수강 과목
📚 문제 설명
이 문제는 2048 게임과 똑같다.
입력으로 N 과 N*N 크기의 보드가 주어진다. 이때 사용자는 상,하,좌,우 4방향으로 움직일 수 있고 움직일 경우 같은 숫자들은 합쳐진다.
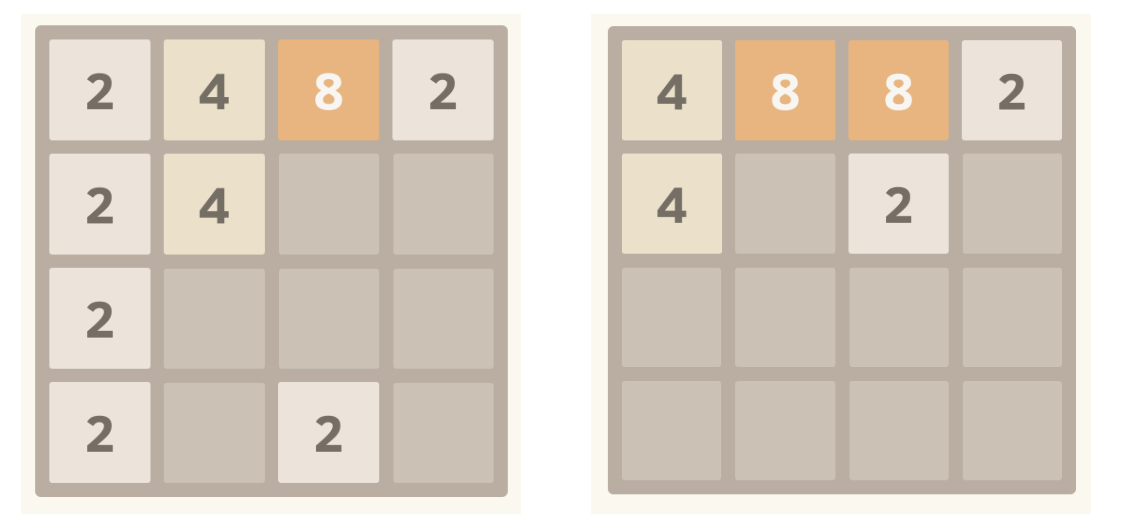
위의 그림은 왼쪽의 초기 상태에서 위로 움직이면 오른쪽 상태처럼 된다.
2-2-2-2에서 한번 합쳐져서4-4가 되면 다시 한번 운직이기 전에는 합쳐지면 안된다.
해당 게임에서 사용자가 최대 5번 움직일 때 최대로 만들 수 있는 숫자를 찾아라.
👨🏻💻 풀이 과정
조금씩 나눠서 생각을 했다.
- 배열을 주면 내부의 숫자를 압축해주는 함수.
- 상,하,좌,우로 움직이는 함수.
- 상,하,좌,우 5번 움직이는 모든 경우의 수를 찾는 함수.
- 전체 경우의 수에서 최댓값을 찾는 함수.
💡숫자를 압축하는 함수
상하좌우로 배열이 알아서 정렬되서 온다고 가정하자.
예를 들어 위로 움직인다고 하면 아래 보드에서 [[2, 0, 2], [2, 4, 8], [0, 0, 8]] 가 들어오는 것이다.
2 2 0
0 4 0
2 8 8그럼 이때 동일한 숫자 2개가 있으면 합쳐서 [[4], [2, 4, 8], [8]] 로 다시 전달하는 함수이다.
기본적인 로직은 스택을 이용했다고 생각하면 이해가 쉽다.
const compressArr = (arr) => {
return arr.map((row) => {
const newArr = []; // 스택
let merged = false; // 이미 합쳐진 결과로 나온 숫자의 경우 합쳐지면 안되기 때문에.
for (let i = 0; i < row.length; i++) {
if (row[i] === 0) continue; // 0이면 빈칸이기 때문에 생략.
if (newArr.length === 0) {
newArr.push(row[i]);
merged = false;
} else {
const last = newArr[newArr.length - 1];
if (!merged && last === row[i]) {
newArr[newArr.length - 1] = last * 2;
merged = true;
} else {
newArr.push(row[i]);
merged = false;
}
}
}
return newArr;
});
};💡상,하,좌,우 방향으로 움직이는 함수
각각의 함수의 전체적인 구조는 다음과 같다.
- 압축하고 싶은 방향의 배열을 만듬.
- 위에서 만든 배열을
compressArr()에 전달. compressArr()의 결과로 받은 배열을 이용해 새로운 보드를 만듬.- 만들어진 새로운 보드 리턴.
