
0. java.time 패키지
- Java의
java.time패키지는 JDK 8부터 도입된 새로운 날짜와 시간 라이브러리로, 기존의java.util.Date와java.util.Calendar의 문제점을 해결하기 위해 설계되었습니다.
java.time 패키지 포스팅 목차
- java.time 패키지 개요
- 주요 클래스 목록 및 용도별 분류
- 핵심 인터페이스 & 단위 및 필드
- 날짜 및 시간의 파싱과 포맷팅
(현재 포스팅) 1. 주요 클래스 목록 및 용도별 분류
이번 포스팅에서는 java.time 패키지에서 제공하는 다양한 Class와 Enum을 용도에따라 정리해보려합니다.
1. 용도별 주요 클래스 (날짜, 시간, 오프셋, 기간)
java.time패키지는 다양한 Class와 Enum을 제공하여 다양한 용도에 맞는 날짜 및 시간 처리를 지원합니다.
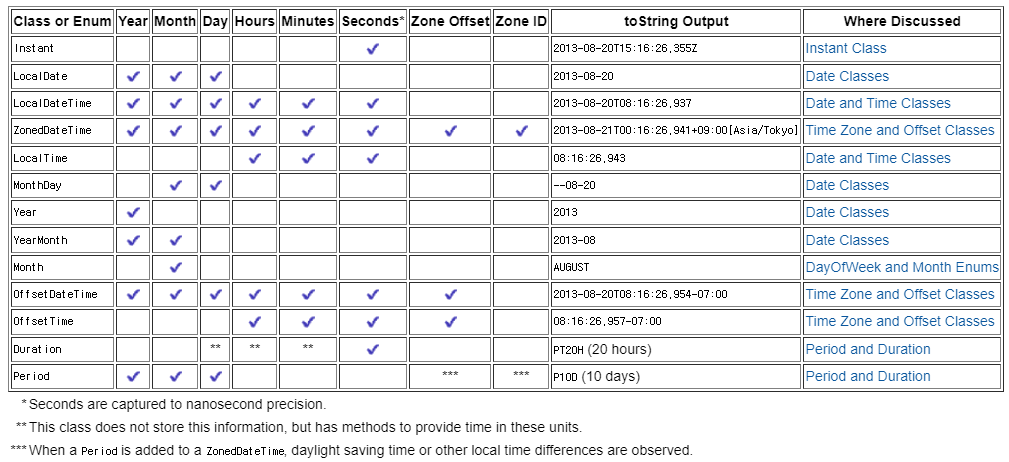
- https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/datetime/iso/overview.html
- 공식 문서에 정리된 주요 클래스 목록표 입니다.
- 모든 것을 다루기엔 거의 쓰이지 않거나 다른 클래스로 대체가능한 클래스들이 있기 때문에, 실무에서 주로 쓰이는 것들을 위주로 정리해보고자합니다.
- 날짜와 시간 요소를 표현하는 Enum :
DayOfWeek,Month - 날짜와 시간 요소를 표현하는 클래스 :
LocalDate,LocalTime,LocalDateTime - 시간대와 오프셋을 고려한 클래스 :
OffsetDateTime,ZonedDateTime,Instant - 시간 간격을 표현하는 클래스 :
Period,Duration
- 날짜와 시간 요소를 표현하는 Enum :
- 참고로
java.time패키지에서 다루는 모든 클래스의 객체는 불변 객체입니다. 따라서 조작을 수행하는 경우엔 새로운 객체에 할당해주어야합니다.
1.1. 날짜와 시간 요소를 표현하는 Enum
DayOfWeek
DayOfWeekEnum은 요일을 나타내며,MONDAY부터SUNDAY까지 정의되어 있습니다.- 각 요일은 1부터 7까지의 숫자 값과 연결되어 있습니다.
