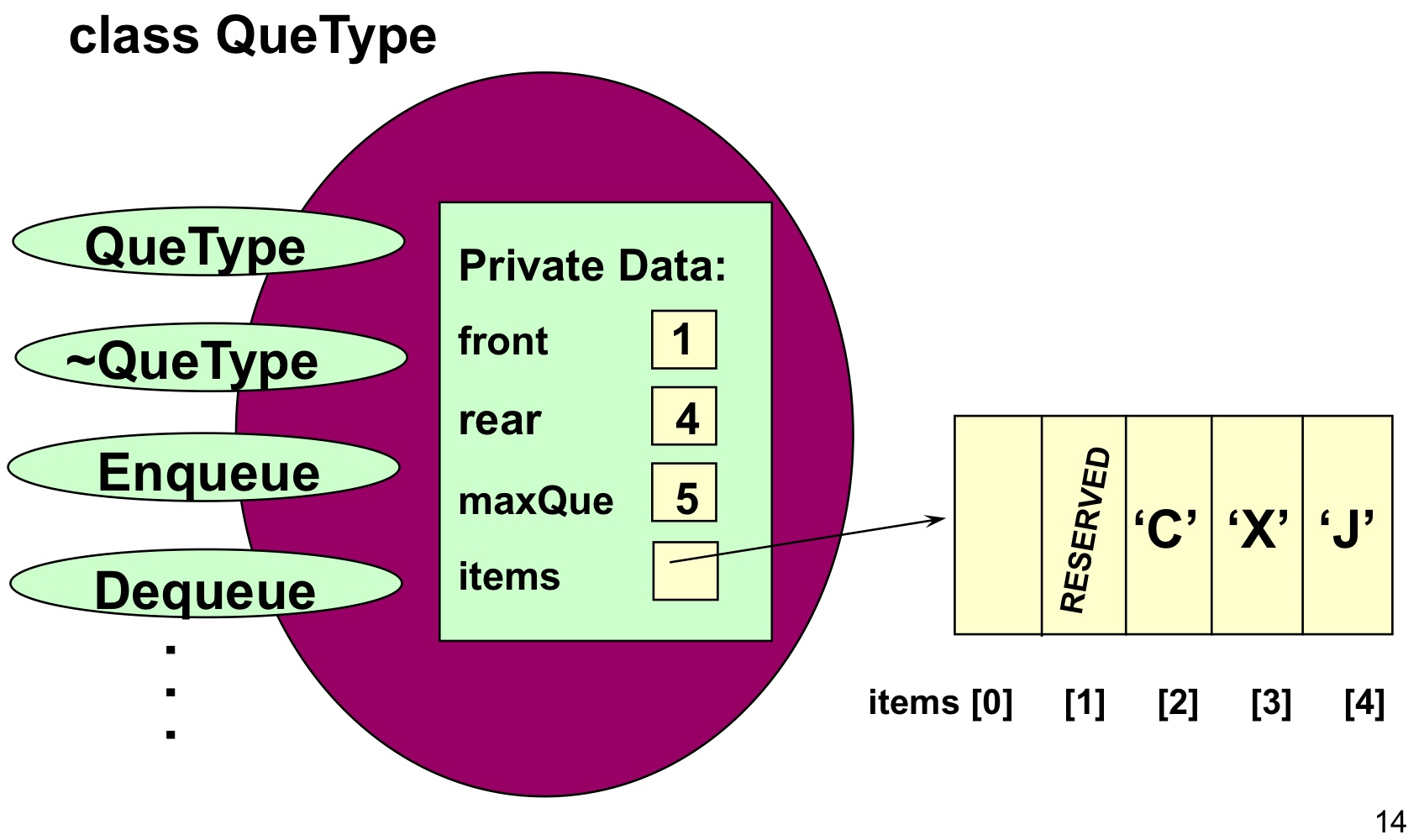
- 큐의 최대 크기를 생성자의 파라미터로 받아서, 고정된 크기의 큐 생성한다.
- 컴파일 시간에 메모리 정적 할당
→ 최대 크기에 제한이 있고, 낭비되는 메모리가 있을 수 있다.
- 연결 리스트 (Linked List)
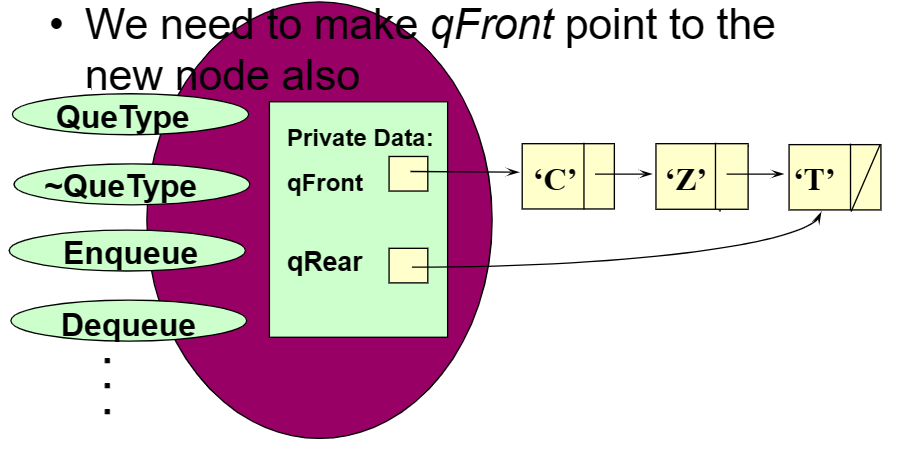
- 큐에 요소를 삽입(Enqueue)할 때마다 동적으로 메모리를 할당한다.
- 큐에 요소를 삽입(Enqueue)할 때마다 동적으로 메모리를 할당한다.
