합승 택시 요금

📚 문제 설명
n개의 지점과 간선 fares 가 주어진다.
무지와 어피치가 s에서 함께 출발하여 각자의 집으로 돌아가려고 할 때
둘이 택시를 적절히 합승하여 택시 요금을 최소로 하고 싶다고 한다.
fares에 각각의 간선에 따른 택시 요금이 나올 때 택시 요금이 최소가 되는 경우를 구하여라.
👨🏻💻 풀이 과정
이 문제는 결국 최단거리 찾는 문제랑 똑같다.
그런데 우리가 그 동안 문제를 풀면 알 수 있듯 최단 거리 구하는 알고리즘은 여러개가 있지만,
이렇게 간선의 거리 또는 중요도가 함께 주어지는 경우에는 다익스트라(Dijkstra) 알고리즘을 이용한다.
전체 로직
DijkStra함수를 이용하여s에서부터 각각의 지점까지의 최소 거리를 구한다.- 반복문을 통해 택시 합승을 할 위치를 모두 계산.
s부터i까지 합승 +i부터a+i부터b- 최솟값 갱신.
- 최솟값 출력.
전체 풀이 (다익스트라, 우선순위큐 코드 생략)
// 로컬 환경 실행을 위한 변수
const fares = [[2, 6, 6], [6, 3, 7], [4, 6, 7], [6, 5, 11], [2, 5, 12], [5, 3, 20], [2, 4, 8], [4, 3, 9]];
const [n, s, a, b] = [6, 4, 5, 6];
const Lines = {};
// 연결 리스트 구조로 간선 저장
for (const [Start, End, Cost] of fares) {
if (!Lines[Start]) Lines[Start] = [];
if (!Lines[End]) Lines[End] = [];
Lines[Start].push([End, Cost]);
Lines[End].push([Start, Cost]);
}
class MinHeap {
//생략
}
const Dijkstra = (now) => {
//생략
};
const EachDistance = () => {
// 회사부터 최소 거리.
const FromCo = Dijkstra(s);
// 회사에서 a,b 까지의 최소거리
let min = Infinity;
// 합승 위치를 반복문으로 모두 확인.
for (let i = 0; i < FromCo.length; i++) {
// 만약 갈 수 없는 정점이라면 생략.
if (Lines[i + 1]) {
let total = 0;
// 합승한 위치부터 각각의 점까지의 최소거리.
let distance = Dijkstra(i + 1);
// 전체 택시 요금.
total += FromCo[i] + distance[a - 1] + distance[b - 1];
min = min > total ? total : min;
}
}
console.log(min);
};
EachDistance();💡다익스트라(Dijkstra) 알고리즘
그럼 이제 다익스트라 알고리즘을 이용해 함수를 만들면 된다.
이전에 부대 복귀 문제에서도 한번 말했지만, 다익스트라 알고리즘은 전체적인 모양을 BFS와 매우 유사하다.
다익스트라 알고리즘과 일반적은 BFS와의 차이는 크게 2개 정도 생각할 수 있다.
- 거리 테이블을 매번 확인 후 진행.
- Queue 대신 Priority Queue 사용. (필수는 아니지만 시간이 더 짧아진다.)
전체적인 로직을 풀어서 설명하면 다음과 같다.
Queue에 해당 위치까지의 최소 거리를 저장.- 현재 위치 (우선순위큐 가장 앞에 있는 값)와 연결된 선 확인.
- 다음 위치까지의 최소 거리 계산.
- 위의 과정 반복.
- 거리 테이블 리턴.
다익스트라(Dijkstra) 코드
const Dijkstra = (now) => {
// 거리 테이블.
let Weight = new Array(n).fill(Infinity);
// 일반 배열 대신 PQ 사용.
const Queue = new MinHeap();
// 시작 위치의 거리는 0이기 때문에 초기값을 이렇게 설정.
Queue.Insert([now, 0]);
// 시작 위치의 거리 갱신.
Weight[now - 1] = 0;
// BFS와 유사하게 while문 진행.
while (Queue.GetLength()) {
// [정점, 거리]
const [End, Cost] = Queue.Pop();
// 연결 리스트 확인.
for (const [next, nextDistance] of Lines[End]) {
// 다음 위치까지의 거리.
const newDistance = Cost + nextDistance;
// 만약 현재 거리 테이블 값보다 작다면.
if (newDistance < Weight[next - 1]) {
// 거리 테이블 갱신.
Weight[next - 1] = newDistance;
Queue.Insert([next, newDistance]);
}
}
}
return Weight;
};이렇게 해서 전체 코드는 다음과 같다.
