- Dynamic Programming Patterns
Fibonacci
function fibonacci(n: number) {
let a = 0,
b = 1,
c = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a = b;
b = c;
c = a + b;
}
return b;
}1. Climbing Stairs (LeetCode #70)
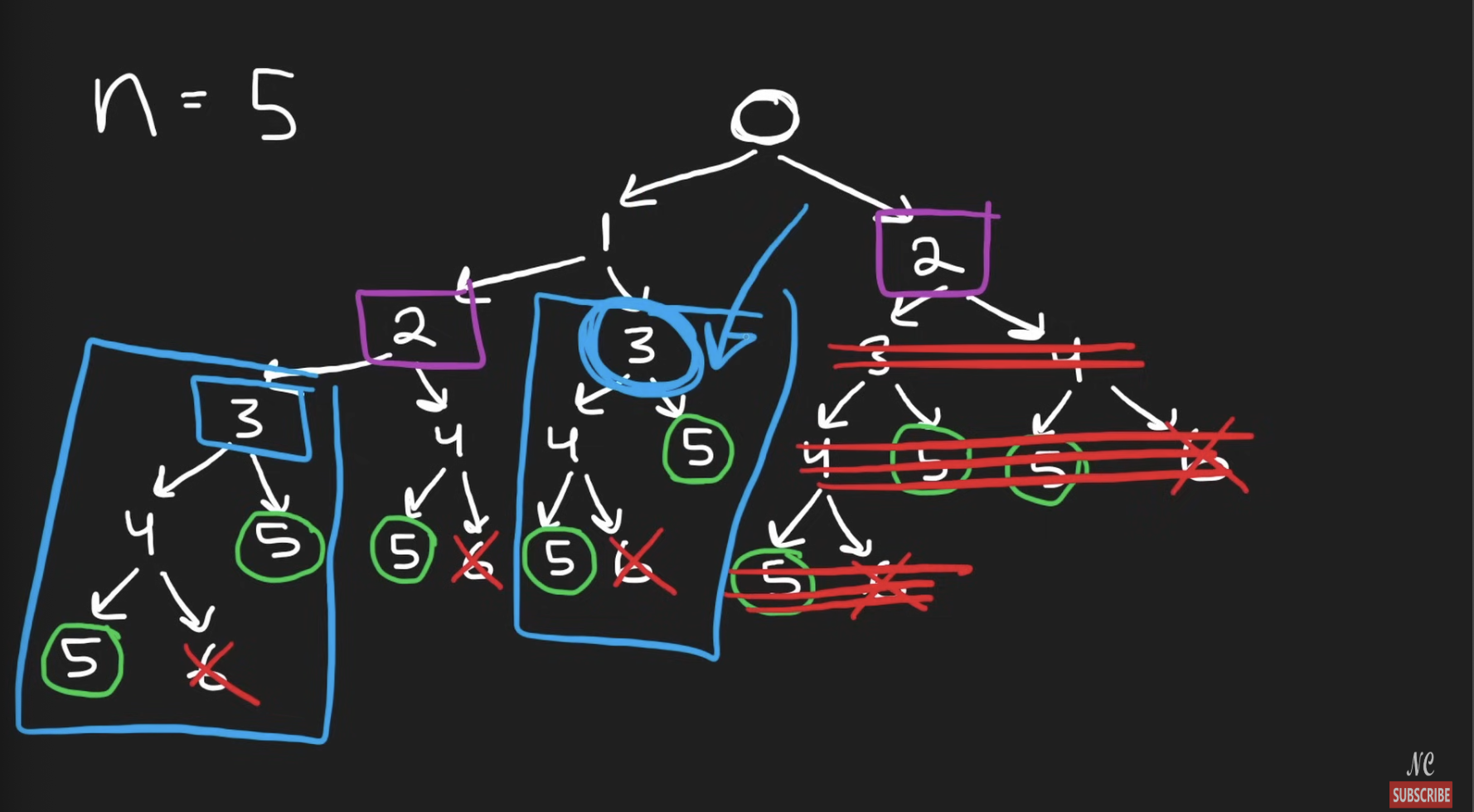
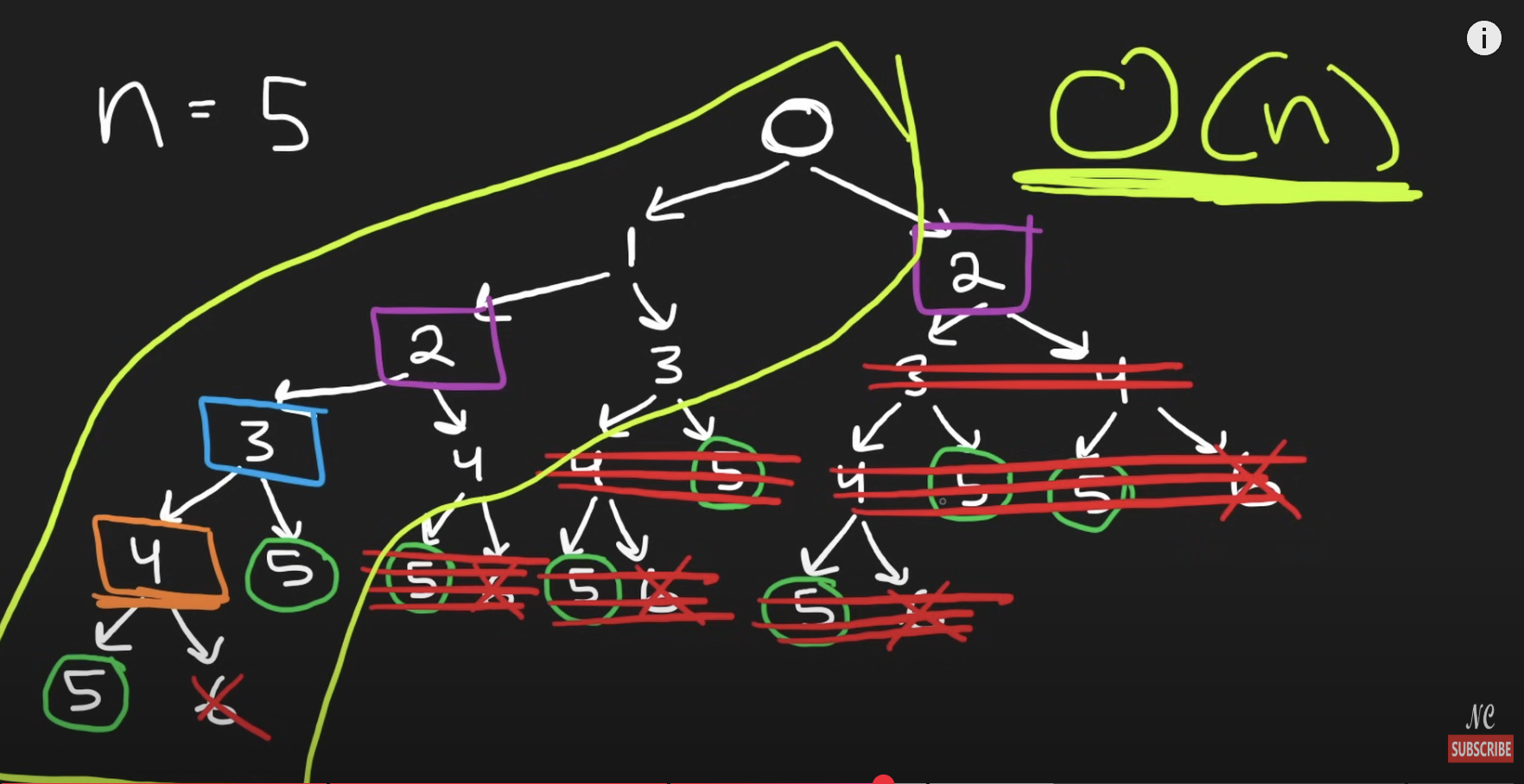
Find a same part and do memoization(cache)
// TOP - DOWN WITH Memoization
helper(5)
├─ helper(4)
│ ├─ helper(3)
│ │ ├─ helper(2)
│ │ │ ├─ helper(1)
│ │ │ └─ helper(0)
│ │ └─ helper(1)
│ └─ helper(2) ← 여기서 이미 memo[2]가 계산되어 있음
└─ helper(3) ← 여기서도 memo[3] 사용
