[Algorithm] 4. Fast & Slow Pointers(Linked List)
- Fast & Slow Pointers(Linked List)
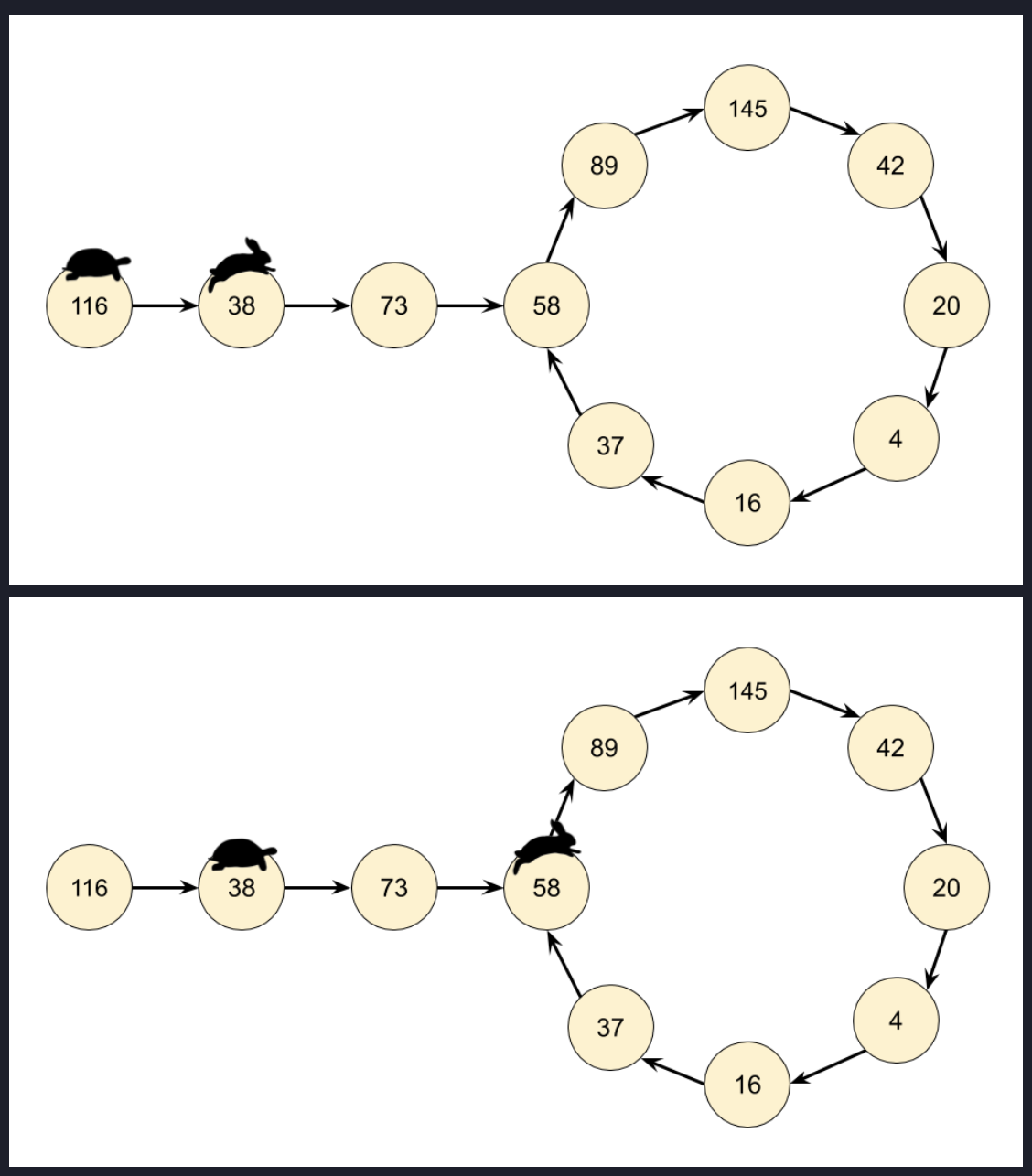
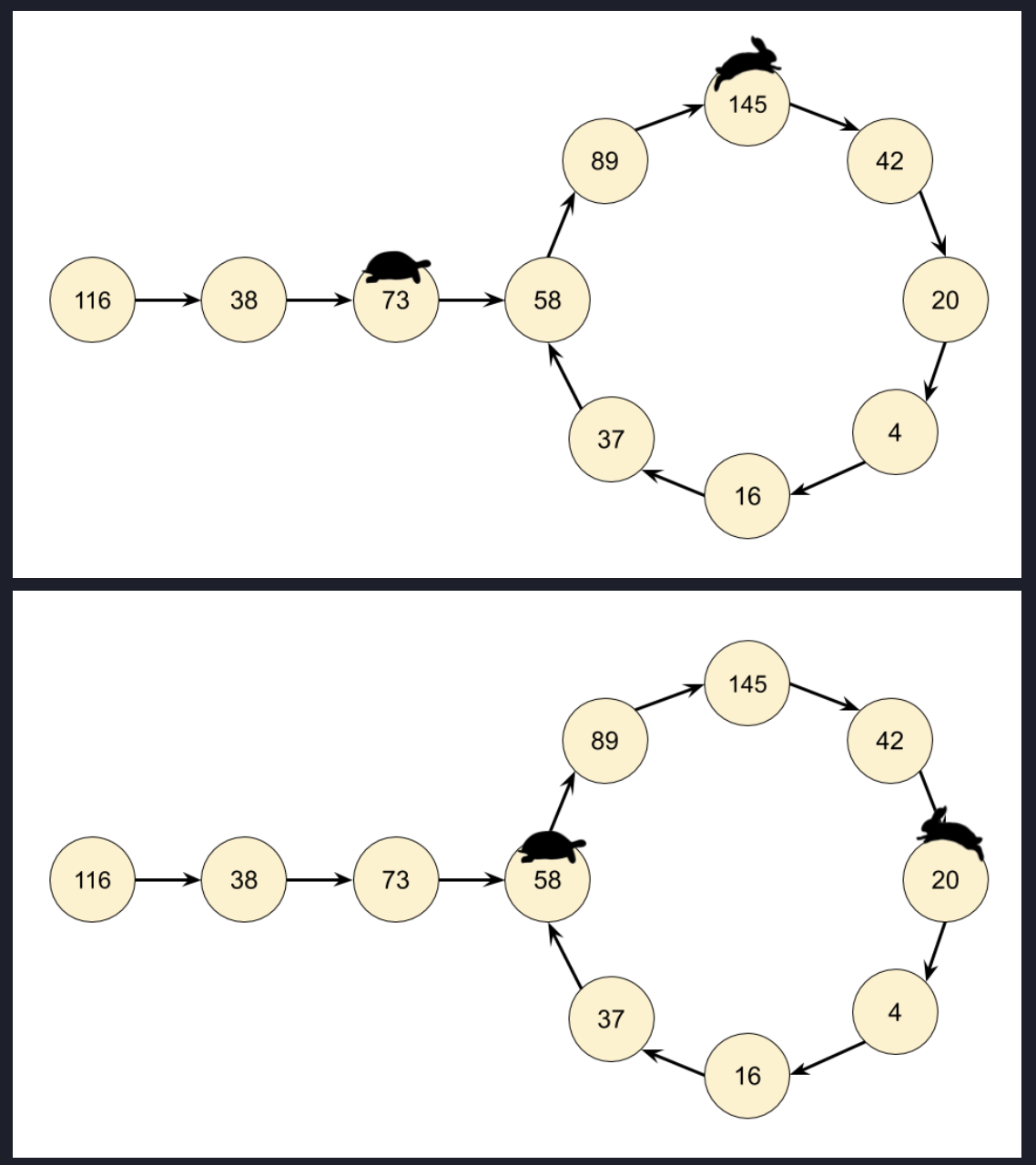
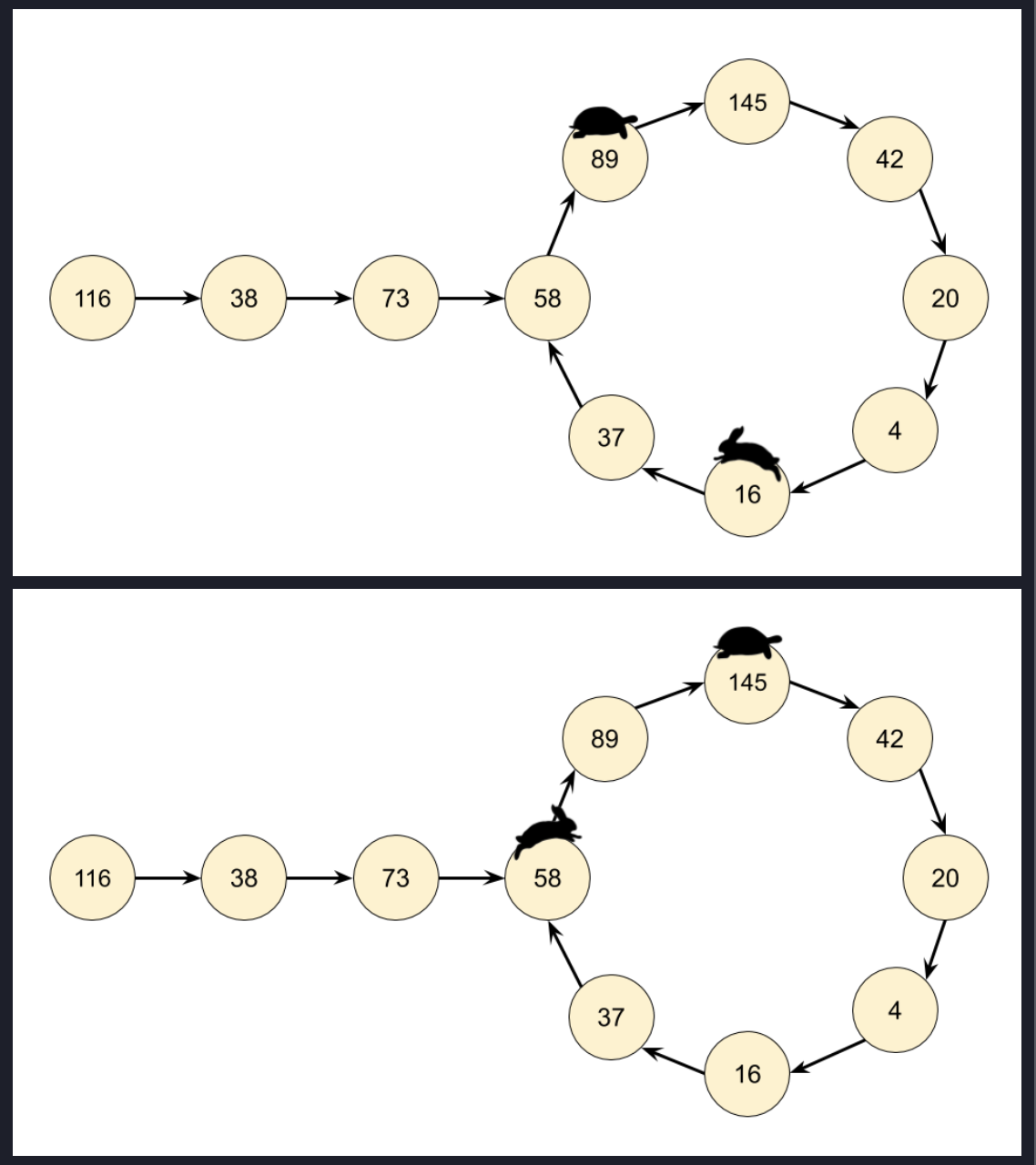
Floyd's tortoise and hare algorithm.
Cycle Detection: The fast and slow pointers will eventually meet inside the cycle if there is one. The slow pointer moves one step at a time, while the fast pointer moves two steps at a time.
Cycle Start: After detecting the cycle (when slow and fast meet),
reset the slow pointer to the head of the list and keep the fast pointer at the point where they met.
Then, move both pointers one step at a time. The point where they meet again will be the start of the cycle.
