
📕 리포지터리(Repository) 란?
리포지터리는 엔티티에 의해 생성된 데이터베이스 테이블에 접근하는 메서드들(예: findAll, save 등)을 사용하기 위한 인터페이스이다. 데이터 처리를 위해서는 테이블에 어떤 값을 넣거나 값을 조회하는 등의 CRUD(Create, Read, Update, Delete)가 필요하다. 이 때 이러한 CRUD를 어떻게 처리할지 정의하는 계층이 바로 리포지터리이다.
📁 리포지터리(Repository) 만들기
QuestionRepository는 리포지터리로 만들기 위해 JpaRepository 인터페이스를 상속했다. JpaRepository를 상속할 때는 제네릭스 타입으로 <Question, Integer> 처럼 리포지터리의 대상이 되는 엔티티의 타입(Question)과 해당 엔티티의 PK의 속성 타입(Integer)을 지정해야 한다. 이것은 JpaRepository를 생성하기 위한 규칙이다.
💾 QuestionRepository
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface QuestionRepository extends JpaRepository<Question, Integer>{
}💾 AnswerRepository
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface AnswerRepository extends JpaRepository<Answer, Integer>{
}💻 리포지터리 테스트
테스트 디렉토리에서 테스트파일 선택!
1. 데이터 저장하기
🔴 SbbApplicationTests 클래스
package com.mysite.sbb;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest // 이 클래스가 테스트 클래스임을 나타냄
class SbbApplicationTests {
@Autowired // 자동으로 객체를 생성해줌
private QuestionRepository questionRepository;
@Test // 테스트 코드
void testJpa() {
Question q1 = new Question();
q1.setSubject("sbb가 무엇인가요?");
q1.setContent("sbb에 대해서 알고 싶습니다.");
q1.setCreateDate(LocalDateTime.now());
this.questionRepository.save(q1); // 첫번째 질문 저장
Question q2 = new Question();
q2.setSubject("스프링부트 모델 질문입니다.");
q2.setContent("id는 자동으로 생성되나요?");
q2.setCreateDate(LocalDateTime.now());
this.questionRepository.save(q2); // 두번째 질문 저장
}
}
- @SpringBootTest 애너테이션 : SbbApplicationTests 클래스가 스프링부트 테스트 클래스임을 의미한다.
- @Autowired 애너테이션 : 스프링의 DI 기능으로 questionRepository 객체를 스프링이 자동으로 생성해 준다. 실제로는 순환참조 문제와 같은 이유로 @Autowired 보다는 생성자를 통한 객체 주입방식이 권장된다.
- @Test 애너테이션 : testJpa 메서드가 테스트 메서드임을 나타낸다. 위 클래스를 JUnit으로 실행하면 @Test 애너테이션이 붙은 메서드가 실행된다.
JUnit은 테스트코드를 작성하고 작성한 테스트코드를 실행하기 위해 사용하는 자바의 테스트 프레임워크이다.