helper(i - 1)이 선행되며, 필요한 모든 i - k 결과들을 미리 메모이제이션 함
그 결과, helper(i - 2)는 이미 계산된 결과를 재사용
이것이 Top-Down with Memoization의 핵심
// TOP - DOWN WITH Memoization
export function climbStairsMemo(n: number): number {
if (n <= 1) return 1;
const memo: number[] = Array(n + 1).fill(-1);
function helper(i: number) {
if (i <= 2) return i; // Base case: if n is 1 or 2, return n directly
if (memo[i] !== -1) {
return memo[i];
}
memo[i] = helper(i - 1) + helper(i - 2);
return memo[i];
}
return helper(n);
}// Bottom-Up
function climbStairs(n) {
if (n <= 1) return 1;
const dp = new Array(n + 1);
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for (let i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
}
return dp[n];
}Simpler version : Space(1)
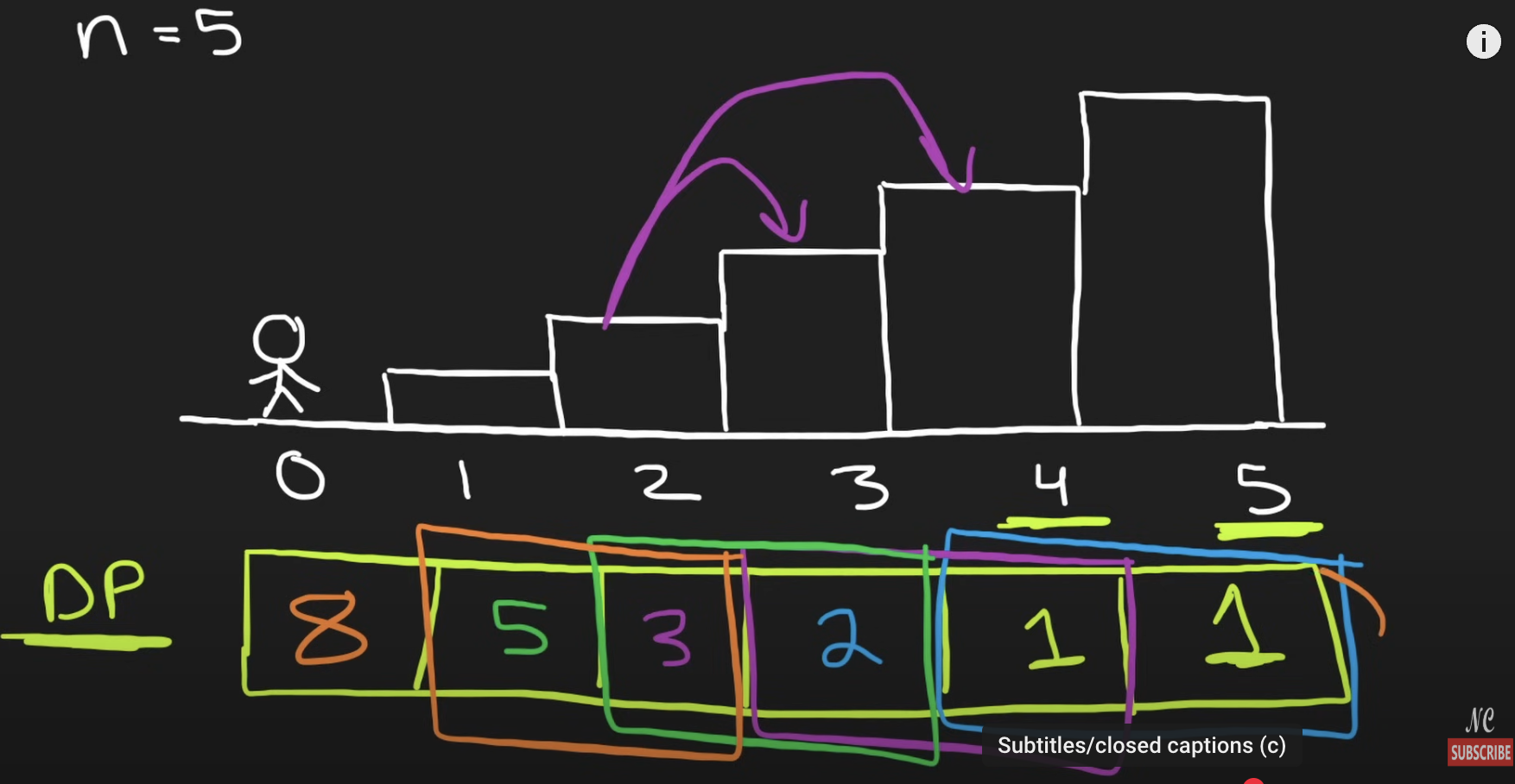
// dp like Memoization = cached
// dp: Bottom-up
// Space Optimization
function climbStairs(n: number): number {
let one = 1,
two = 1;
for (let i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
let temp = one;
one = one + two;
two = temp;
}
return one;
}2. House Robber (LeetCode #198)
function rob(nums: number[]): number {
let rob1 = 0,
rob2 = 0;
// [rob1, rob2, n, n+1 ,...]