연결리스트로 구현된 큐
-
QueType.htemplate<class ItemType> class QueType { public: // private: NodeType<ItemType>* qFront; NodeType<ItemType>* qRear; } -
연산
- 생성자 및 소멸자
- QueType()
template<class ItempType> QueType<ItemType>::QueType() { qFront = NULL; qRear = NULL; } - ~QueType()
template<class ItemType> class ~QueType { //Post: queue is empty and all items have been deallocated. NodeType<ItemType>* tempPtr; while (qFront != NULL) { tempPtr = qFront; qFront = qFront->next; delete tempPtr; } qRear = NULL; }
- QueType()
- 변환자
- Enqueue
: 큐의 ‘rear’에 새로운 요소 삽입template<class ItemType> void QueType<ItemTye>::Enqueue(ItemType newItem) { NodeType<ItemType>* ptr; ptr = new NodeType<ItemType>; ptr->info = newItem; ptr->next = NULL; If (qRear == NULL) qFront = ptr; else qRear->next = ptr; qRear = ptr; }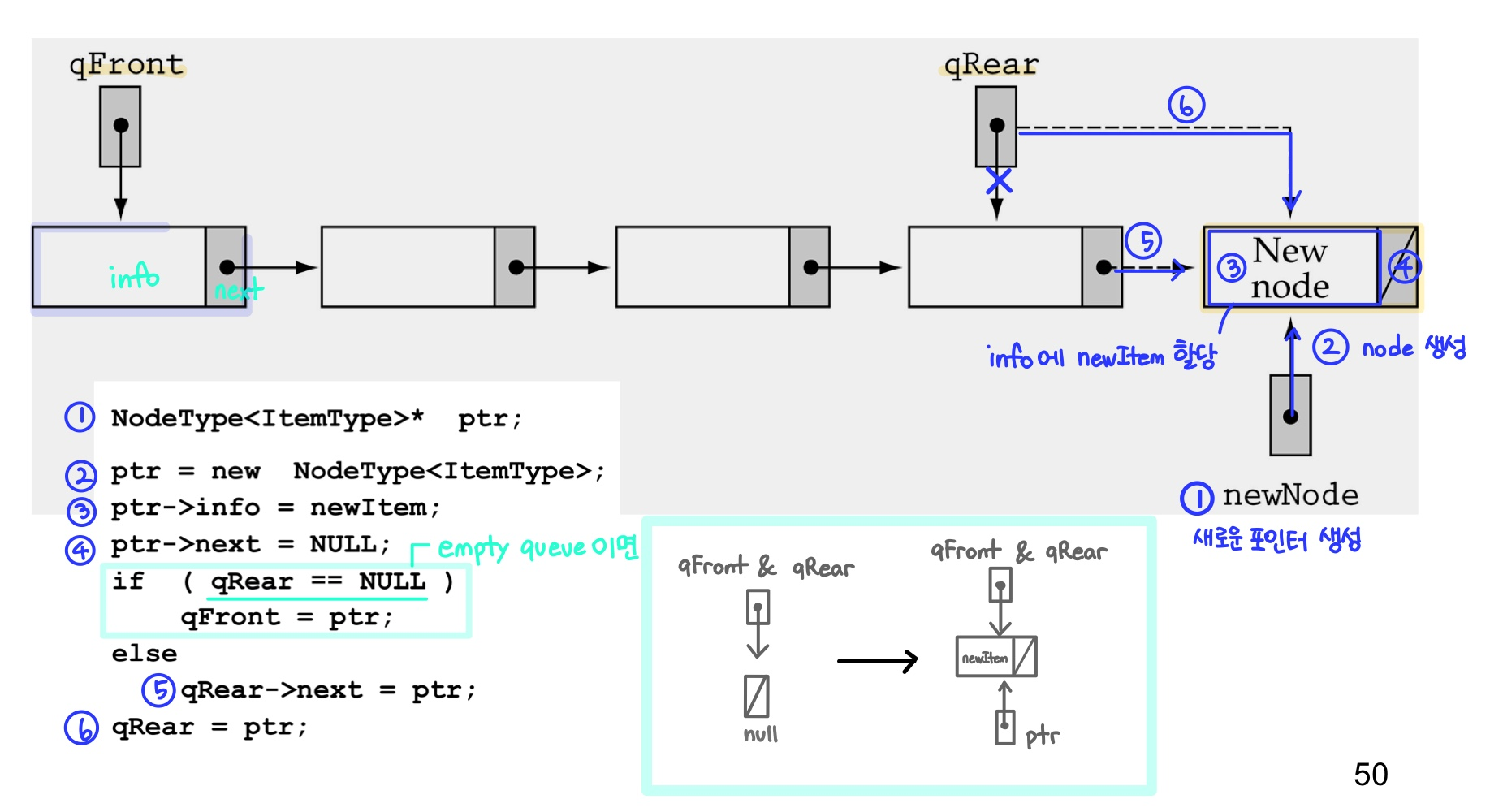
- Dequeue
: 큐의 front에서 요소 제거template<class ItemType> void QueType<ItemType>::Dequeue(ItemType& item) { // 함수가 종료되어도 변경된 item 값이 유지되어야 하기 때문에 레퍼런스로 받는다. NodeType<ItemType>* tempPtr; tempPtr = qFront; item = qFront->info; qFront = qFront->next; if (qFront == NULL) qRear = NULL; delete tempPtr; }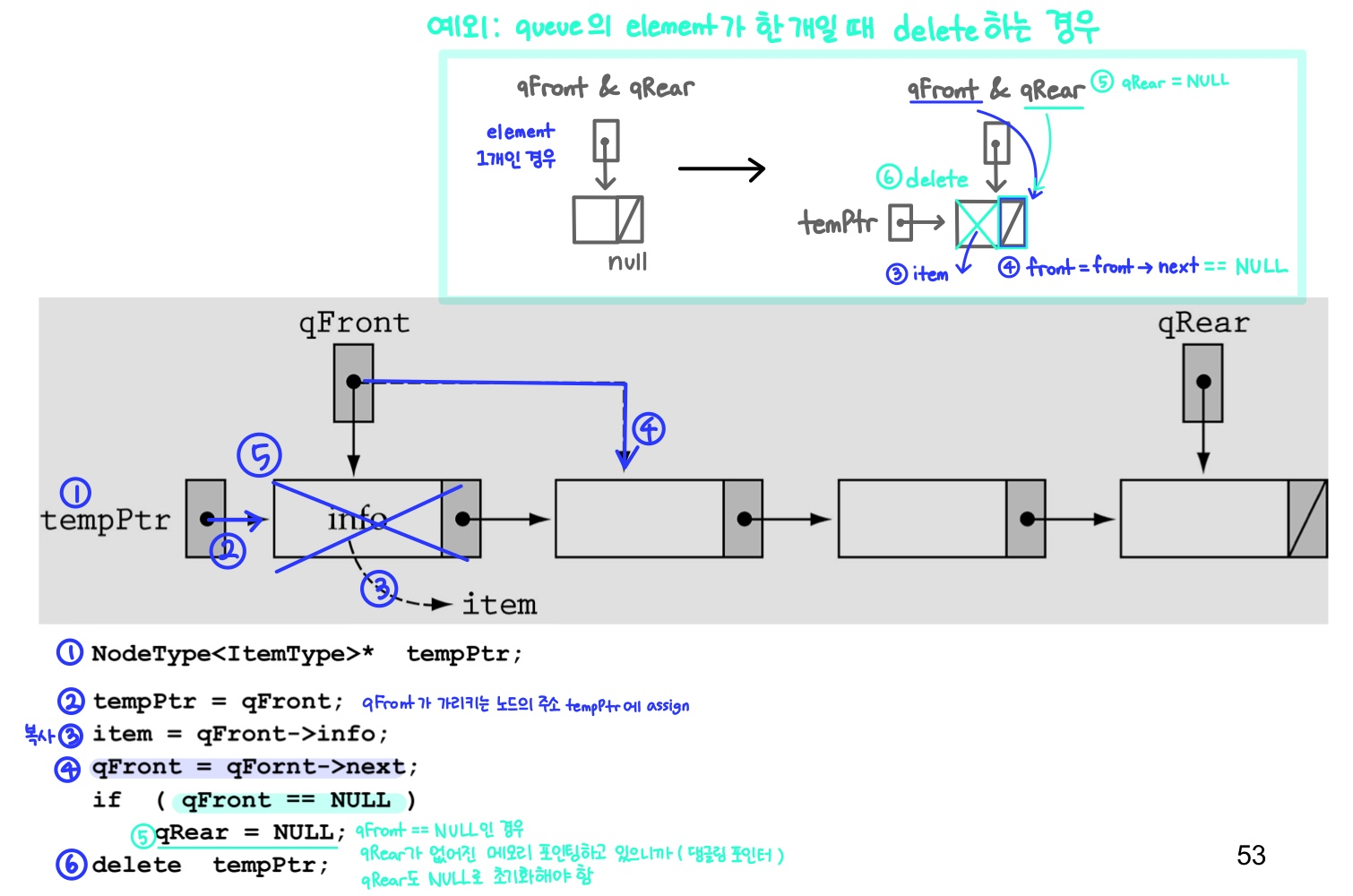
- Enqueue
- 관찰자
- IsEmpty