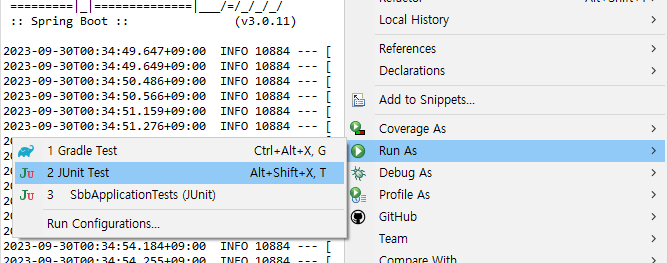
코드 작성 후 우클릭 > Run As > JUnit Test
🔵 h2 DB에서 저장된 데이터 확인
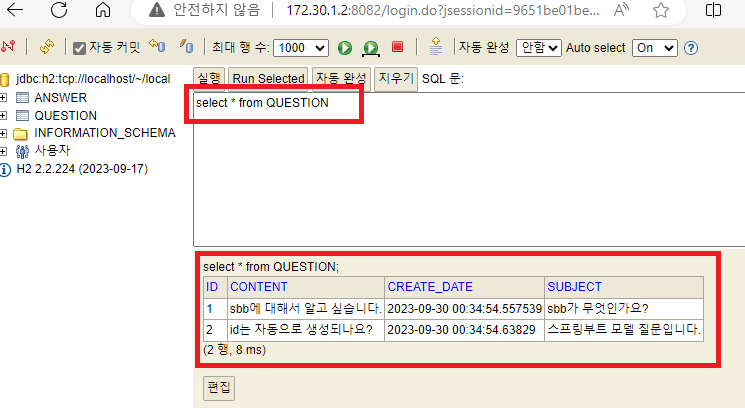
2. 데이터 조회하기
📝 2-1 모든 데이터 조회하기(findall() 메서드)
🔴 SbbApplicationTests 클래스(findall() 메서드)
package com.mysite.sbb;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class SbbApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private QuestionRepository questionRepository;
@Test
void testJpa() {
List<Question> all = this.questionRepository.findAll(); // 데이터를 조회할 때 사용하는 메서드
assertEquals(2, all.size()); // 기댓값(질문 2개), 실제 all 배열의 크기
Question q = all.get(0); // 인덱스 0번의 값을 q에 저장
assertEquals("sbb가 무엇인가요?", q.getSubject()); // 질문이 맞는지
assertEquals("sbb에 대해서 알고 싶습니다.", q.getContent()); // 내용이 맞는지
}
}- findAll() : 데이터를 조회할때 사용하는 메서드이다.
- assertEquals(기대값, 실제값) : JUnit의 메서드로 기대값과 실제값이 동일한지를 조사한다. 만약 기대값과 실제값이 동일하지 않다면 테스트는 실패로 처리된다.
📝 2-2 ID로 데이터 조회하기(findById() 메서드)
🔴 SbbApplicationTests 클래스(findById() 메서드)
package com.mysite.sbb;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class SbbApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private QuestionRepository questionRepository;
@Test
void testJpa() {
Optional<Question> oq = this.questionRepository.findById(1);
if(oq.isPresent()) { // 널이 아니면 true
Question q = oq.get();
assertEquals("sbb가 무엇인가요?", q.getSubject());
assertEquals("sbb에 대해서 알고 싶습니다.", q.getContent());
}
}
}- findById() : id 값으로 데이터를 조회하기 위한 메서드. 단, findById의 리턴 타입은 Question이 아닌 Optional임에 주의하자. Optional은 null 처리를 유연하게 처리하기 위해 사용하는 클래스로 위와 같이 isPresent로 null이 아닌 지를 확인한 후에 get으로 실제 Question 객체 값을 얻어야 한다.
💡 기본적으로 제공되는 메서드가 아닌 경우
📝 2-3 Subject로 데이터 조회하기(findBySubject() 메서드)
🔴 QuestionRepository 인터페이스(findBySubject() 메서드추가)
package com.mysite.sbb;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface QuestionRepository extends JpaRepository<Question, Integer>{
Question findBySubject(String subject);
}QuestionRepository는 findBySubject 메서드를 기본적으로 제공하지 않기 때문에 메서드를 선언해야함.
🔴 SbbApplicationTests 클래스(findBySubject() 메서드)
package com.mysite.sbb;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class SbbApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private QuestionRepository questionRepository;
@Test
void testJpa() {
Question q = this.questionRepository.findBySubject("sbb가 무엇인가요?");
assertEquals(1, q.getId());
assertEquals("sbb에 대해서 알고 싶습니다.", q.getContent());
}
}Q. findBySubject()메서드를 선언만하고 구현하지 않았는데 어떻게 사용되었는가?
JpaRepository를 상속한 QuestionRepository 객체가 생성될때 벌어진다. (DI에 의해 스프링이 자동으로 QuestionRepository 객체를 생성한다. 이 때 프록시 패턴이 사용된다고 한다.) 리포지터리 객체의 메서드가 실행될때 JPA가 해당 메서드명을 분석하여 쿼리를 만들고 실행한다.
