문제 링크
문제 설명
N개의 강의가 주어지고 해당 강의들의 시작 시간 , 종료 시간이 주어진다.
이 떄 필요한 강의실 갯수의 최소 갯수를 구하는 문제이다.
예를 들어
A강의가 1에 시작 3에 종료
B강의가 2에 시작 3에 종료
C강의가 3에 시작 5에 종료
일 경우 C강의는 A강의나 B강의가 종료한 후에 해당 강의실에서 진행하면 되기 때문에 강의실은 최소 2개가 필요하다.
풀이 과정
- 강의의 시작 시작 순서로 정렬
- 그 후 해당 순서대로 우선 순위 큐에 삽입
- 해당 우선 순위 큐는 끝나는 시간을 기준으로 최상단에는 강의 끝나는 시간이 제일 빠른 아이템이 있음
- 우선 순위 큐에 삽이 전 가장 빨리 끝나는 시간의 강의와 이제 삽입할 강의의 시작 시간을 비교
- 시작 시간이 더 크거나 같을 경우 우선순위 큐 최상단을 제거
- 시작 시간이 더 작을 경우 우선 순위 큐에 해당 강의의 종료 시간 삽입
- 우선 순위 큐의 길이가 강의실에 갯수
아래 과정을 보면 더 이해하기 편할 것이다.
정렬 했을 때 강의
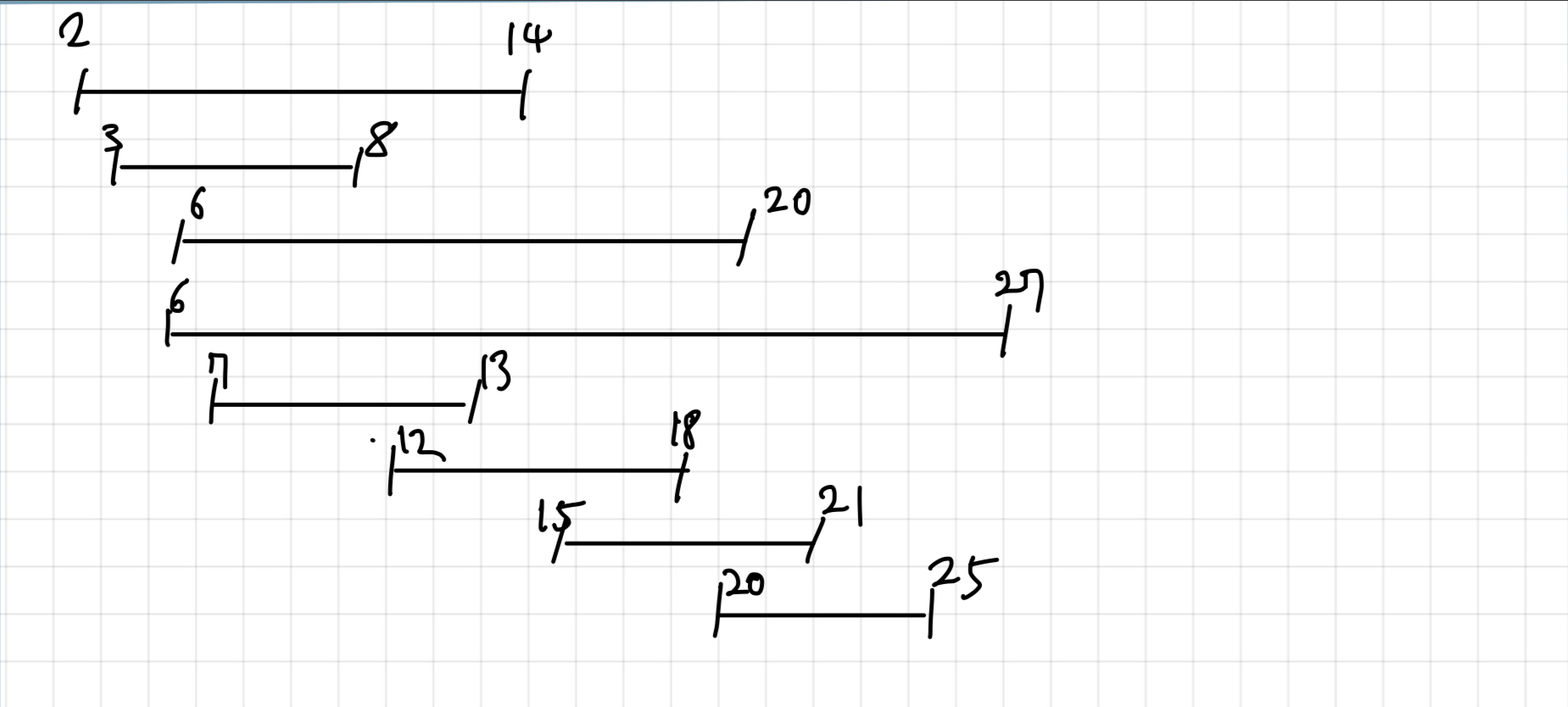
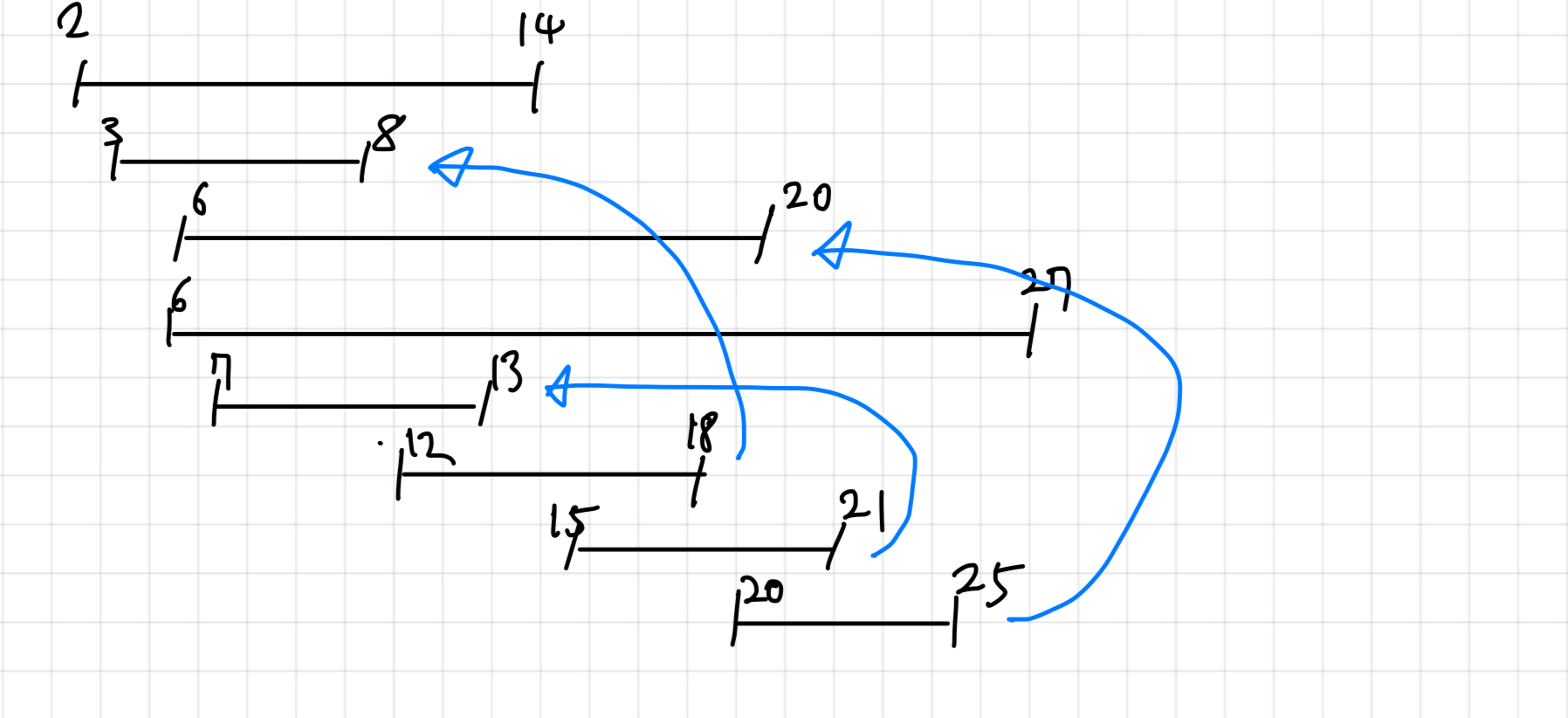
가장 빨리 끝나는 강의실을 빨리 시작하는 강의 순서대로 그 자리에
JavaScript Priority Queue
자바 스크립트에서는 우선 순위 큐를 지원하지 않는다.
따라서 해당 코드를 직접 구현해야 하는데 이는 두가지 방식으로 구현 가능하다.
- 일반 배열을 이용
- 힙을 이용
각각의 방식으로 구현한 우선순위 큐는 다음과 같다.
배열을 이용한 방식
class PRIORITY_QUEUE {
constructor() {
this.queue = [];
}
insert(element) {
if (this.queue.length) {
// 반복문을 이용하여 배열 전체를 돌며 비교하며, 적절한 자리에 삽입
for (let i = 0; i < this.queue.length; i++) {
if (this.queue[i] > element) {
this.queue.splice(i, 0, element);
return;
}
}
}
this.queue.push(element);
}
getQue() {
return this.queue;
}
delete() {
this.queue.shift();
}
getSize(){
return this.queue.length;
}
getTop(){
return this.queue[0];
}
}힙을 이용하여 구현한 코드를 보기 전에 트리 구조를 유념하며 보면 이해가 더 빠를 것이다.