- 주요 메서드
.getValue(): 요일에 해당하는 숫자 값을 반환합니다..plus(long days): 현재 요일에서 지정된 일수를 더한 요일을 반환합니다..minus(long days): 현재 요일에서 지정된 일수를 뺀 요일을 반환합니다.
import java.time.DayOfWeek;
DayOfWeek today = DayOfWeek.MONDAY;
System.out.println("Today: " + today); // 출력: Today: MONDAY
System.out.println("Numeric Value: " + today.getValue()); // 출력: Numeric Value: 1
DayOfWeek twoDaysLater = today.plus(2);
System.out.println("Two Days Later: " + twoDaysLater); // 출력: Two Days Later: WEDNESDAYMonth
MonthEnum은 연중 각 달을 나타내며,JANUARY부터DECEMBER까지 정의되어 있습니다.- 각 월은 1부터 12까지의 숫자 값과 연결되어 있습니다.
- 주요 메서드
.getValue(): 해당 월의 숫자 값을 반환합니다..length(boolean leapYear): 해당 월의 일 수를 반환합니다. 윤년 여부를 고려하여 2월의 일수를 28 또는 29로 반환할 수 있습니다..plus(long months): 현재 월에서 지정된 개월 수를 더한 월을 반환합니다..minus(long months): 현재 월에서 지정된 개월 수를 뺀 월을 반환합니다.
import java.time.Month;
Month currentMonth = Month.AUGUST;
System.out.println("Current Month: " + currentMonth); // 출력: Current Month: AUGUST
System.out.println("Numeric Value: " + currentMonth.getValue()); // 출력: Numeric Value: 8
int daysInMonth = currentMonth.length(false); // 윤년 여부에 따라 일 수가 달라집니다.
System.out.println("Days in Month: " + daysInMonth); // 출력: Days in Month: 311.2. 날짜와 시간 요소를 표현하는 클래스
LocalDate
LocalDate클래스는 날짜를 나타내며, 연도, 월, 일로 구성됩니다.- 시간 정보는 포함하지 않으며, 불변(immutable) 객체로 설계되어 있습니다.
- 주요 메서드
.now(): 현재 날짜를 반환합니다..of(int year, int month, int dayOfMonth): 지정된 연도, 월, 일로LocalDate객체를 생성합니다..plusDays(long daysToAdd): 현재 날짜에 지정된 일수를 더한LocalDate를 반환합니다.plusYears,plusMonths,plusWeeks,plusDays, 등..plus를minus로 바꾸면 지정된 단위를 뺀LocalDate를 반환합니다.
.getDayOfWeek(): 현재 날짜의 요일을 반환합니다. (DayOfWeek타입 반환)getYear,getMonth,getDayofMonth,getDayofWeek, 등..
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.DayOfWeek;
import java.time.Month;
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
System.out.println("Today's Date: " + today); // 출력: Today's Date: 2024-08-29
LocalDate specificDate = LocalDate.of(2023, Month.DECEMBER, 25);
System.out.println("Specific Date: " + specificDate); // 출력: Specific Date: 2023-12-25
DayOfWeek dayOfWeek = specificDate.getDayOfWeek();
System.out.println("Day of the Week: " + dayOfWeek); // 출력: Day of the Week: MONDAYLocalTime
LocalTime클래스는 시간을 나타내며, 시, 분, 초, 나노초로 구성됩니다.- 날짜 정보는 포함하지 않으며, 불변 객체로 설계되어 있습니다.
- 주요 메서드
.now(): 현재 시간을 반환합니다..of(int hour, int minute, int second): 지정된 시, 분, 초로LocalTime객체를 생성합니다.- 인수를 하나 더 추가하면 나노초를 포함한
LocalTime객체를 생성합니다. (없으면 나노초는0으로 초기화됩니다.)
- 인수를 하나 더 추가하면 나노초를 포함한
.plusHours(long hoursToAdd): 현재 시간에 지정된 시간을 더한LocalTime을 반환합니다.plusHours,plusMinutes,plusSeconds,plusNanos, 등..plus를minus로 바꾸면 지정된 단위를 뺀LocalTime를 반환합니다.