🔎 실행되는 쿼리를 로그에서 보고싶을 때
📁 application.properties파일 수정하기
✅ spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql=true 추가
✅ spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.show_sql=true 추가
🔴 application.properties파일
# DATABASE
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
spring.h2.console.path=/h2-console
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:tcp://localhost/~/local
spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=
server.port=8082
# JPA
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.show_sql=true🔵 JUnit 실행하기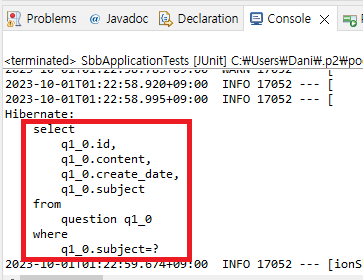
SbbApplicationTests 클래스에서 JUnit을 재실행하면 위와 같이 쿼리를 볼 수 있다.
📝 2-4 논리합(And)으로 데이터 조회하기(findBySubjectAndContent() 메서드)
🔴 QuestionRepository 인터페이스(findBySubjectAndContent() 메서드추가)
package com.mysite.sbb;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface QuestionRepository extends JpaRepository<Question, Integer>{
Question findBySubject(String subject);
Question findBySubjectAndContent(String subject, String content); // 메서드 추가
}🔴 SbbApplicationTests 클래스(findBySubjectAndContent() 메서드)
package com.mysite.sbb;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class SbbApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private QuestionRepository questionRepository;
@Test
void testJpa() {
Question q = this.questionRepository.findBySubjectAndContent("sbb가 무엇인가요?", "sbb에 대해서 알고 싶습니다.");
assertEquals(1, q.getId());
}
}🔵 JUnit 실행하기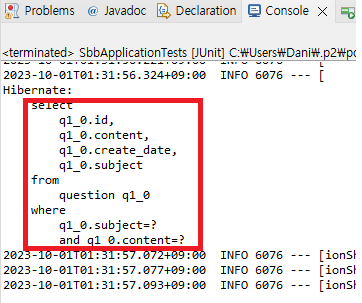
📝 2-5 제목에 특정 문자열이 포함되어 있는 데이터 조회하기(findBySubjectLike() 메서드)
🔴 QuestionRepository 인터페이스(findBySubjectAndContent() 메서드추가)
package com.mysite.sbb;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface QuestionRepository extends JpaRepository<Question, Integer>{
Question findBySubject(String subject);
Question findBySubjectAndContent(String subject, String content);
List<Question> findBySubjectLike(String subject); // 메서드 추가
}🔴 SbbApplicationTests 클래스(findBySubjectAndContent() 메서드)
package com.mysite.sbb;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class SbbApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private QuestionRepository questionRepository;
@Test
void testJpa() {
List<Question> qList = this.questionRepository.findBySubjectLike("sbb%");
Question q = qList.get(0);
assertEquals("sbb가 무엇인가요?", q.getSubject());
assertEquals("sbb에 대해서 알고 싶습니다.", q.getContent());
}
}- sbb%: "sbb"로 시작하는 문자열
- %sbb: "sbb"로 끝나는 문자열
- %sbb%: "sbb"를 포함하는 문자열
🔵 JUnit 실행하기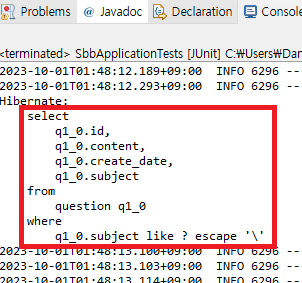
3. 데이터 수정하기
🔴 SbbApplicationTests 클래스
package com.mysite.sbb;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class SbbApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private QuestionRepository questionRepository;
@Test
void testJpa() {
Optional<Question> oq = this.questionRepository.findById(1); // id가 1인 데이터
assertTrue(oq.isPresent()); // 값이 true인지 테스트
Question q = oq.get();
q.setSubject("수정된 제목");
q.setContent("수정된 내용");
q.setCreateDate(LocalDateTime.now());
this.questionRepository.save(q);
}
}-
assertTrue(값) : 값이 true인지를 테스트한다.
