스레드
스레드를 생성하는 방법
- Thread클래스 상속
- Runnable 인터페이스를 구현
의 방법이 있다. Runnable을 상속받으면 쓰레드를 만들 수 있다. 스레드를 만들 수 있다는 것은 메인 메소드 외에 동작시킬 수 있는 또 다른 클래스 스레드를 만들어 돌린다는 것.
Car
public class Car extends Thread{
/*Car 스레드로 수행할 작업 내용 작성하는 메소드*/
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i=0; i<1000; i++) {
System.out.println("Car Driving....");
/*의도적으로 지연시킨다.*/
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}- Thread를 상속받으면
run()을 오버라이딩 할 수 있다. Thread.sleep(정수값): 너무 빠르니 의도적으로 멈추어 준다.- Thread 타입이기도 하고 Runnable타입이다.
Tank
public class Tank extends Thread{
public void run(){
for (int i=0; i<1000; i++) {
System.out.println("Tank Shooting....");
/*의도적으로 지연시킨다.*/
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}- Tank도 Thread타입이고, Runnable타입이다.
Plane
public class Plane implements Runnable {
public void run() {
for (int i=0; i<1000; i++) {
System.out.println("Plane flying....");
/*의도적으로 지연시킨다.*/
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}- Plane은 Runnable이다.
- Runnable이 있어서 run()을 오버라이딩할 수 있다.
실행
Thread t1 = new Car();
Thread t2 = new Tank();- 위와 같이 Thread 객체를 만들어줄 수 있다.
- 그러나 Runnable은 인스턴스 생성 방법이 다르다.
Thread t3 = new Plane(); //Runnable만 가지고 있어서 타입오류- Plane은 Runnable이 아니기 때문에 아래와 같이 선언한다.
Thread t3 = new Thread(new Plane());- new Thread(new Runnable클래스()) 와 같은 형식으로 선언하면 된다.
실행-Priority
t1.getPriority();- 스레드의 우선순위를 확인할 수 있다. 우리엑 주어진 우선순위는 동일하게 5이다.
- 우선순위를 높이고, 낮출 수도 있다.
t1.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); //10
t2.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); //1- 우선순위를 더 높이고 싶을 수 있으나, 사실 OS에서 스레드의 우선순위를 제한시킨다. 따라서 100, 1000으로 우선순위를 높여도 OS에서 돌아가는 중요도를 넘을 수는 없다.
실행-클래스-Thread.sleep()
- 이제 Car, Tank, Plane을 돌려보자
t1.run();
t2.run();
t3.run();결과는 아래와 같다.
.
.
.
Car running..
.
.
Tank shooting...
.
.
Plane flying....
Plane flying....
Plane flying....
Plane flying....
Plane flying....
Plane flying....
Plane flying....- run() 메소드 호출 시 별도의 스레드로 동작하지 않고 메인 스레드가 메소드를 호출하는 방식으로 동작한다.
- 순차적으로 동작하는 것을 볼 수 있다.
실행-thread 시작하기
start()를 통해 별도의 호출 스택을 사용하여 각각의 스레드가 동작한다.
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();결과는 다음과 같다.
.
Car Driving....
Plane flying....
Car Driving....
Tank Shooting...
.
.
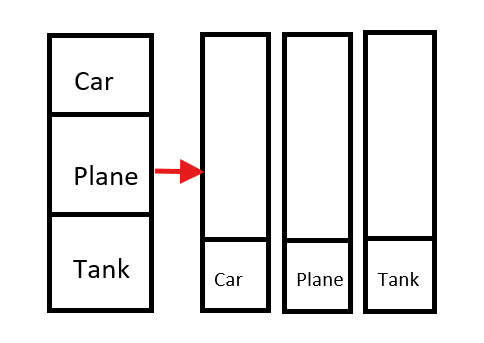
.- 왜 이렇게 나오는가.
start()를 통해서 아래 그림의 우측처럼 별도의 스택으로 동작하기 때문이다.