.getHour(): 시간의 시(hour) 부분을 반환합니다.getHour,getMinute,getSecond,getNano, 등..
import java.time.LocalTime;
LocalTime now = LocalTime.now();
System.out.println("Current Time: " + now); // 출력: Current Time: 14:30:45.123
LocalTime specificTime = LocalTime.of(10, 30);
System.out.println("Specific Time: " + specificTime); // 출력: Specific Time: 10:30
LocalTime plusHours = specificTime.plusHours(2);
System.out.println("Time After Two Hours: " + plusHours); // 출력: Time After Two Hours: 12:30
LocalDateTime
LocalDateTime클래스는 날짜와 시간을 함께 나타내며,LocalDate와LocalTime을 결합한 형태로 연도, 월, 일, 시, 분, 초, 나노초 정보를 모두 포함합니다.- 이 역시 불변 객체로 설계되어 있습니다.
- 주요 메서드
.now(): 현재 날짜와 시간을 반환합니다..of(int year, int month, int dayOfMonth, int hour, int minute): 지정된 연도, 월, 일, 시, 분으로 LocalDateTime 객체를 생성합니다.- 인수를 추가하면 초와 나노초도 설정할 수 있습니다.
.plusXxx()&.minusXxx(): 위에서 언급한LocalDate와LocalTime의 메서드와 동일합니다..toLocalDate():LocalDateTime에서 날짜 부분만을 반환하는LocalDate객체를 생성합니다..toLocalTime():LocalDateTime에서 시간 부분만을 반환하는LocalTime객체를 생성합니다.
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.time.Month;
LocalDateTime currentDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println("Current DateTime: " + currentDateTime); // 출력: Current DateTime: 2024-08-29T14:30:45.123
LocalDateTime specificDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2023, Month.DECEMBER, 25, 10, 30);
System.out.println("Specific DateTime: " + specificDateTime); // 출력: Specific DateTime: 2023-12-25T10:30
LocalDate datePart = specificDateTime.toLocalDate();
System.out.println("Date Part: " + datePart); // 출력: Date Part: 2023-12-25
LocalTime timePart = specificDateTime.toLocalTime();
System.out.println("Time Part: " + timePart); // 출력: Time Part: 10:30
1.3. 시간대와 오프셋을 고려한 클래스
java.time패키지에는 시간대와 오프셋을 고려한 날짜와 시간을 다룰 수 있는 클래스들이 포함되어 있습니다.- 이들은 글로벌한 시간 계산이나 특정 시간대에서의 시간 처리에 매우 유용합니다.
- 여기서는
OffsetDateTime,ZonedDateTime,Instant클래스에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
OffsetDateTime
OffsetDateTime클래스는 날짜와 시간 정보에 시간대 오프셋(예: UTC+09:00)을 포함한 형태로, 로컬 시간에 특정 시간대의 오프셋을 적용한 시간을 나타냅니다.- DST(써머타임) 혹은 지역 시간대 정보는 포함하지 않으며, 오프셋만을 통해 시간 차이를 표현합니다.
- 불변(immutable) 객체로 설계되어 있습니다.
- 참고로
OffsetDateTime에서는 동일 패키지의LocalDateTime과ZoneOffset클래스를 참조하는 형태입니다.
- 주요 메서드
.now(): 현재 날짜와 시간을 기본 오프셋으로 반환합니다..of(LocalDateTime dateTime, ZoneOffset offset): 지정된LocalDateTime과ZoneOffset으로OffsetDateTime객체를 생성합니다.- 인수(연도~초)들을 추가하여
LocalDateTime를 대체할 수도 있습니다.
- 인수(연도~초)들을 추가하여
.getOffset(): 현재OffsetDateTime의 오프셋을 반환합니다..withOffsetSameLocal(ZoneOffset offset): 지정된 오프셋으로 동일한 로컬 날짜와 시간을 반환합니다..withOffsetSameInstant(ZoneOffset offset): 지정된 오프셋으로 같은 인스턴트의 시간을 반환합니다.Instant는 아래에서 다시 다룹니다.