🔵 JUnit 실행하기
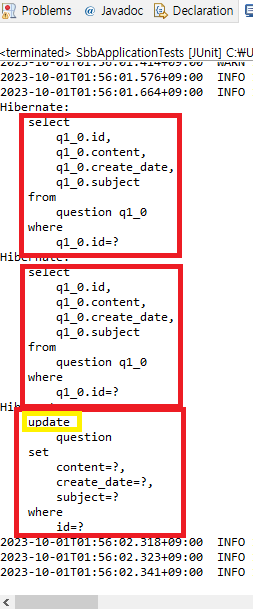
update 문이 실행되었다!
🔵 H2 db 확인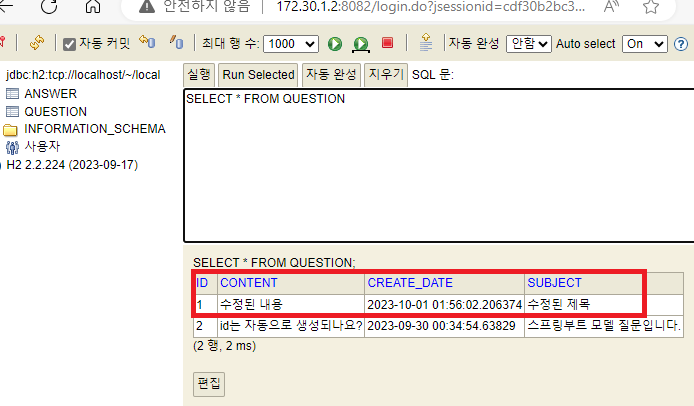
4. 데이터 삭제하기
🔴 SbbApplicationTests 클래스
package com.mysite.sbb;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class SbbApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private QuestionRepository questionRepository;
@Test
void testJpa() {
assertEquals(2, this.questionRepository.count()); // 질문이 두개가 맞는 지 확인
Optional<Question> op = this.questionRepository.findById(2); // ID가 2인 질문 조회 후 op에 저장
Question q = op.get(); // op의 데이터를 Question 타입으로 저장
this.questionRepository.delete(q); // 삭제하기
assertEquals(1, this.questionRepository.count()); // 질문이 한개가 되었는지(삭제되었는지 확인)
}
}🔵 JUnit 실행하기!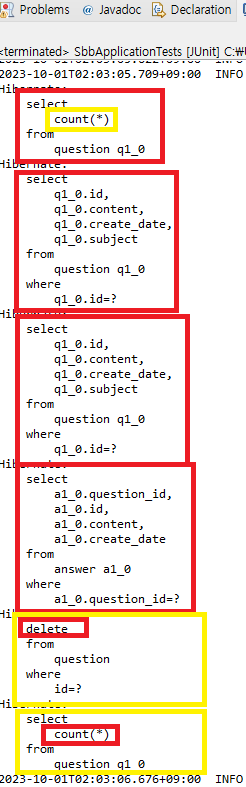
delete 문이 실행되었다!
🔵 H2 db 확인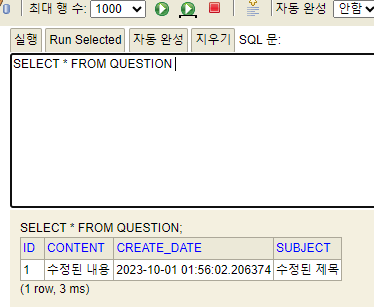
5. 답변 데이터 생성 후 저장하기
🔴 SbbApplicationTests 클래스
package com.mysite.sbb;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class SbbApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private QuestionRepository questionRepository;
@Autowired
private AnswerRepository answerRepository;
@Test
void testJpa() {
Optional<Question> oq = this.questionRepository.findById(1); // id가 1인 질문 조회 2. 데이터 저장
assertTrue(oq.isPresent()); // 널값이 아니면 true
Question q = oq.get(); // Question 타입으로 저장
Answer a = new Answer(); // Answer 타입의 인스턴스 생성
a.setContent("답변 추가해보기"); // 답변저장
a.setQuestion(q); // 어떤 질문에 대한 답변인지 저장
a.setCreateDate(LocalDateTime.now()); // 시간 저장
this.answerRepository.save(a); // 저장
}
}🔵 JUnit 실행하기!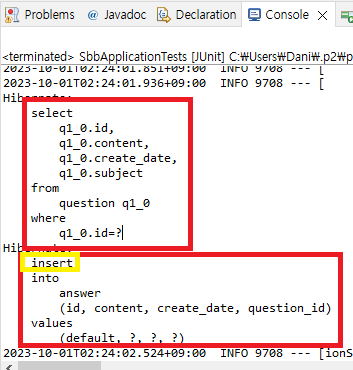
insert 문이 실행되었다!