1차 제출 코드
function solution(n, s, a, b, fares) {
const Lines = {};
let answer = 0;
// 연결 리스트 구조로 간선 저장
for (const [Start, End, Cost] of fares) {
if (!Lines[Start]) Lines[Start] = [];
if (!Lines[End]) Lines[End] = [];
Lines[Start].push([End, Cost]);
Lines[End].push([Start, Cost]);
}
class MinHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [null];
}
Insert(item) {
let Current = this.heap.length;
while (Current > 1) {
const Parent = Math.floor(Current / 2);
if (this.heap[Parent][1] > item[1]) {
this.heap[Current] = this.heap[Parent];
Current = Parent;
} else break;
}
this.heap[Current] = item;
}
Pop() {
if (this.heap.length > 2) {
const PopItem = this.heap[1];
this.heap[1] = this.heap.pop();
let Current = 1;
let Left = Current * 2;
let Right = Current * 2 + 1;
while (this.heap[Left]) {
let Compare = Left;
if (this.heap[Right] && this.heap[Left][1] > this.heap[Right][1]) {
Compare = Right;
}
if (this.heap[Compare][1] < this.heap[Current][1]) {
[this.heap[Compare], this.heap[Current]] = [this.heap[Current], this.heap[Compare]];
Current = Compare;
Left = Current * 2;
Right = Current * 2 + 1;
} else break;
}
return PopItem;
} else if (this.heap.length === 2) {
return this.heap.pop();
} else {
return null;
}
}
GetLength() {
return this.heap.length - 1;
}
}
const Dijkstra = (now) => {
// 거리 테이블.
let Weight = new Array(n).fill(Infinity);
// 일반 배열 대신 PQ 사용.
const Queue = new MinHeap();
// 시작 위치의 거리는 0이기 때문에 초기값을 이렇게 설정.
Queue.Insert([now, 0]);
// 시작 위치의 거리 갱신.
Weight[now - 1] = 0;
// BFS와 유사하게 while문 진행.
while (Queue.GetLength()) {
// [정점, 거리]
const [End, Cost] = Queue.Pop();
// 연결 리스트 확인.
for (const [next, nextDistance] of Lines[End]) {
// 다음 위치까지의 거리.
const newDistance = Cost + nextDistance;
// 만약 현재 거리 테이블 값보다 작다면.
if (newDistance < Weight[next - 1]) {
// 거리 테이블 갱신.
Weight[next - 1] = newDistance;
Queue.Insert([next, newDistance]);
}
}
}
return Weight;
};
const EachDistance = () => {
// 회사부터 최소 거리.
const FromCo = Dijkstra(s);
// 회사에서 a,b 까지의 최소거리
let min = Infinity;
// 합승 위치를 반복문으로 모두 확인.
for (let i = 0; i < FromCo.length; i++) {
// 만약 갈 수 없는 정점이라면 생략.
if (Lines[i + 1]) {
let total = 0;
// 합승한 위치부터 각각의 점까지의 최소거리.
let distance = Dijkstra(i + 1);
// 전체 택시 요금.
total += FromCo[i] + distance[a - 1] + distance[b - 1];
min = min > total ? total : min;
}
}
answer = min;
};
EachDistance();
return answer;
}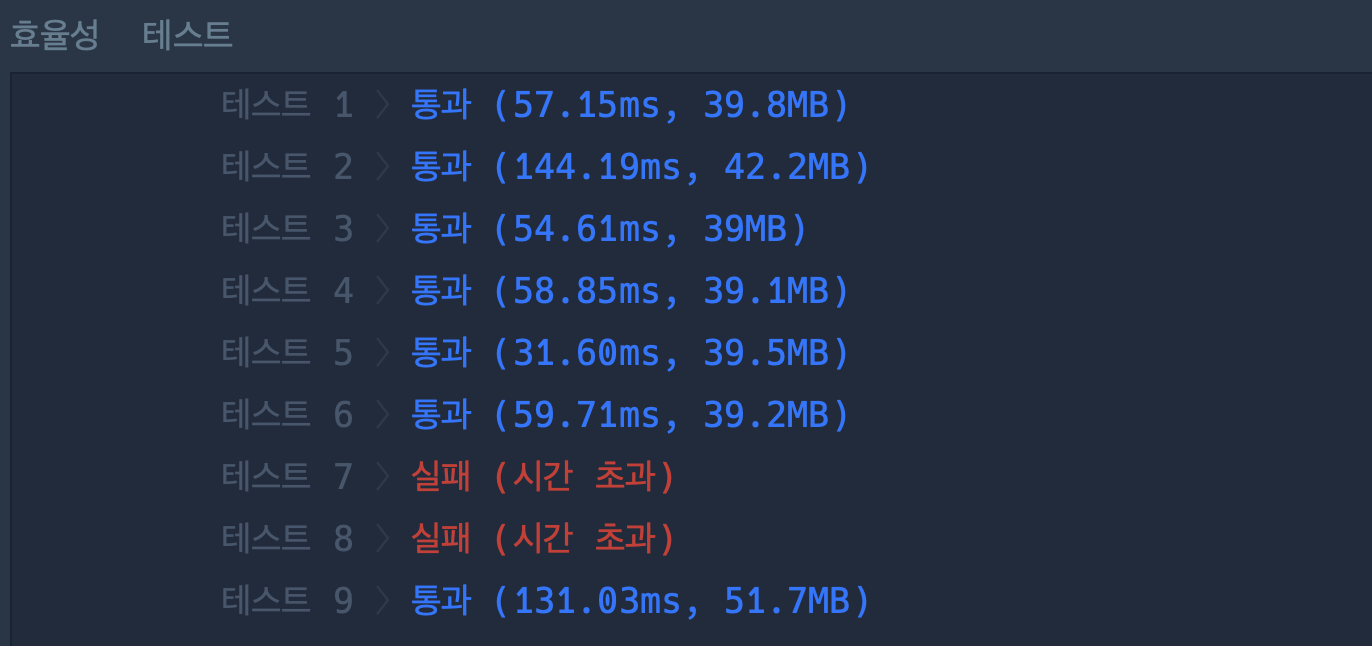
그런데 이렇게 제출을 하면 테스트7번과 테스트 8번이 시간초과가 나게 된다.