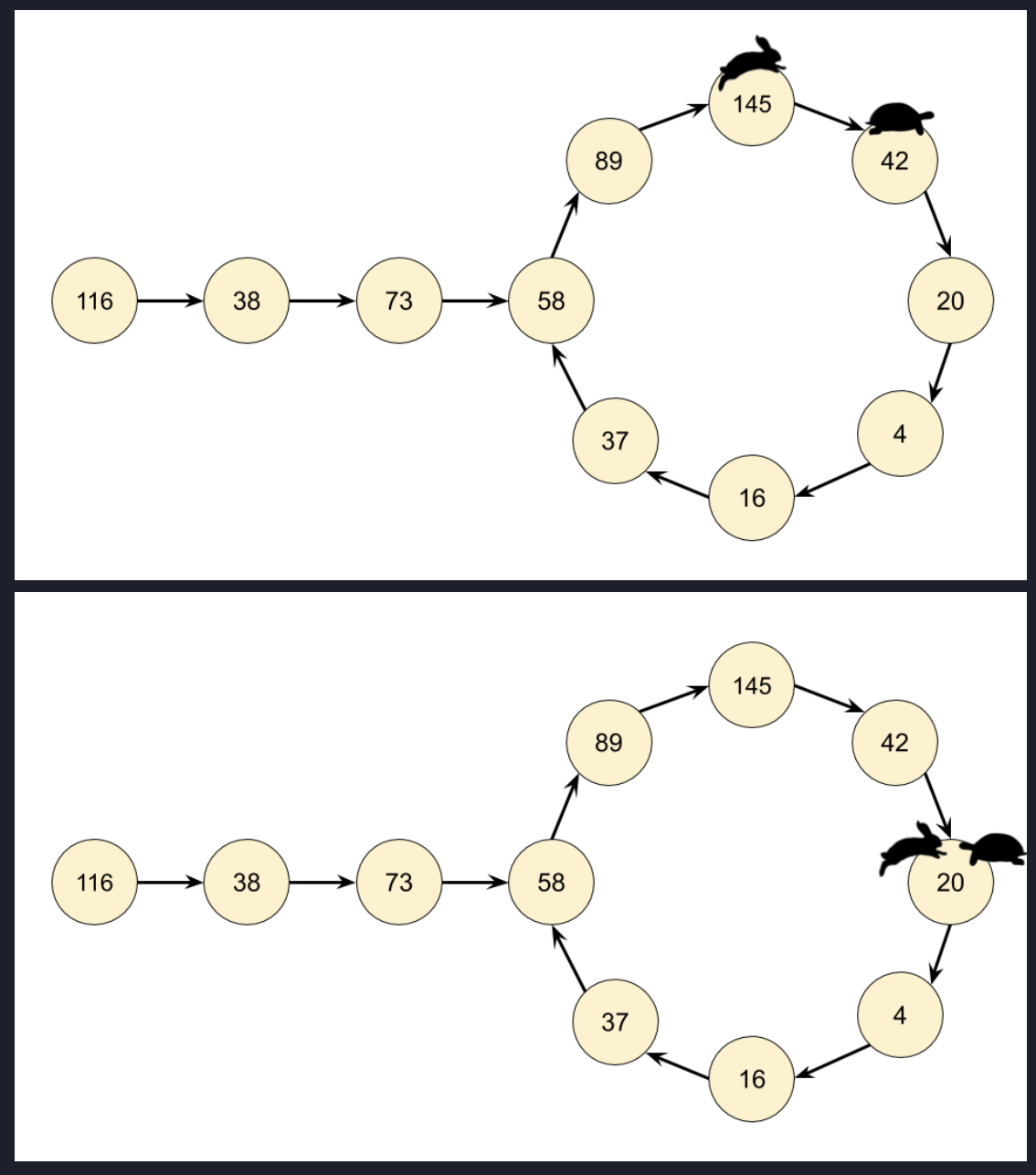
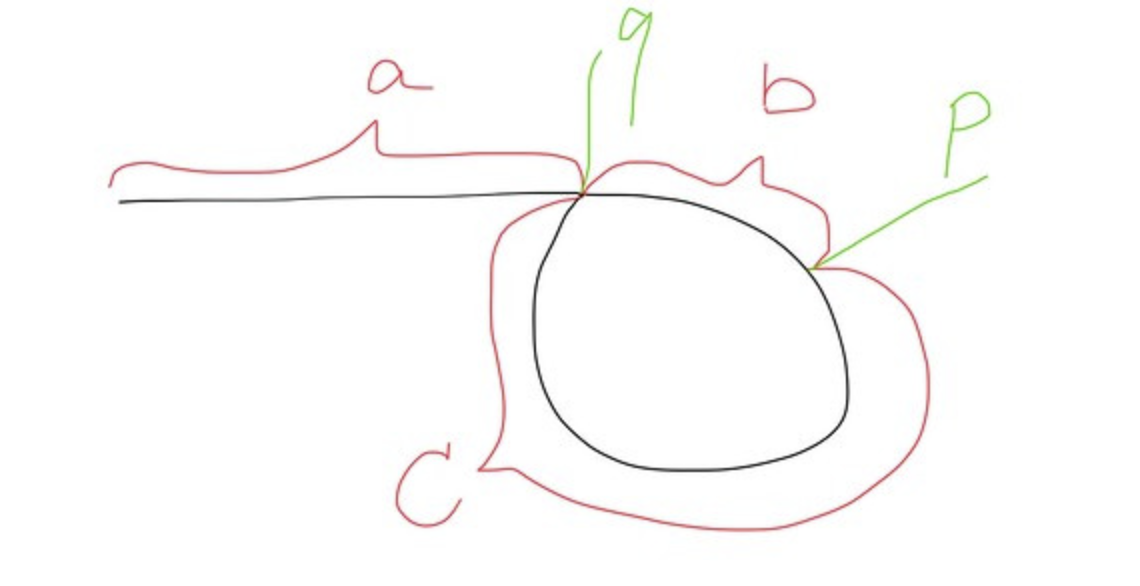
플로이드의 순환 탐색 알고리즘(Floyd's cycle detection algorithm)을 이용한 방법입니다.