🔵 H2 db 확인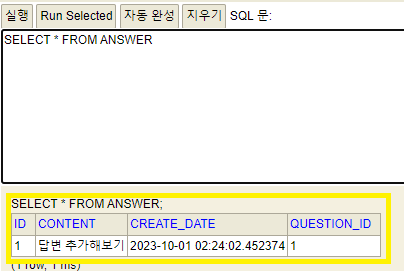
6. 답변 데이터 조회하기
🔴 SbbApplicationTests 클래스
package com.mysite.sbb;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class SbbApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private AnswerRepository answerRepository;
@Test
void testJpa() {
Optional<Answer> oa = this.answerRepository.findById(1);
assertTrue(oa.isPresent());
Answer a = oa.get();
assertEquals(1, a.getQuestion().getId());
assertEquals("답변 추가해보기", a.getContent());
}
}🔵 JUnit 실행하기!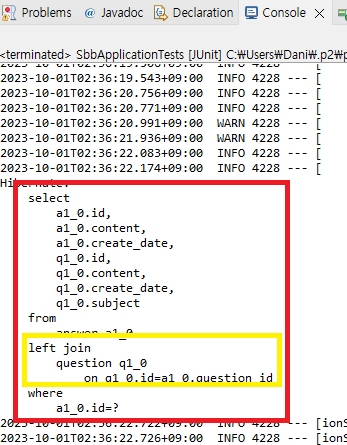
left join이 사용 됨!
7. 질문에서 답변 데이터 조회하기
🔴 SbbApplicationTests 클래스
package com.mysite.sbb;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class SbbApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private QuestionRepository questionRepository;
@Test
void testJpa() {
Optional<Question> oq = this.questionRepository.findById(1); // ID가 1인 질문 저장
assertTrue(oq.isPresent()); // 널값이 아니면 true
Question q = oq.get(); // Question타입으로 인스턴스 생성
List<Answer> a = q.getAnswerList(); // 답변리스트를 리스트로 저장
assertEquals(1, a.size()); // 답변이 1개인지 확인
assertEquals("답변 추가해보기", a.get(0).getContent()); // 인덱스가 0인 답변의 내용 조회
}
}🔵 JUnit 실행하기!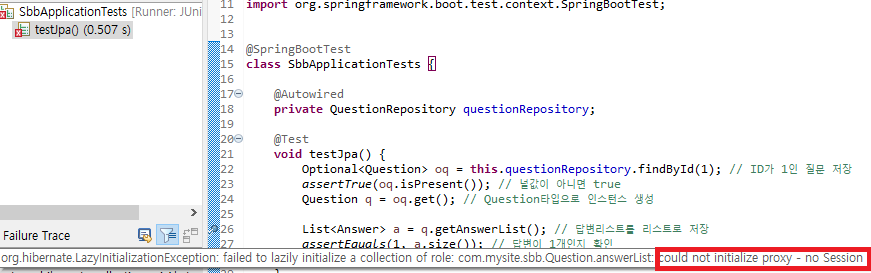
Q.
com.mysite.sbb.Question.answerList, could not initialize proxy - no Session에러가 나는 이유?
Question 리포지터리가 findById를 호출하여 Question 객체를 조회하고 나면 DB세션이 끊어지기 때문이다. 그 이후에 실행되는 q.getAnswerList() 메서드는 세션이 종료되어 오류가 발생한다. 답변 데이터 리스트는 q 객체를 조회할때 가져오지 않고 q.getAnswerList() 메서드를 호출하는 시점에 가져오기 때문이다.