for (const money of nums) {
let newMaxRob = Math.max(money + rob1, rob2);
rob1 = rob2;
rob2 = newMaxRob;
}
return rob2;
}3. Coin Change (LeetCode #322)
input : [1,2,5]
amount : 11
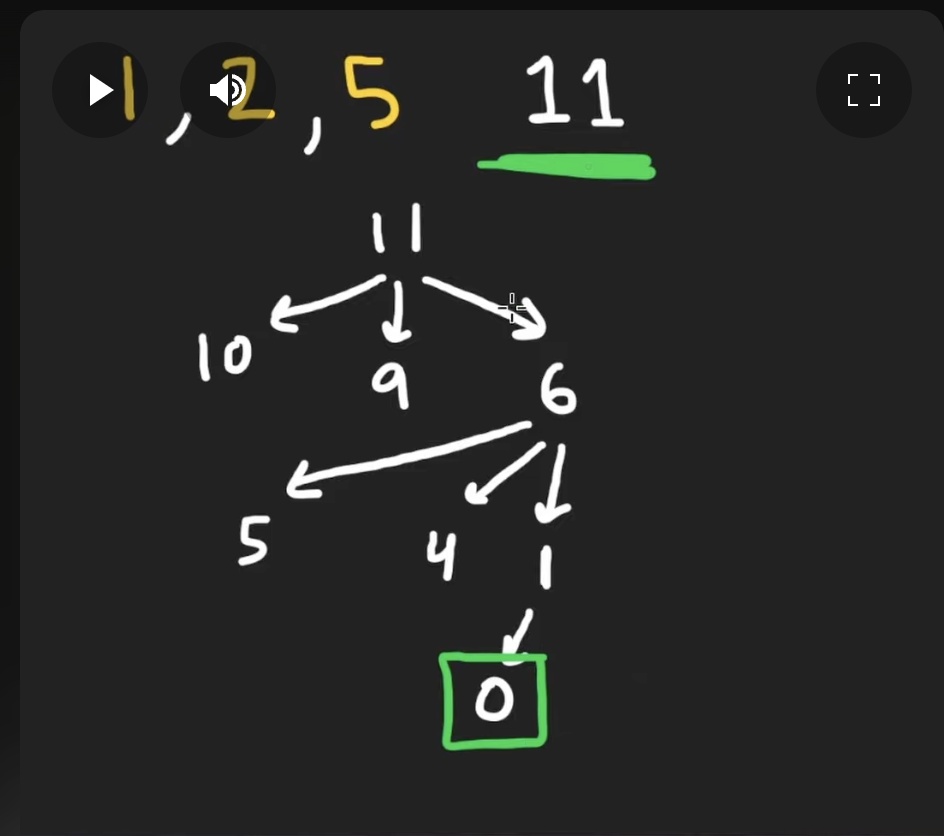
DP
// DP (bottom-up)
function coinChange(coins: number[], amount: number): number {
const dp: number[] = new Array(amount + 1).fill(Infinity);
dp[0] = 0;
for(const coin of coins){
for(let money = coin; money <= amount; money++){
dp[money] = Math.min(dp[money], dp[money - coin] + 1);
}
}
return dp[amount] === Infinity ? -1 : dp[amount]
}
BFS
// BFS
function coinChange(coins: number[], amount: number): number {
if(amount === 0) return 0;
const queue : number[] = [amount] ;
const visited : Set<number> = new Set();
let numberOfCoins = 0;
while(queue.length > 0){
let size = queue.length;
numberOfCoins++;
while(size > 0){
size--;
const remaining = queue.shift()!;
for(const coin of coins){
const newRemaining = remaining - coin;
if(newRemaining === 0) return numberOfCoins;
if(newRemaining > 0 && !visited.has(newRemaining)){
visited.add(newRemaining);
queue.push(newRemaining);
}
}
}
}
return -1;
};4. Longest Common Subsequence (LCS) (LeetCode #1143)
// bottom-up DP = Top Down DP (Memoization)
// Time: O(m n)
// Space: O(m n)
// from end of string to start of string
export function longestCommonSubsequence(text1: string, text2: string): number {
const m = text1.length,
n = text2.length;
const dp: number[][] = Array.from({ length: m + 1 }, () =>
Array(n + 1).fill(0)
);
for (let i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (let j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (text1[i] === text2[j]) {
dp[i][j] = 1 + dp[i + 1][j + 1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j + 1], dp[i + 1][j]);
}
}
}
return dp[0][0];
}
// from start of string to end of string
export function longestCommonSubsequence2(
text1: string,
text2: string
): number {
const m = text1.length,
n = text2.length;
const memo = Array.from({ length: m }, () => Array(n).fill(-1));
function longest(i: number, j: number): number {
if (i === m || j === n) return 0;
if (memo[i][j] !== -1) return memo[i][j];
if (text1[i] === text2[j]) {
return (memo[i][j] = 1 + longest(i + 1, j + 1));
}
return (memo[i][j] = Math.max(longest(i, j + 1), longest(i + 1, j)));
}
return longest(0, 0);
}Without DP Memoization
// Time Limit Exceeded
export function longestCommonSubsequenceTLE(