const moveUp = (boards) => {
const numArr = Array.from({length: N}, _ => []);
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (boards[i][j] !== 0) {
numArr[j].push(boards[i][j]);
}
}
}
const afterArr = compressArr(numArr);
let nextBoard = Array.from({length: N}, _ => Array(N).fill(0));
afterArr.forEach((arr, y) => {
arr.forEach((num, x) => {
nextBoard[x][y] = num;
})
});
return nextBoard;
};
const moveDown = (boards) => {
const numArr = Array.from({length: N}, _ => []);
for (let i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (let j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (boards[i][j] !== 0) {
numArr[j].push(boards[i][j]);
}
}
}
const afterArr = compressArr(numArr);
let nextBoard = Array.from({length: N}, _ => Array(N).fill(0));
afterArr.forEach((arr, y) => {
arr.forEach((num, x) => {
nextBoard[N - 1 - x][y] = num;
})
});
return nextBoard;
};
const moveLeft = (boards) => {
const afterArr = compressArr(boards);
let nextBoard = Array.from({length: N}, _ => Array(N).fill(0));
afterArr.forEach((arr, x) => {
arr.forEach((num, y) => {
nextBoard[x][y] = num;
})
});
return nextBoard;
};
const moveRight = (boards) => {
const afterArr = compressArr(boards.map(v => [...v].reverse()));
let nextBoard = Array.from({length: N}, _ => Array(N).fill(0));
afterArr.forEach((arr, x) => {
arr.forEach((num, y) => {
nextBoard[x][N - 1 - y] = num;
})
});
return nextBoard;
};💡조합 함수 & 메인 함수
// 0: 상, 1: 하, 2: 좌, 3: 우
const combination = (arr, result) => {
if (arr.length === 5) {
result.push(arr);
return;
}
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
combination([...arr, i], result);
}
};
const solution = () => {
const everyCombinations = [];
combination([], everyCombinations);
let max = 0;
everyCombinations.forEach((actions) => {
let tmpBoards = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(boards));
actions.forEach(action => {
if (action === 0) {
tmpBoards = moveUp(tmpBoards);
}
if (action === 1) {
tmpBoards = moveDown(tmpBoards);
}
if (action === 2) {
tmpBoards = moveLeft(tmpBoards);
}
if (action === 3) {
tmpBoards = moveRight(tmpBoards);
}
});
max = Math.max(...tmpBoards.flat(), max);
});
console.log(max);
};💡전체 코드
let input = require("fs").readFileSync(0, 'utf-8').toString().trim().split("\n");
const N = Number(input.shift());
let boards = input.map(v => v.split(' ').map(Number));
const compressArr = (arr) => {
return arr.map((row) => {
const newArr = [];
let merged = false;
for (let i = 0; i < row.length; i++) {
if (row[i] === 0) continue;
if (newArr.length === 0) {
newArr.push(row[i]);
merged = false;
} else {
const last = newArr[newArr.length - 1];
if (!merged && last === row[i]) {
newArr[newArr.length - 1] = last * 2;
merged = true;
} else {
newArr.push(row[i]);
merged = false;
}
}
}
return newArr;
});
};
const moveUp = (boards) => {
const numArr = Array.from({length: N}, _ => []);
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (boards[i][j] !== 0) {
numArr[j].push(boards[i][j]);
}
}
}
const afterArr = compressArr(numArr);
let nextBoard = Array.from({length: N}, _ => Array(N).fill(0));
afterArr.forEach((arr, y) => {
arr.forEach((num, x) => {
nextBoard[x][y] = num;
})
});
return nextBoard;
};
const moveDown = (boards) => {
const numArr = Array.from({length: N}, _ => []);
for (let i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (let j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (boards[i][j] !== 0) {
numArr[j].push(boards[i][j]);
}
}
}
const afterArr = compressArr(numArr);
let nextBoard = Array.from({length: N}, _ => Array(N).fill(0));
afterArr.forEach((arr, y) => {
arr.forEach((num, x) => {
nextBoard[N - 1 - x][y] = num;
})
});
return nextBoard;
};
const moveLeft = (boards) => {
const afterArr = compressArr(boards);
let nextBoard = Array.from({length: N}, _ => Array(N).fill(0));
afterArr.forEach((arr, x) => {
arr.forEach((num, y) => {
nextBoard[x][y] = num;
})
});
return nextBoard;
};
const moveRight = (boards) => {
// 각 행을 복사해서 reverse
const afterArr = compressArr(boards.map(v => [...v].reverse()));
let nextBoard = Array.from({length: N}, _ => Array(N).fill(0));
afterArr.forEach((arr, x) => {
arr.forEach((num, y) => {
nextBoard[x][N - 1 - y] = num;
})
});
return nextBoard;
};
// 0: 상, 1: 하, 2: 좌, 3: 우
const combination = (arr, result) => {
if (arr.length === 5) {
result.push(arr);
return;
}
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
combination([...arr, i], result);
}
};
const solution = () => {
const everyCombinations = [];
combination([], everyCombinations);
let max = 0;
everyCombinations.forEach((actions) => {
let tmpBoards = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(boards));
actions.forEach(action => {
if (action === 0) {
tmpBoards = moveUp(tmpBoards);
}
if (action === 1) {
tmpBoards = moveDown(tmpBoards);
}
if (action === 2) {
tmpBoards = moveLeft(tmpBoards);
}
if (action === 3) {
tmpBoards = moveRight(tmpBoards);
}
});
max = Math.max(...tmpBoards.flat(), max);
});
console.log(max);
};
solution();🧐 후기
전체 로직을 생각하는 것에는 시간이 오래 걸리지 않았다.
하지만 compressArr()를 생성하며 merged 라는 플레그를 만들지 않아서 반례가 생겨서 해당 부분을 찾는데 시간이 걸렸다.