- Lazy 방식 : 필요한 시점에 데이터를 가져오는 방식
- Eager 방식 : 객체를 조회할때 답변 리스트를 모두 가져오는 방식
@OneToMany, @ManyToOne 애너테이션의 옵션으로 fetch=FetchType.LAZY 또는 fetch=FetchType.EAGER 처럼 가져오는 방식을 설정할 수 있다.
💡 해결방안
- 애너테이션 옵션으로
fetch=FetchType.EAGER방식을 설정한다.- @Transactional 애너테이션을 사용한다. @Transactional 애너테이션을 사용하면 메서드가 종료될 때까지 DB 세션이 유지된다.
1. fetch=FetchType.EAGER 방식을 설정한다.
🔴 Question 클래스
public class Question {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
@Column(length = 200)
private String subject;
@Column(columnDefinition = "TEXT")
private String content;
private LocalDateTime createDate;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "question", cascade = CascadeType.REMOVE, fetch=FetchType.EAGER)
// fetch=FetchType.EAGER 을 추가한다.
private List<Answer> answerList;
}🔵 JUnit 실행하기!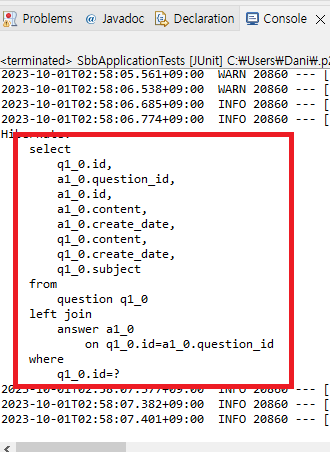
2. @Transactional 애너테이션을 사용
🔴 SbbApplicationTests 클래스
package com.mysite.sbb;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@SpringBootTest
class SbbApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private QuestionRepository questionRepository;
@Transactional // 애너테이션 추가
@Test
void testJpa() {
Optional<Question> oq = this.questionRepository.findById(1);
assertTrue(oq.isPresent());
Question q = oq.get();
List<Answer> a = q.getAnswerList();
assertEquals(1, a.size());
assertEquals("답변 추가해보기", a.get(0).getContent());
}
}🔵 JUnit 실행하기!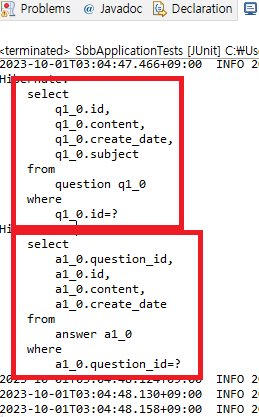
📑 리포지터리의 쿼리 생성 규칙
| 항목 | 예제 | 설명 | JPQL 스니펫 |
|---|---|---|---|
| And | findBySubjectAndContent(String subject, String content) | 여러 칼럼을 And로 검색 | … where x.subject = ?1 and x.content = ?2 |
| Or | findBySubjectOrContent(String subject, String content) | 여러 컬럼을 or 로 검색 | … where x.subject = ?1 or x.content = ?2 |
| Between | findByCreateDateBetween(LocalDateTime fromDate, LocalDateTime toDate) | 컬럼을 between으로 검색 | … where x.createdate between ?1 and ?2 |
| LessThan | findByIdLessThan(Integer id) | 작은 항목 검색 | … where x.id < ?1 |
| GreaterThanEqual | findByIdGraterThanEqual(Integer id) | 크거나 같은 항목 검색 | … where x.id >= ?1 |
| Like | findBySubjectLike(String subject) | like 검색 | … where x.subject like ?1 |
| In | findBySubjectIn(String[] subjects) | 여러 값중에 하나인 항목 검색 | … where x.subject in ?1 |
| OrderBy | findBySubjectOrderByCreateDateAsc(String subject) | 검색 결과를 정렬하여 전달 | … where x.subject = ?1 order by x.createdate desc |
참고 : https://docs.spring.io/spring-data/jpa/docs/current/reference/html/#jpa.query-methods.query-creation


정리가 아주 빡세게 하셨네요 덕분에 많이 배우고 갑니다
혹시 자료를 인용해서 제 블로그에 정리하고 싶은데
출처 남겨서 사용해도 될까요??