.toInstant():OffsetDateTime을 UTC 기준의Instant로 변환합니다.Instant는 아래에서 다시 다룹니다.
.toZonedDateTime(): 해당OffsetDateTime을 기본 시간대와 함께ZonedDateTime으로 변환합니다.ZonedDateTime은 바로 다음 파트에서 다룹니다.
import java.time.OffsetDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneOffset;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
import java.time.Instant;
OffsetDateTime currentOffsetDateTime = OffsetDateTime.now();
System.out.println("Current OffsetDateTime: " + currentOffsetDateTime); // 출력: Current OffsetDateTime: 2024-08-29T14:30:45.123+09:00
OffsetDateTime specificOffsetDateTime = OffsetDateTime.of(LocalDateTime.of(2023, 12, 25, 10, 30), ZoneOffset.of("+02:00"));
System.out.println("Specific OffsetDateTime: " + specificOffsetDateTime); // 출력: Specific OffsetDateTime: 2023-12-25T10:30+02:00
ZoneOffset offset = specificOffsetDateTime.getOffset();
System.out.println("Zone Offset: " + offset); // 출력: Zone Offset: +02:00
OffsetDateTime changedOffsetSameInstant = specificOffsetDateTime.withOffsetSameInstant(ZoneOffset.of("+01:00"));
System.out.println("Changed Offset (Same Instant): " + changedOffsetSameInstant); // 출력: Changed Offset (Same Instant): 2023-12-25T09:30+01:00
OffsetDateTime changedOffsetSameLocal = specificOffsetDateTime.withOffsetSameLocal(ZoneOffset.of("+01:00"));
System.out.println("Changed Offset (Same Local): " + changedOffsetSameLocal); // 출력: Changed Offset (Same Local): 2023-12-25T10:30+01:00
Instant instant = specificOffsetDateTime.toInstant();
System.out.println("Instant: " + instant); // 출력: Instant: 2023-12-25T08:30:00Z
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = specificOffsetDateTime.toZonedDateTime();
System.out.println("ZonedDateTime: " + zonedDateTime); // 출력: ZonedDateTime: 2023-12-25T10:30+02:00
ZonedDateTime
- ZonedDateTime 클래스는 날짜와 시간 정보에 시간대(예: Asia/Seoul)를 포함하여 전 세계의 특정 지역 시간대를 반영한 날짜와 시간을 나타냅니다.
- 오프셋과 시간대 정보를 모두 포함하여, 특정 시간대에서의 정확한 시간을 관리할 수 있습니다. (지역에 따른 DST(써머타임)시행 여부도 포함됩니다)
- 불변 객체로 설계되어 있습니다.
- 참고로
ZonedDateTime에서는 동일 패키지의LocalDateTime과ZoneOffset그리고ZoneId클래스를 참조하는 형태입니다.
- 주요 메서드
.now(): 현재 날짜와 시간을 기본 시간대로 반환합니다..of(LocalDateTime dateTime, ZoneId zone): 지정된LocalDateTime과ZoneId로ZonedDateTime객체를 생성합니다.- 인수(연도~초)들을 추가하여
LocalDateTime를 대체할 수도 있습니다.
- 인수(연도~초)들을 추가하여
.ofInstant(Instant instant, ZoneId zone): 특정Instant를 지정된 시간대로 변환하여ZonedDateTime을 생성합니다.Instant는 바로 다음 파트에서 다룹니다.
.getZone(): 현재ZonedDateTime의 시간대 정보(ZoneId)를 반환합니다..getOffset(): 현재ZonedDateTime의 오프셋을 반환합니다..withZoneSameInstant(ZoneId zone): 같은 순간의 시간을 다른 시간대로 변환하여 반환합니다..withZoneSameLocal(ZoneId zone): 동일한 로컬 날짜와 시간을 지정된 시간대의ZonedDateTime으로 변환하여 반환합니다..toOffsetDateTime(): 해당 ZonedDateTime을 오프셋을 포함한 OffsetDateTime으로 변환합니다..toInstant(): ZonedDateTime을 UTC 기준의 Instant로 변환합니다.