fast와 slow 포인터가 점 p에서 만날 때 그들이 달린 길이는 'a+2b+c'와 'a+b'이고 fast가 2배 빠르게 이동하기 때문에 a+2b+c == 2(a+b)가 됩니다. 최종적으로 우리는 'a==c'를 얻을 수 있습니다.
slow포인터와 fast 포인터를 이동하면서 최초 만나는지점 p를 찾아냅니다.
slow포인터를 head 로 위치시킵니다.
slow포인터와 fast포인터를 동시에 한칸씩 전진하며 만나는지점 q를 찾아 반환합니다.
시간 복잡도 : O(N)
공간 복잡도 : O(1)
Usage : Detect cycles
Q1.Linked List Cycle (LeetCode #141)
using Hare and Tortoise Algoritm.
Q2.Happy Number (LeetCode #202)
Floyd's Tortoise And Hare
function isHappy (n: number): boolean {
let slow = n , fast = getNext(n) ;
function getNext (nn: number) {
let sum = 0;
while(nn !== 0){
const digit = nn % 10 ;
nn = Math.floor(nn / 10);
sum += digit * digit;
}
return sum;
}
while(fast !== 1 && slow !== fast ){
fast = getNext(getNext(fast));
slow = getNext(slow);
}
return fast === 1;
}Reduce
function isHappy(n: number): boolean {
let sum = n;
const seen = new Set<number>();
while (sum !== 1) {
if(seen.has(sum)){return false;}
seen.add(sum);
sum = sum.toString().split("").reduce((acc, n) => {
return acc + (Number(n) ** 2);
}, 0)
}
return true;
};Q3.Find the Duplicate Number (LeetCode #287)
Making Linked List
class ListNode {
constructor(val = 0, next = null) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
let node11 = new ListNode(11);
let node10 = new ListNode(10, node11);
let node9 = new ListNode(9, node10);
let node8 = new ListNode(8, node9);
let node7 = new ListNode(7, node8);
let node6 = new ListNode(6, node7);
let node5 = new ListNode(5, node6);
let node4 = new ListNode(4, node5);
let node3 = new ListNode(3, node4);
let node2 = new ListNode(2, node3);
let node1 = new ListNode(1, node2);
// Create a cycle: Node 10 points back to node 7
node11.next = node7;
// with Loop
// Create nodes dynamically
const nodes = [];
for (let i = 1; i <= 11; i++) {
nodes.push(new ListNode(i));
}
// Link the nodes together
for (let i = 0; i < nodes.length - 1; i++) {
nodes[i].next = nodes[i + 1];
}
const head = nodes[0]
// Create a cycle: Node 11 points back to node 7
nodes[10].next = nodes[6]; // node11.next = node7function makeLinkedList
class ListNode {
constructor(val = 0, next = null) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
const makeLinkedList = (length) => {
// with Loop
// Create nodes dynamically
const nodes = [];
for (let i = 1; i <= length; i++) {
nodes.push(new ListNode(i));
}
// Link the nodes together
for (let i = 0; i < nodes.length - 1; i++) {
nodes[i].next = nodes[i + 1];
}
return nodes[0]
}
let head = makeLinkedList(5);