template<class ItempType> bool QueType<ItempType>::IsEmpty() const { return (qFront == NULL) } - IsFull
bool QueType::IsFull() const { NodeType* location; try { location = new NodeType; delete location; return false; } catch (std::bad_alloc exception) { return true; } }
- IsEmpty
- 생성자 및 소멸자
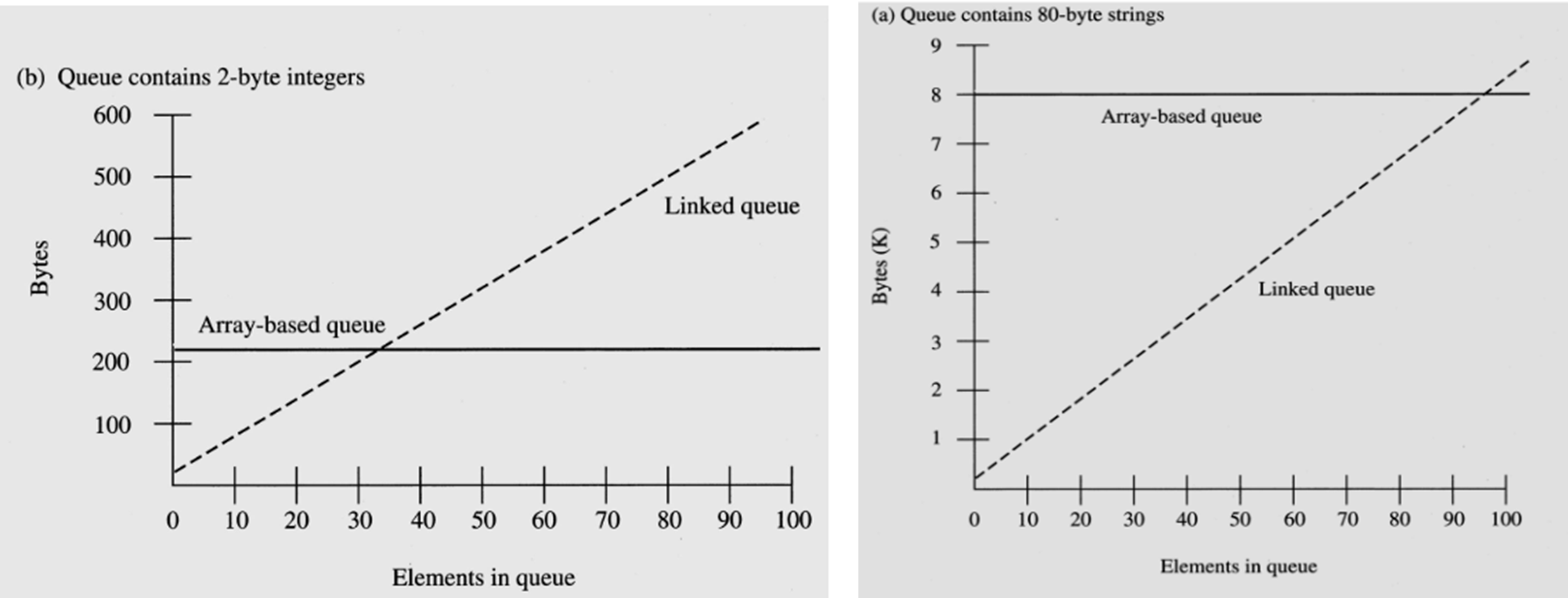
큐 연산의 비교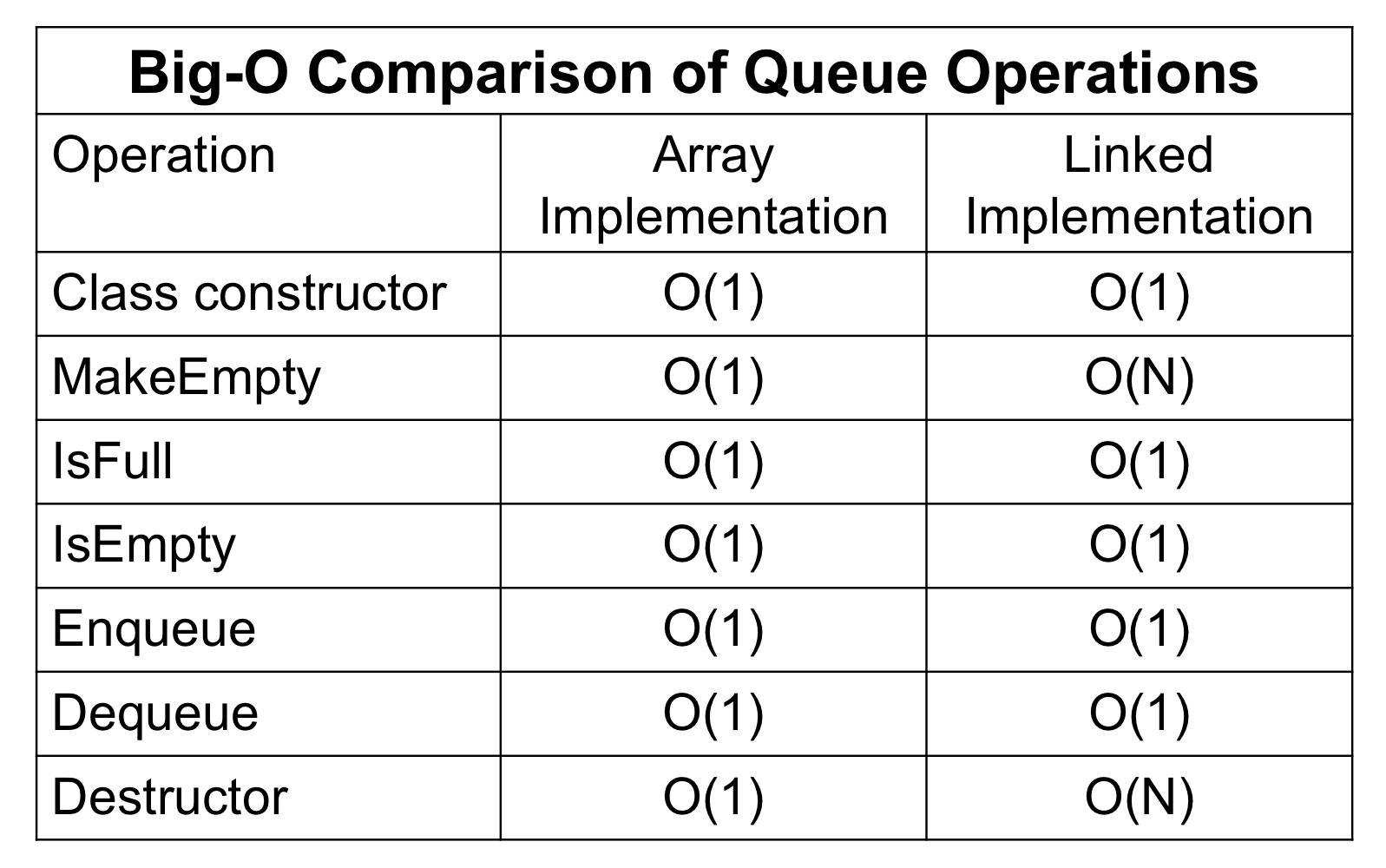
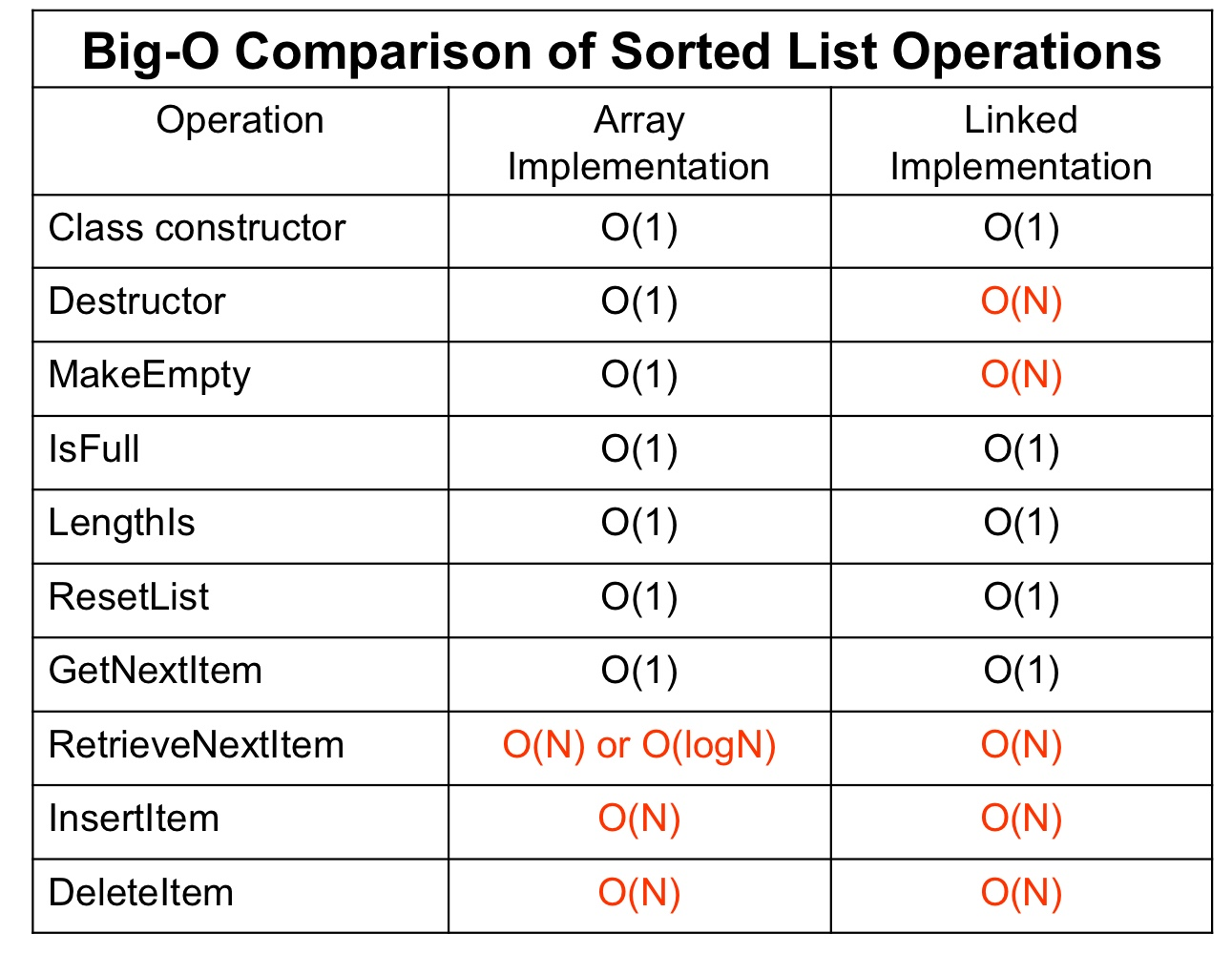
비정렬 리스트 (Unsorted List)
비정렬 리스트의 구현
- 배열
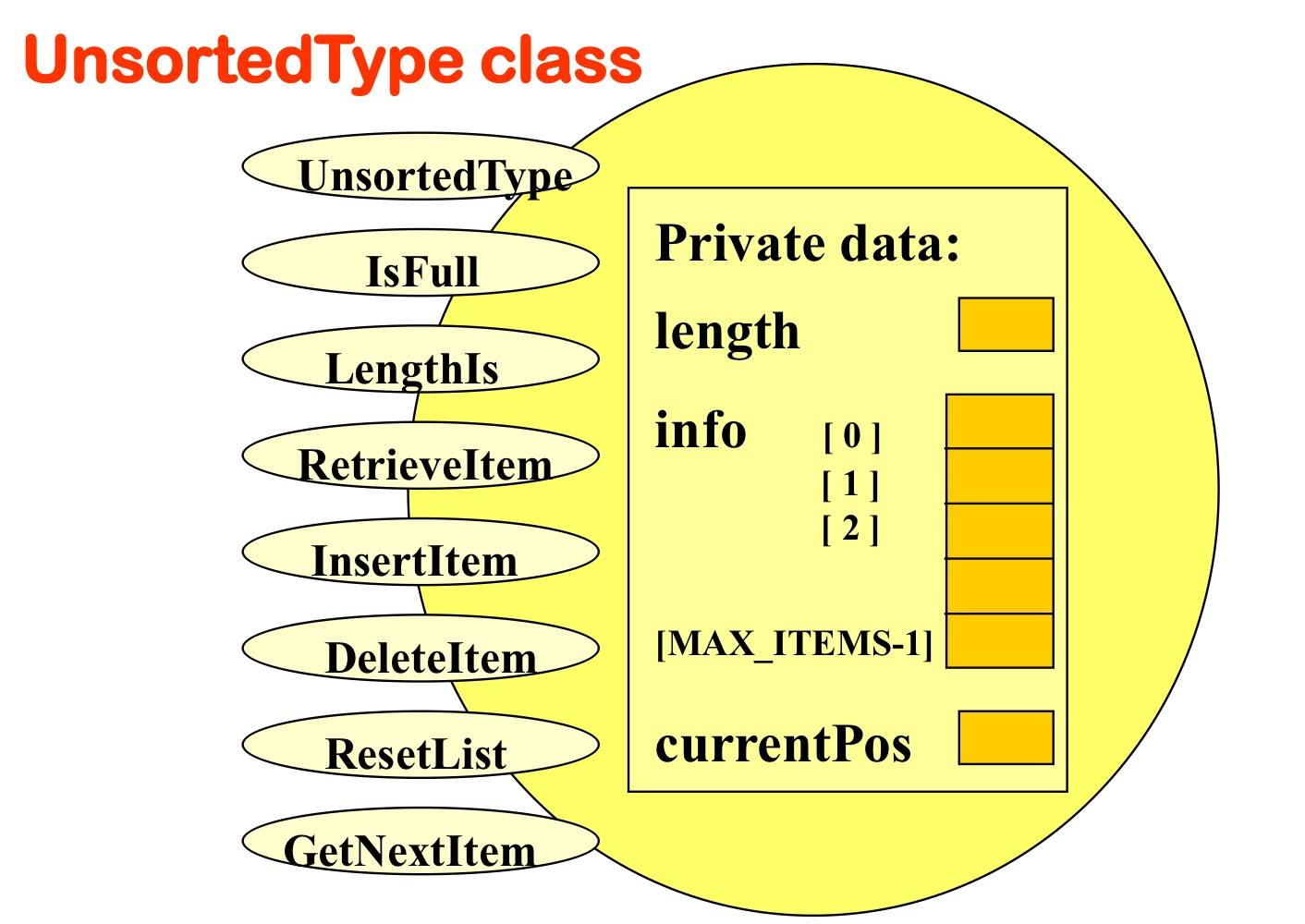
ItemType.h에서 지정한 리스트의 크기(MAX_ITEMS)만큼의 리스트를 생성한다.- 컴파일 시간에 메모리 정적 할당
→ 최대 크기에 제한이 있고, 낭비되는 메모리가 있을 수 있다.