이 문제의 경우 한가지만 수정하면 된다.
Dijkstra 함수에 한가지 조건만 추가해주면 된다.
if (Weight[End - 1] < Cost) continue;기존의 함수의 경우 최솟값이 갱신이 되어도 Queue에 있는 값이라면, 반복문을 진행한다.
그러나 해당 코드를 넣을 경우 아무리 Queue에 있는 값이라도 최솟값이 아니라면 생략하게 된다.
수정 코드
function solution(n, s, a, b, fares) {
const Lines = {};
let answer = 0;
// 연결 리스트 구조로 간선 저장
for (const [Start, End, Cost] of fares) {
if (!Lines[Start]) Lines[Start] = [];
if (!Lines[End]) Lines[End] = [];
Lines[Start].push([End, Cost]);
Lines[End].push([Start, Cost]);
}
class MinHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [null];
}
Insert(item) {
let Current = this.heap.length;
while (Current > 1) {
const Parent = Math.floor(Current / 2);
if (this.heap[Parent][1] > item[1]) {
this.heap[Current] = this.heap[Parent];
Current = Parent;
} else break;
}
this.heap[Current] = item;
}
Pop() {
if (this.heap.length > 2) {
const PopItem = this.heap[1];
this.heap[1] = this.heap.pop();
let Current = 1;
let Left = Current * 2;
let Right = Current * 2 + 1;
while (this.heap[Left]) {
let Compare = Left;
if (this.heap[Right] && this.heap[Left][1] > this.heap[Right][1]) {
Compare = Right;
}
if (this.heap[Compare][1] < this.heap[Current][1]) {
[this.heap[Compare], this.heap[Current]] = [this.heap[Current], this.heap[Compare]];
Current = Compare;
Left = Current * 2;
Right = Current * 2 + 1;
} else break;
}
return PopItem;
} else if (this.heap.length === 2) {
return this.heap.pop();
} else {
return null;
}
}
GetLength() {
return this.heap.length - 1;
}
}
const Dijkstra = (now) => {
// 거리 테이블.
let Weight = new Array(n).fill(Infinity);
// 일반 배열 대신 PQ 사용.
const Queue = new MinHeap();
// 시작 위치의 거리는 0이기 때문에 초기값을 이렇게 설정.
Queue.Insert([now, 0]);
// 시작 위치의 거리 갱신.
Weight[now - 1] = 0;
// BFS와 유사하게 while문 진행.
while (Queue.GetLength()) {
// [정점, 거리]
const [End, Cost] = Queue.Pop();
// 테스트 7, 8번 에러 원인.
if (Weight[End - 1] < Cost) continue;
// 연결 리스트 확인.
for (const [next, nextDistance] of Lines[End]) {
// 다음 위치까지의 거리.
const newDistance = Cost + nextDistance;
// 만약 현재 거리 테이블 값보다 작다면.
if (newDistance < Weight[next - 1]) {
// 거리 테이블 갱신.
Weight[next - 1] = newDistance;
Queue.Insert([next, newDistance]);
}
}
}
return Weight;
};
const EachDistance = () => {
// 회사부터 최소 거리.
const FromCo = Dijkstra(s);
// 회사에서 a,b 까지의 최소거리
let min = Infinity;
// 합승 위치를 반복문으로 모두 확인.
for (let i = 0; i < FromCo.length; i++) {
// 만약 갈 수 없는 정점이라면 생략.
if (Lines[i + 1]) {
let total = 0;
// 합승한 위치부터 각각의 점까지의 최소거리.
let distance = Dijkstra(i + 1);
// 전체 택시 요금.
total += FromCo[i] + distance[a - 1] + distance[b - 1];
min = min > total ? total : min;
}
}
answer = min;
};
EachDistance();
return answer;
}
🧐 후기
처음 구현했을 때, 테스트 7,8번 때문에 너무 고생을 했던 문제였다.
다른 코드를 확인한 후에도 아무리 생각해도 전체적인 로직은 똑같은데 왜 통과를 못하는지 이해가 되지않았다.
그렇게 포기하고 하루 정도 생각할 시간을 가진 후에 다시 코드를 확인하니 코드 한줄을 더 적으면 효율성이 오를 것 같다는 생각을 하게 되어 추가하니 통과할 수 있었다.