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.OffsetDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneOffset;
ZonedDateTime currentZonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.now();
System.out.println("Current ZonedDateTime: " + currentZonedDateTime); // 출력: Current ZonedDateTime: 2024-08-29T14:30:45.123+09:00[Asia/Seoul]
ZonedDateTime specificZonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.of(LocalDateTime.of(2023, 12, 25, 10, 30), ZoneId.of("Europe/Paris"));
System.out.println("Specific ZonedDateTime: " + specificZonedDateTime); // 출력: Specific ZonedDateTime: 2023-12-25T10:30+01:00[Europe/Paris]
ZoneId zoneId = specificZonedDateTime.getZone();
System.out.println("Zone ID: " + zoneId); // 출력: Zone ID: Europe/Paris
ZoneOffset offset = specificZonedDateTime.getOffset();
System.out.println("Zone Offset: " + offset); // 출력: Zone Offset: +01:00
ZonedDateTime changedZoneSameInstant = specificZonedDateTime.withZoneSameInstant(ZoneId.of("Asia/Tokyo"));
System.out.println("Changed Zone (Same Instant): " + changedZoneSameInstant); // 출력: Changed Zone (Same Instant): 2023-12-25T18:30+09:00[Asia/Tokyo]
ZonedDateTime changedZoneSameLocal = specificZonedDateTime.withZoneSameLocal(ZoneId.of("Asia/Tokyo"));
System.out.println("Changed Zone (Same Local): " + changedZoneSameLocal); // 출력: Changed Zone (Same Local): 2023-12-25T10:30+09:00[Asia/Tokyo]
OffsetDateTime offsetDateTime = specificZonedDateTime.toOffsetDateTime();
System.out.println("OffsetDateTime: " + offsetDateTime); // 출력: OffsetDateTime: 2023-12-25T10:30+01:00
Instant instant = specificZonedDateTime.toInstant();
System.out.println("Instant: " + instant); // 출력: Instant: 2023-12-25T09:30:00ZInstant
Instant클래스는 1970년 1월 1일 00:00:00 UTC를 기준으로 하는 특정 순간을 초 단위와 나노초 단위로 표현합니다.- 이러한 시간을 Unix Timestamp 혹은 Epoch Time으로 부릅니다.
- 날짜나 시간대와 무관하게 전 세계적으로 동일한 시간을 표현할 때 사용됩니다. (예를들면, 서버시간, 등)
- 불변 객체로 설계되어 있으며, 주로 타임스탬프나 전송 시점 등을 다룰 때 유용합니다.
- 주요 메서드
.now(): 현재 UTC 기준의Instant를 반환합니다..ofEpochSecond(long epochSecond): 지정된 에포크 초로부터Instant를 생성합니다..ofEpochMilli(long epochMilli): 지정된 에포크 밀리초로부터Instant를 생성합니다..getEpochSecond(): 현재Instant를 기준으로 하는 에포크 초를 반환합니다..getNano(): 현재Instant의 나노초 부분을 반환합니다..plusSeconds(long secondsToAdd): 지정된 초를 현재Instant에 더한 값을 반환합니다.- plus를 minus로 바꾸면 뺀 값을 반환합니다.
- 참고로 단위는
plusSeconds,plusMillis,plusNanos만 사용가능합니다.
.atZone(ZoneId zone): 현재 Instant를 지정된 시간대의 ZonedDateTime으로 변환합니다..atOffset()도 사용 가능합니다.
.toEpochMilli():Instant시간을 밀리초 단위의 타임스탬프로 반환합니다.