- 연결 리스트
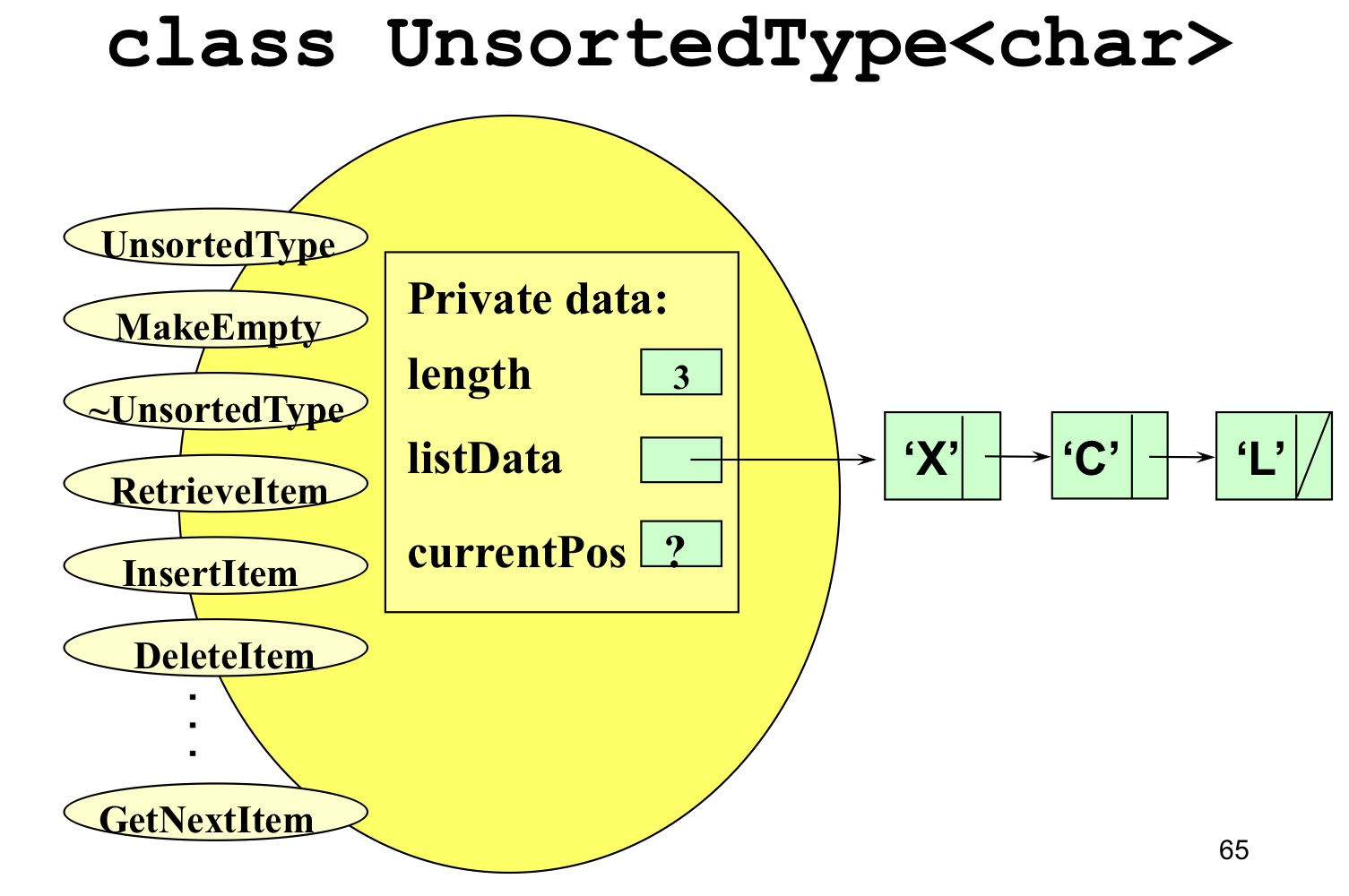
- 리스트에 요소를 삽입(InsertItem)할 때마다 동적으로 메모리를 할당한다.
- 리스트에 요소를 삽입(InsertItem)할 때마다 동적으로 메모리를 할당한다.
비정렬 연결 리스트 (Unsorted Linked List)
-
UnsortedType.htemplate<class ItemType> class UnsortedType { public: // private: NodeType<ItemType>* listData; // 리스트의 첫번째 요소를 가리키는 포인터 NodeType<ItemType>* currentPost; // iterator에서 사용하는 포인터 int length; } -
연산
-
생성자 및 소멸자
- UnsortedType()
template<class ItemType> UnsortedType<ItemType>::UnsortedType() { length = 0; listData = NULL; } - ~UnsortedType()
template <class ItemType> UnsortedType<ItemType>::UnsortedType() { // Post: List is empty; all items have been deallocated. NodeType<ItemType>* tempPtr; while (listData != NULL) { tempPtr = listData; listData = listData->next; delete tempPtr; } }
- UnsortedType()
-
변환자
- InsertItem
: 리스트에 새로운 요소 삽입 (순서 상관 X)template<class ItemType> void UnsortedType<ItemType>::InsertItem(ItemType item) { // pre: list is not full and item is not in list. // post: item is in the list. length has been