text1: string,
text2: string
): number {
let m = text1.length,
n = text2.length;
function longest(i: number, j: number): number {
if (i === m || j === n) return 0;
if (text1[i] === text2[j]) return 1 + longest(i + 1, j + 1);
return Math.max(longest(i, j + 1), longest(i + 1, j));
}
return longest(0, 0);
}
5. Longest Increasing Subsequence (LIS) (LeetCode #322)
// 1 Top-down
// 2 Bottom-up
// 3 Binary Search
/**
* Complexity
Time complexity:
topDownSolution: O(n2) (due to recursive calls and memoization)
bottomUpSolution: O(n2) (nested loops for each pair of elements)
binarySearchSolution: O(nlogn) (binary search for each element)
Space complexity:
topDownSolution: O(n) (for the memo array and recursion stack)
bottomUpSolution: O(n) (for the memo array)
binarySearchSolution: O(l), where l is the length of the LIS (in the worst case, l=n)
**/
export function lengthOfLIS(nums: number[]): number {
return topDownSolution(nums);
// return bottomUpSolution(nums);
// return binarySearchSolution(nums);
}
// TLE(Time Limit Exceeded)
const binarySearchSolution = (nums: number[]): number => {
const memo: number[] = [];
for (const num of nums) {
let left = 0,
right = memo.length;
while (left < right) {
const mid = Math.floor((left + right) / 2);
if (memo[mid] < num) {
console.log(memo, mid, left, right);
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
if (left < memo.length) {
memo[left] = num;
} else {
memo.push(num);
}
}
return memo.length;
};
const bottomUpSolution = (nums: number[]): number => {
const memo: number[] = [];
let max = 1;
memo[nums.length - 1] = 1;
for (let right = nums.length - 2; right >= 0; right--) {
let maxSequence = 0;
for (let left = right; left < nums.length; left++) {
if (nums[right] < nums[left]) {
maxSequence = Math.max(maxSequence, memo[left]);
}
memo[right] = 1 + maxSequence;
max = Math.max(max, memo[right]);
}
}
return max;
};
const topDownSolution = (nums: number[]): number => {
const memo: number[] = [];
function LISByIndex(index: number): number {
if (!memo[index]) {
let maxSize = 1;
for (let i = index + 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[index] < nums[i]) {
const size = 1 + LISByIndex(i);
maxSize = Math.max(maxSize, size);
}
}
memo[index] = maxSize;
}
return memo[index];
}
let maxSize = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
const size = LISByIndex(i);
maxSize = Math.max(maxSize, size);
}
return maxSize;
};