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneId;
Instant currentInstant = Instant.now();
System.out.println("Current Instant: " + currentInstant); // 출력: Current Instant: 2024-08-29T05:30:45.123Z
Instant epochInstant = Instant.ofEpochSecond(1609459200);
System.out.println("Instant from Epoch Seconds: " + epochInstant); // 출력: Instant from Epoch Seconds: 2021-01-01T00:00:00Z
long epochSecond = currentInstant.getEpochSecond();
System.out.println("Epoch Second: " + epochSecond); // 출력: Epoch Second: 1693299045
Instant instantPlusSeconds = currentInstant.plusSeconds(3600);
System.out.println("Instant Plus 1 Hour: " + instantPlusSeconds); // 출력: Instant Plus 1 Hour: 2024-08-29T06:30:45.123Z
Instant instantMinusMillis = currentInstant.minusMillis(1000);
System.out.println("Instant Minus 1 Second: " + instantMinusMillis); // 출력: Instant Minus 1 Second: 2024-08-29T05:30:44.123Z
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = currentInstant.atZone(ZoneId.of("Asia/Seoul"));
System.out.println("ZonedDateTime from Instant: " + zonedDateTime); // 출력: ZonedDateTime from Instant: 2024-08-29T14:30:45.123+09:00[Asia/Seoul]
1.4. 시간 간격을 표현하는 클래스
java.time패키지에는 시간 간격을 표현하는 두 가지 주요 클래스가 있습니다:Period와Duration.- 이 두 클래스는 각각 다른 단위의 시간 간격을 표현하며, 특정 시간 간의 차이를 계산하거나 조작하는 데 유용합니다.
Period
Period클래스는 연, 월, 일 단위의 시간 간격을 표현합니다.- 예를 들어, "2년 3개월 4일"과 같은 기간을 나타낼 수 있습니다.
- 날짜 간의 차이를 계산할 때 주로 사용됩니다.
- 불변(immutable) 객체로 설계되어 있습니다.
Period클래스에서 데이터 형태는PxYxMxD입니다.
- 주요 메서드
.of(int years, int months, int days): 지정된 연, 월, 일로Period객체를 생성합니다..between(LocalDate startDateInclusive, LocalDate endDateExclusive): 두 날짜 사이의 기간을 계산하여Period객체를 반환합니다..getYears(): Period의 연 단위 값을 반환합니다..getMonths(),getDays()도 사용 가능합니다.
.plusYears(long yearsToAdd): 지정된 연수를 더한 새로운Period를 반환합니다.- plus를 minus로 바꾸면 지정된 연수를 뺀 새로운
Period를 반환합니다. .plusMonths,.plusDays도 사용 가능합니다.plus(Period)형태로도 사용 가능합니다.
- plus를 minus로 바꾸면 지정된 연수를 뺀 새로운
.multipliedBy(int scalar): 현재Period를 지정된 배수만큼 곱한 새로운Period를 반환합니다..isNegative():Period가 음수인지 여부를 반환합니다..negated(): 현재Period의 부호를 반전시킨 새로운Period를 반환합니다.
import java.time.Period;
import java.time.LocalDate;
Period period = Period.of(2, 3, 4);
System.out.println("Period: " + period); // 출력: Period: P2Y3M4D
LocalDate startDate = LocalDate.of(2022, 1, 1);
LocalDate endDate = LocalDate.of(2024, 5, 10);
Period betweenDates = Period.between(startDate, endDate);
System.out.println("Period Between Dates: " + betweenDates); // 출력: Period Between Dates: P2Y4M9D
int years = betweenDates.getYears();
int months = betweenDates.getMonths();
int days = betweenDates.getDays();
System.out.println("Years: " + years + ", Months: " + months + ", Days: " + days); // 출력: Years: 2, Months: 4, Days: 9
Period addedPeriod = period.plusYears(1).plusMonths(2).plusDays(3);
System.out.println("Added Period: " + addedPeriod); // 출력: Added Period: P3Y5M7D
Period multipliedPeriod = period.multipliedBy(2);
System.out.println("Multiplied Period: " + multipliedPeriod); // 출력: Multiplied Period: P4Y6M8D
boolean isNegative = period.isNegative();
System.out.println("Is Negative: " + isNegative); // 출력: Is Negative: false
Period negatedPeriod = period.negated();
System.out.println("Negated Period: " + negatedPeriod); // 출력: Negated Period: P-2Y-3M-4D
Duration
Duration클래스는 초와 나노초 단위의 시간 간격을 표현합니다.- 예를 들어, "5시간 30분" 또는 "120초"와 같은 시간을 나타낼 수 있습니다.