incremented; NodeType<ItemType>* location; location = new NodeType<ItemType>; location->info = item; location->next = listData; listData = location; length++; }비정렬 리스트이므로 순서는 상관없지만, listData가 가리키고 있는 요소의 앞에 새로운 요소를 삽입하는 것이 가장 합리적이다. (그 외에는 next로 계속 가야하니까 비효율적)
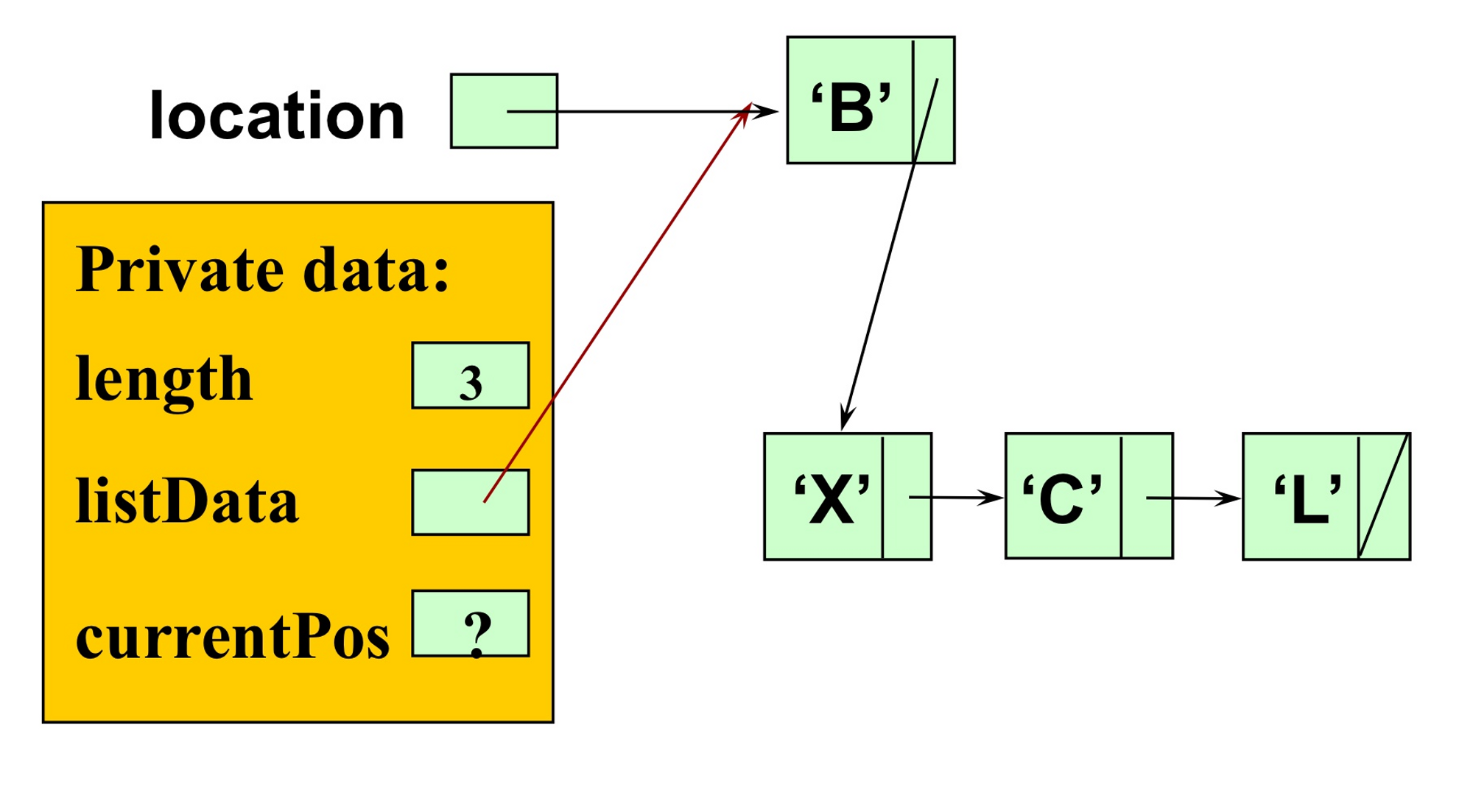
- DeleteItem
: 리스트에서 특정 요소 제거 (순서 상관 X)template<class ItemType> void UnsortedType<ItemType>::DeleteItem(ItemType item) { NodeType<ItemType>* location = listData; NodeType<ItemType>* tempLocation; // 예외 처리 if (item == listData->info) { tempLocation = location; listData = listData->next; } else { while(!(item == (location->next)->info)) //1️⃣ location = location->next; //2️⃣ tempLocation = location->next; //3️⃣ location->next = (location->next)->next; //4️⃣ } delete tempLocation; //5️⃣ length--; }예외 처리
: 첫번째 노드를 삭제하는 경우로, item과 (location→next)→info를 비교하기 때문에
이때 listData->next 는 NULLitem과(location→next)->next비교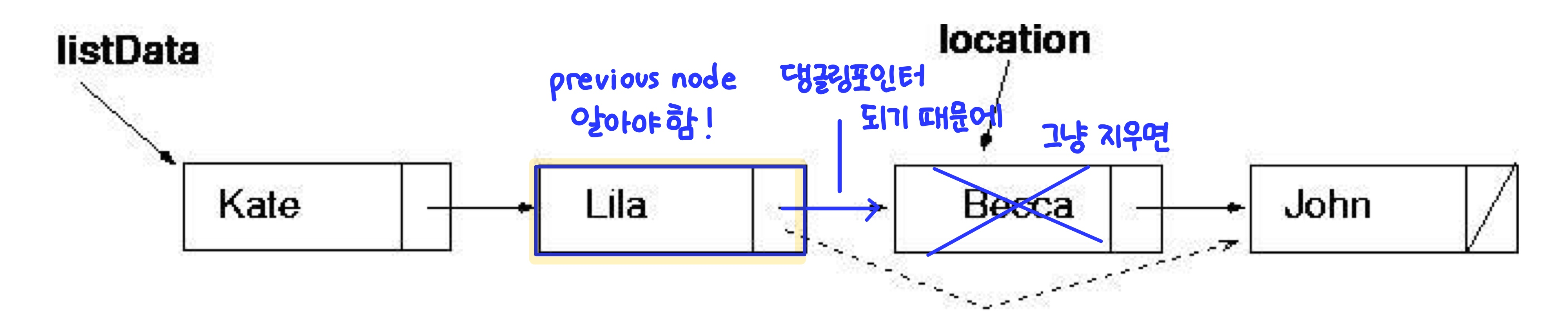
댕글링 포인터 문제를 막으려면 이전의 노드를 알아야 하기 때문에, item과 location→info를 비교하는 대신 (location→next)→info를 비교한다.