힙을 이용한 방식
class MinHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [null];
}
insert(item) {
// 가장 마지막 노드부터 비교하며 위치를 찾는 방식
let current = this.heap.length;
while (current > 1) {
const parent = Math.floor(current / 2);
if (this.heap[parent] > item) {
this.heap[current] = this.heap[parent];
current = parent;
} else break;
}
this.heap[current] = item;
}
remove() {
let min = this.heap[1];
if (this.heap.length > 2) {
// 힙의 최상단을 제거
this.heap[1] = this.heap[this.heap.length - 1];
this.heap.splice(this.heap.length - 1);
// 최상단부터 비교
let current = 1;
let leftChild = current * 2;
let rightChild = current * 2 + 1;
// 트리 구조이기 때문에 왼쪽 자식이 없을 때까지 확인하면 됨
while (this.heap[leftChild]) {
let CompareItem = leftChild;
if (this.heap[rightChild] && this.heap[CompareItem] > this.heap[rightChild]) {
CompareItem = rightChild;
}
// 구조 분해 할당을 이용한 값 교체
if (this.heap[current] > this.heap[CompareItem]) {
[this.heap[current], this.heap[CompareItem]] = [this.heap[CompareItem], this.heap[current]];
current = CompareItem;
} else break;
leftChild = current * 2;
rightChild = current * 2 + 1;
}
} else if (this.heap.length === 2) {
this.heap.splice(1, 1);
} else {
return null;
}
return min;
}
getMin() {
return this.heap[1];
}
getHeap() {
return this.heap;
}
getSize() {
return this.heap.length - 1;
}
}해당 문제에서는 힙 방식으로 한 풀이가 정답이다. 그 이유는 시간복잡도에서 차이를 보이기 때문이다.
배열을 이용한 방식의 경우는 결국 모든 배열은 확인해야 하기 때문에 O(n)이 된다.
그러나 힙을 이용한 방식의 경우 삭제를 할 때 확인을 하면 분할 정복과 유사한 것을 확인할 수 있다.
자식으로 내려가서 다 작은 노드를 찾고 그 아래로 내려가기 때문이다.
따라서 힙 방식의 경우 O(log n) 이라고 볼 수 있다.
이제 전체 코드 흐름은 다음과 같다.
- 강의를 시작순으로 정렬
- 시작 시간이 같은 경우 끝나는 시간을 보고 정렬
- 우선순위큐에 첫번째 강의 먼저 삽입
- 그 후 우선 순위 큐에 있는 끝나는 시간과 정렬한 강의의 시작 시간을 비교
- 강의 시작 시간 < 우선 순위큐 상단
- 우선 순위 큐에 해당 강의의 종료 시간 삽입
- 강의 시작 시간 >= 우선 순위큐 상단
- 우선순위 큐 최상단을 제거
- 강의 시작 시간 < 우선 순위큐 상단
전체 코드
let N = input.shift();
input = input.map(v => v.split(' ').map(Number)).sort((a, b) => {
if (a[1] === b[1]) {
return a[2] - b[2];
}
return a[1] - b[1];
});
class MinHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [null];
}
insert(item){
let current = this.heap.length;
while (current > 1) {
const parent = Math.floor(current / 2);
if (this.heap[parent] > item) {
this.heap[current] = this.heap[parent];
current = parent;
}else break;
}
this.heap[current] = item;
}
remove() {
let min = this.heap[1];
if (this.heap.length > 2) {
this.heap[1] = this.heap[this.heap.length - 1];
this.heap.splice(this.heap.length - 1);
let current = 1;
let leftChild = current * 2;
let rightChild = current * 2 + 1;
while (this.heap[leftChild]) {
let CompareItem = leftChild;
if (this.heap[rightChild] && this.heap[CompareItem] > this.heap[rightChild]) {
CompareItem = rightChild;
}
if (this.heap[current] > this.heap[CompareItem]) {
[this.heap[current], this.heap[CompareItem]] = [this.heap[CompareItem], this.heap[current]];
current = CompareItem;
}else break;
leftChild = current * 2;
rightChild = current * 2 + 1;
}
}else if (this.heap.length === 2) {
this.heap.splice(1, 1);
} else {
return null;
}
return min;
}
getMin() {
return this.heap[1];
}
getHeap(){
return this.heap;
}
getSize(){
return this.heap.length - 1;
}
}
function CHECK_BOUNDERY(INPUT) {
let Priority_Queue = new MinHeap();
Priority_Queue.insert(INPUT[0][2]);
if (INPUT.length === 1) return 1;
for (let i = 1; i < INPUT.length; i++) {
if (INPUT[i][1] < Priority_Queue.getMin()) {
Priority_Queue.insert(INPUT[i][2]);
}else{
Priority_Queue.remove();
Priority_Queue.insert(INPUT[i][2]);
}
}
return Priority_Queue.getSize();
}
console.log(CHECK_BOUNDERY(input));
후기
JavaScript는 우선순위큐 라이브러리를 제공하지 않아서 직접 구현을 해야해서 많이 힘들었다.
그러나 이번 기회에 우선순위큐를 확실히 공부할 수 있었던 것 같아서 매우 의미 있었다.