- 시간 간의 차이를 밀리초 이하의 정밀도로 계산할 때 주로 사용됩니다.
- 불변 객체로 설계되어 있습니다.
Duration클래스에서 데이터 형태는PTxHxMx.xS입니다. (.뒤는 밀리초 및 나노초 단위)
- 주요 메서드
.ofDays(long days): 지정된 일 수를 초 단위로 변환하여Duration객체를 생성합니다.ofHours(long hours),ofMinutes(long minutes),ofSeconds(long seconds, long nanoAdjustment), 등
.between(Temporal startInclusive, Temporal endExclusive): 두 시간 간의 차이를 계산하여Duration객체를 반환합니다.Temporal인터페이스는 다음 포스팅에서 다룹니다.
.toDays():Duration을 일 단위로 반환합니다.toHours(),toMinutes(),toSeconds(),toMillis(), 등
.plus(Duration durationToAdd): 지정된Duration을 더한 새로운Duration을 반환합니다.- plus를 minus로 바꾸면 뺀 결과가 반환됩니다.
.multipliedBy(long multiplicand): 현재Duration을 지정된 배수만큼 곱한 새로운Duration을 반환합니다..isNegative():Duration이 음수인지 여부를 반환합니다..negated(): 현재Duration의 부호를 반전시킨 새로운Duration을 반환합니다.
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
Duration duration = Duration.ofHours(5);
System.out.println("Duration: " + duration); // 출력: Duration: PT5H
LocalTime startTime = LocalTime.of(8, 30);
LocalTime endTime = LocalTime.of(14, 0);
Duration betweenTimes = Duration.between(startTime, endTime);
System.out.println("Duration Between Times: " + betweenTimes); // 출력: Duration Between Times: PT5H30M
long hours = betweenTimes.toHours();
long minutes = betweenTimes.toMinutes();
System.out.println("Hours: " + hours + ", Minutes: " + minutes); // 출력: Hours: 5, Minutes: 330
Duration addedDuration = duration.plusMinutes(30);
System.out.println("Added Duration: " + addedDuration); // 출력: Added Duration: PT5H30M
Duration subtractedDuration = duration.minusMinutes(30);
System.out.println("Subtracted Duration: " + subtractedDuration); // 출력: Subtracted Duration: PT4H30M
Duration multipliedDuration = duration.multipliedBy(2);
System.out.println("Multiplied Duration: " + multipliedDuration); // 출력: Multiplied Duration: PT10H
boolean isNegative = duration.isNegative();
System.out.println("Is Negative: " + isNegative); // 출력: Is Negative: false
Duration negatedDuration = duration.negated();
System.out.println("Negated Duration: " + negatedDuration); // 출력: Negated Duration: PT-5H
마무리
-
이번 포스팅에서는 java.time 패키지에서 제공하는 주요 클래스들 중 날짜, 시간, 오프셋, 기간을 표현하는 클래스들에 대해 다뤘습니다.
LocalDate, LocalTime, LocalDateTime과 같은 날짜와 시간을 표현하는 클래스부터,OffsetDateTime, ZonedDateTime, Instant와 같이 시간대와 오프셋을 고려한 클래스들, 그리고Period, Duration과 같은 시간 간격을 다루는 클래스들에 대해 살펴보았습니다.
-
이러한 클래스들은 각각의 용도에 맞게 설계되어 있어, 다양한 시간 관련 작업을 쉽게 처리할 수 있도록 도와줍니다.
-
다음 포스팅에서는
java.time패키지에서 시간 및 날짜 조작을 위한 핵심 인터페이스인Temporal계열 인터페이스들과, 다양한 시간 단위와 필드를 표현하는ChronoUnit, ChronoField를 통해 날짜와 시간 데이터를 보다 세밀하게 다루는 방법을 알아볼 것입니다.