item != (location->next)->info인 경우 다음 노드로 이동item == (location->next)->info인 경우 tempLocation이 location의 다음 노드를 가리키도록 함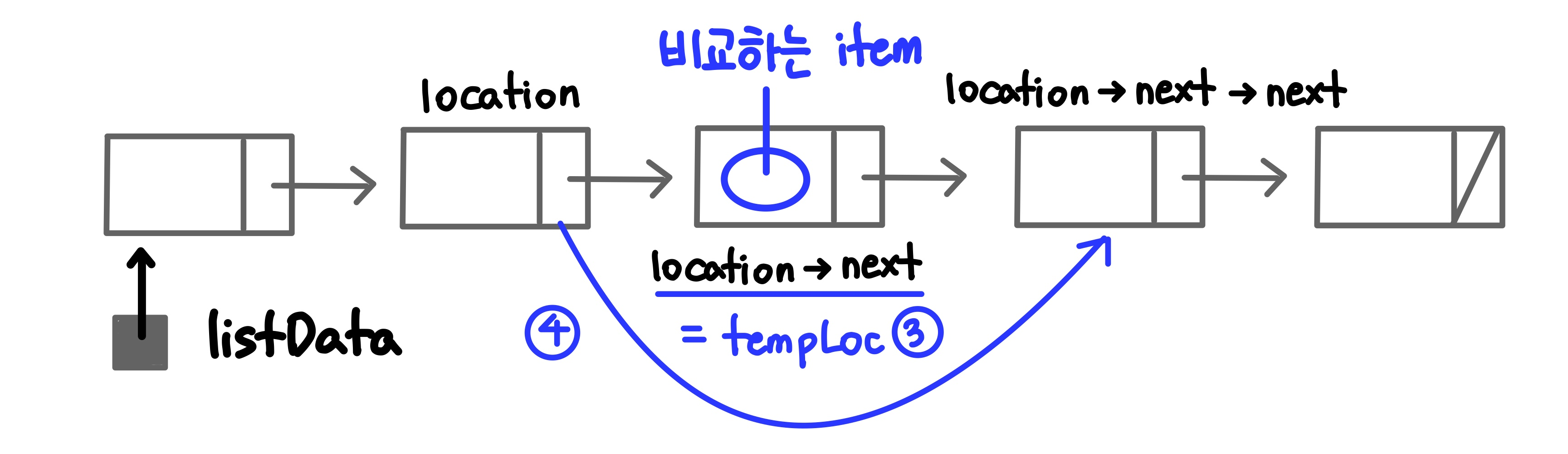
- InsertItem
-
관찰자
- LengthIs
int template<class ItemType>::LengthIs() const { return length; } - IsEmpty
bool template<class ItemType>::IsEmpty() const { return (length == 0); } - RetrieveItem
template<class ItemType> void UnsortedType<ItemType>::RetrieveItem(ItemType& item, bool& found) { NodeType<ItemType>* location; location = listData; found = false; while ((location != NULL) && !found) { if (item == location ->info) { found = true; item = location->info; } else location = location->next; } }
- LengthIs
-
비정렬 리스트의 연산의 비교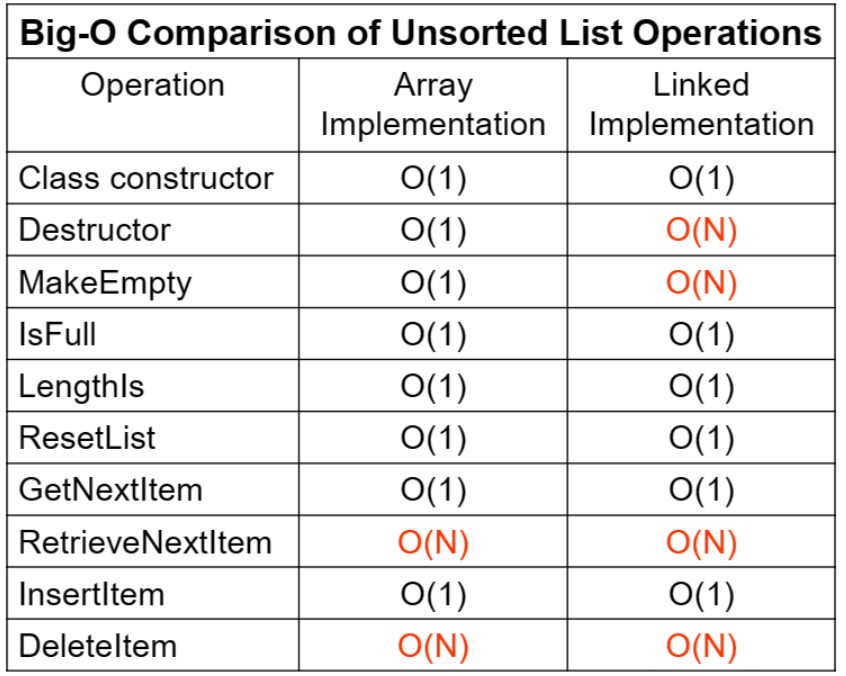
정렬 리스트 (Sorted List)
정렬 리스트의 구현
- 배열
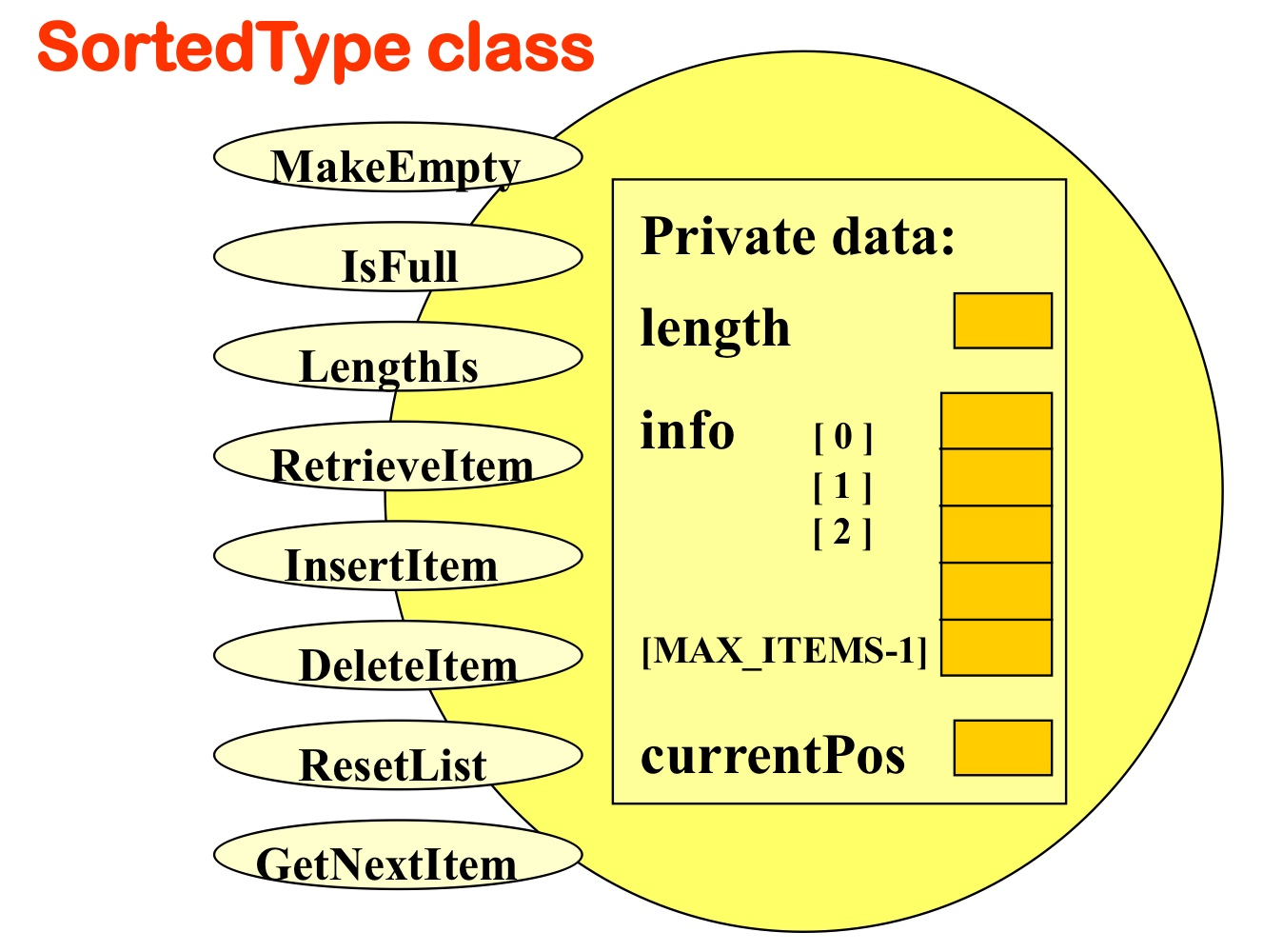
ItemType.h에서 지정한 리스트의 크기(MAX_ITEMS)만큼의 리스트를 생성한다.- 컴파일 시간에 메모리 정적 할당
→ 최대 크기에 제한이 있고, 낭비되는 메모리가 있을 수 있다.
- 연결 리스트
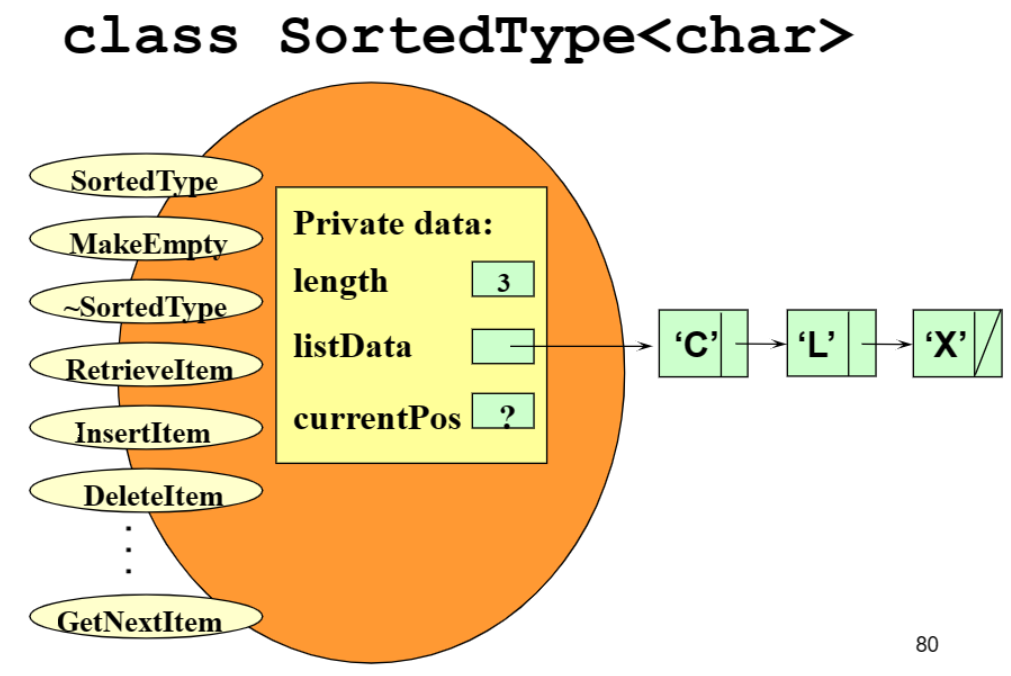
- 리스트에 요소를 삽입(InsertItem)할 때마다 동적으로 메모리를 할당한다.