데몬스레드
데몬 스레드(Daemon Thread) 다른 스레드의 작업을 돕는 보조적인 역할을 수행하는 스레드이다. 데몬 스레드 이외의 스레드들이 모두 종료되면 데몬 스레드는 강제적으로 종료된다.
ex) 가비지 컬렉션, 워드 프로세서의 자동저장, 화면 자동갱신 등
demonthread 예시 실행
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
for(int i = 10; i > 0; i--) {
System.out.println(i);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
/* setDaemon() 메소드로 데몬 스레드 설정을 할 수 있으며 start() 이전에 설정해야 한다. */
t.setDaemon(true);
t.start();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("카운트 다운을 멈추려면 아무 키나 입력하세요 : ");
String str = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("입력한 값 : " + str);
System.out.println("main end ===================");t.setDaemon(값): 데몬 스레드를 실행 시킨다. 이를 주석처리하고 실행시키지 않으면, 카운트 다운이 종료 되어도 종료 되지 않는다.
8
7
6
5
4
323
입력한 값 : 32
main end ===================
2
1
3 - 계속 이어감t.setDaemon(값): 활성화시키면 다음과 같이 잘 멈춘다.
8
7
6
5
4
stop
입력한 값 : stop
main end ===================동기화 노트
- 클래스 종류
Buffer: 공유자원 관리자 :set(),get()구현Producer: 생산자 → 공유 데이터의(자원) 값 생산:set()Consumer: 소비자 → 공유 데이터의(자원) 값 소비:get()
- 여러 스레드가 서로 다른 타이밍에 동작할 때 어떤 방식으로 동기화할지 알아보자.
Consumerpublic class Consumer extends Thread { /*자원 소비*/ private final Buffer criticalData; public Consumer(Buffer criticalData) { //객체타입의 값을 항상 가져오는 생성자 this.criticalData = criticalData; } @Override public void run() { for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { criticalData.getData(); // 값 가져오기 try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } }Producerpublic class Producer extends Thread { private final Buffer criticalData; public Producer(Buffer criticalData) { this.criticalData = criticalData; } @Override public void run() { for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { criticalData.setData(i); try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } }Bufferpublic class Buffer { private int data; private boolean empty = false; public synchronized void getData(){ if(empty){ //empty 가 True가 되면 여기 들어온다. 비어있으면 자원을 가져가서는 안된다. System.out.println("getData wait"); try { /* 실행 중인 스레드를 일시 정지 시킨다. 다른 스레드에서 notify()가 호출 되면 깨어나게 된다. */ wait(); //소비하는 입장에서 비어있지 않아야 한다.-> 대기 } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } System.out.println("소비자 : " + data + " 번 상품을 소비하였습니다."); empty = true; /* 대기 중인 스레드를 하나 깨워서 다시 실행 대기 상태로 전환 시킨다. */ notify(); } public synchronized void setData(int data){ if(!empty) { // 비어있지 않으면 정지시킨다. -> 자원이 있는데 또 만들지 않는다. -> 자원이 고갈되면 그 때 notify() 를 통해 생성한다. System.out.println("setData wait"); try { /* 실행 중인 스레드를 일시 정지 시킨다. 다른 스레드에서 notify()가 호출 되면 깨어나게 된다. */ wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } this.data = data; System.out.println("생산자 : " + data + " 번 상품을 생산하였습니다."); empty = false; /* 대기 중인 스레드를 하나 깨워서 다시 실행 대기 상태로 전환 시킨다. */ notify(); } }mainpublic static void main(String[] args) { Buffer buffer = new Buffer(); Thread b1 = new Producer(buffer); Thread b2 = new Consumer(buffer); // 동일한 인스턴스에 대해 공유하는 스레드 두 개를 생성한다. b1.start(); b2.start();Synchronized예약어 스레드의 동기화 작업을 진행시켜준다. 이 예약어를 제외시킨다면, 스레드 간 공유자원을 사용하면서 동기화를 하지 않아 문제가 발생한다.