- 리스트에 요소를 삽입(InsertItem)할 때마다 동적으로 메모리를 할당한다.
정렬 연결 리스트 (Sorted Linked List)
SortedType.htemplate<class ItemType> class SortedType { public: // private: NodeType<ItemType>* listData; // 리스트의 첫번째 요소를 가리키는 포인터 NodeType<ItemType>* currentPost; // iterator에서 사용하는 포인터 int length; }- 연산
- 생성자 및 소멸자
- UnsortedType()
template<class ItemType> UnsortedType<ItemType>::UnsortedType() { length = 0; listData = NULL; } - ~UnsortedType()
template <class ItemType> UnsortedType<ItemType>::SortedType() { // Post: List is empty; all items have been deallocated. NodeType<ItemType>* tempPtr; while (listData != NULL) { tempPtr = listData; listData = listData->next; delete tempPtr; } }
- UnsortedType()
- 변환자
- InsertItem
: 리스트에 새로운 요소 삽입 (순서 상관 O)
- 새로운 요소를 정렬 리스트의 적절한 위치에 삽입하기 위해서는, 현재의 노드를 가리키는 포인터(location) 뿐만 아니라, 이전 노드를 가리키는 포인터(preLoc)도 필요하다.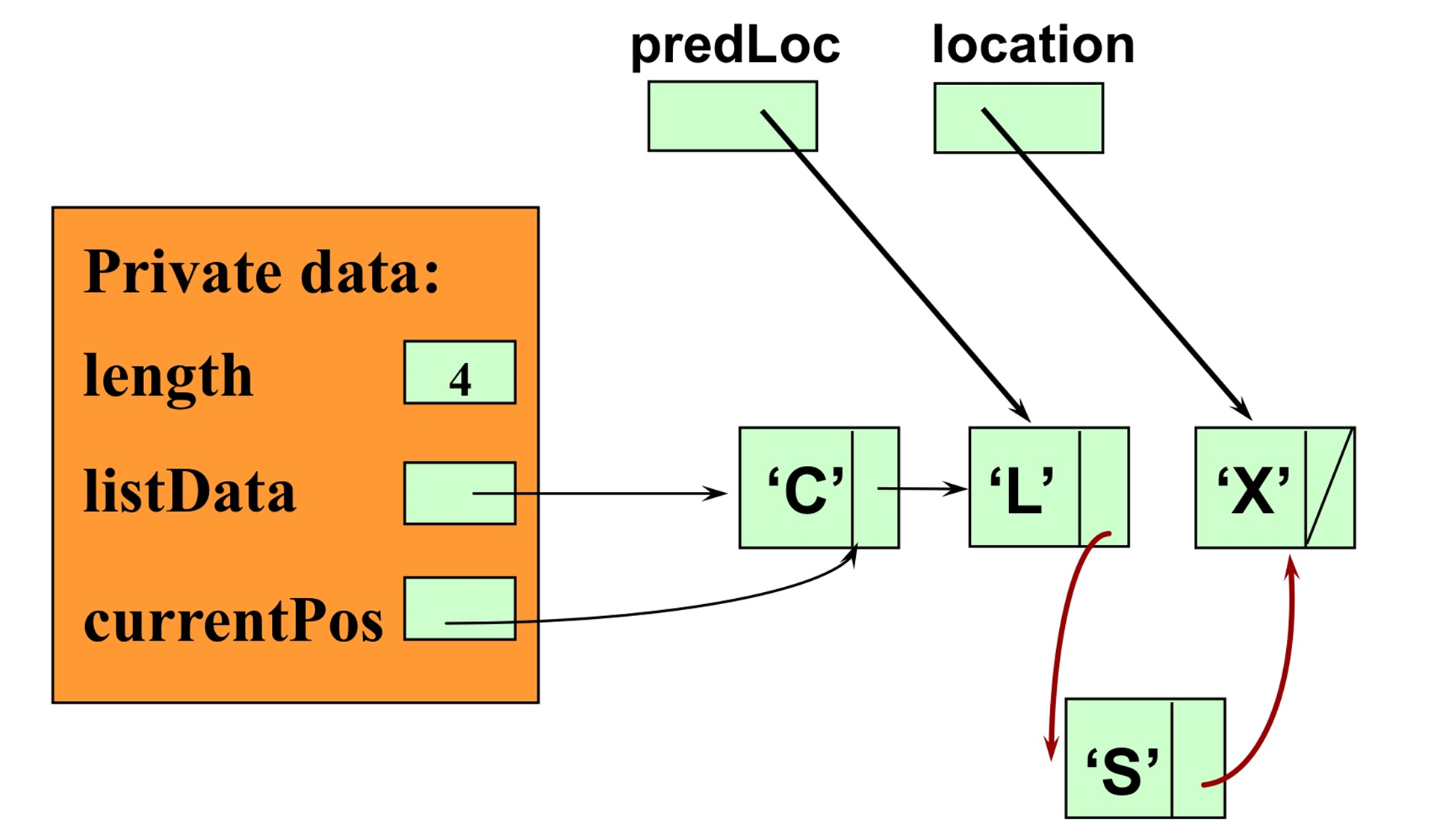
(location→next)→info을 사용할 경우 추가하고 싶은 항목이 가장 마지막 위치에 추가해야 할 경우 오류가 발생하고, 예외처리도 불가능하기 때문에preLoc을 사용하는 것✏️ 초기화
preLoc = NULL; location = listData;✏️ predLoc을 먼저 업데이트 한 후, location을 업데이트 해야 한다.
preLoc = location; location = location->next; - DeleteItem
: 리스트에서 특정 요소 제거 (순서 상관 O)
- InsertItem
- 관찰자
- LengthIs
int template<class ItemType>::LengthIs() const { return length; } - IsEmpty
bool template<class ItemType>::IsEmpty() const { return (length == 0); } - RetrieveItem
: 연결 리스트로 구현한 정렬 리스트는 배열로 구현한 정렬 리스트와는 다르게, 이진 검색(binary search) 대신 선형 검색(linear search)을 이용해 아이템을 검색한다. 이진 검색을 활용할 경우 middle을 알기 위해선 next로 계속 가서 확인해야 하기 때문에 비효율적다.template<class ItemType> void UnsortedType<ItemType>::RetrieveItem(ItemType& item, bool& found) { NodeType<ItemType>* location; location = listData; found = false; while ((location != NULL) && !found) { if (item > location->info) location = location->next; else if (location->info == item) { found = true; item = location->info; } else location = NULL //item < location->info인 경우 } }
- LengthIs
- 생성자 및 소멸자