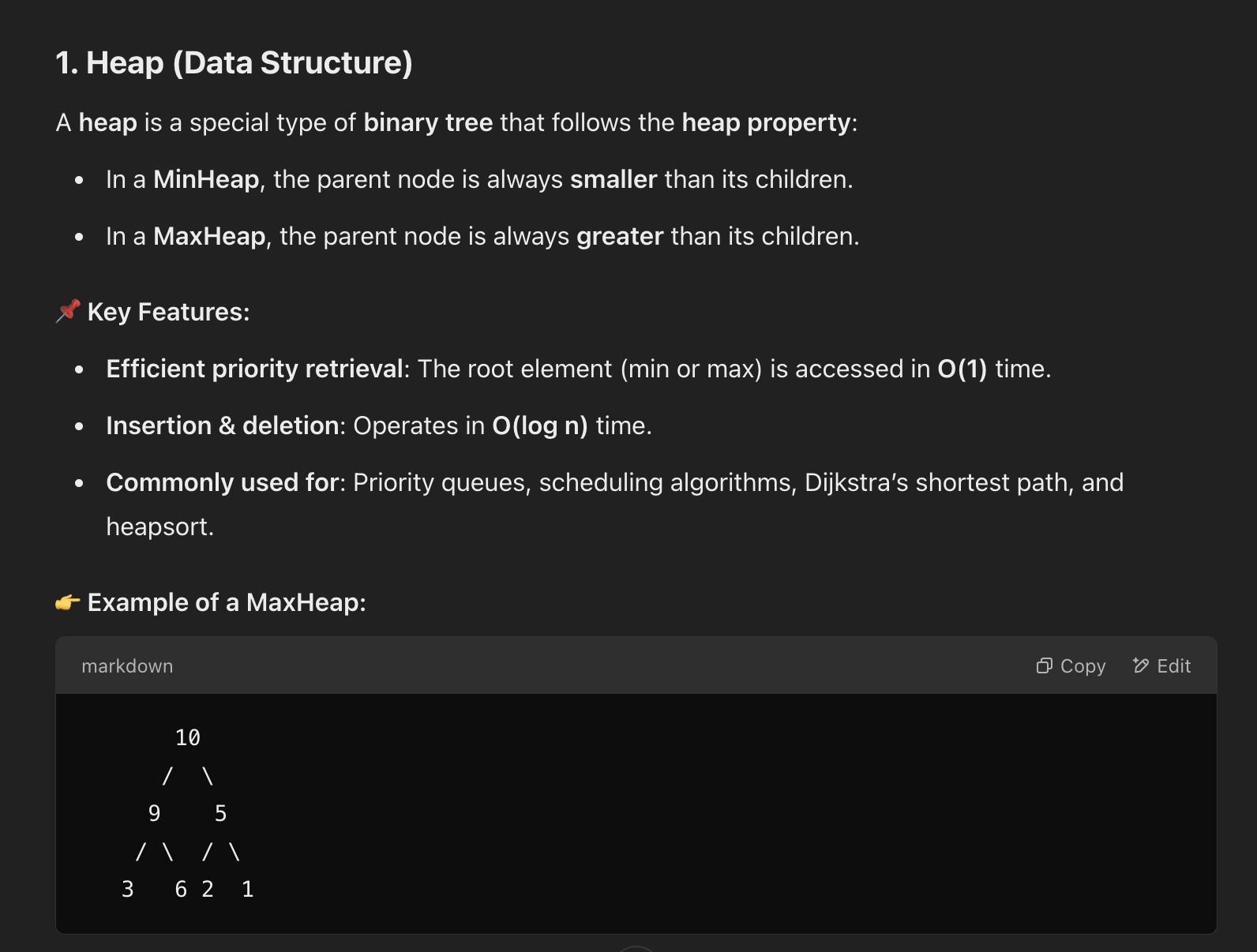
7.Top ‘K’ Elements With Heap
Why using heap?
To find largest or smallest element or stream of data using heaps or sorting.
find kth element => heap[0] element is largest or smallest
heap.pop() k time would find kth largest or smallest element.
[3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6, 5, 3, 5]
-> [9, 6, 4, 5, 5,3, 2, 1, 1, 3,3] //_**not like sorted **_
9
/ \
6 4
/ \ / \
5 5 3 2
/ \ /
1 1 3
/
5*heap?
Finding a index of Parent or Child node
- parent to child
left child index : parentIdx x 2 + 1
right child index : parentIdx x 2 + 2
- child to parent
parent index : Math.floor((childIndex - 1) / 2)
Time Complexity of JavaScript sort():
Best Case (already sorted array):
Timsort: O(n)
QuickSort (if used): O(n log n)
Average Case (random array):
Timsort: O(n log n)
QuickSort (if used): O(n log n)
Worst Case (reverse sorted or difficult cases):
Timsort: O(n log n)
QuickSort (if used): O(n^2)
1. Kth Largest Element in an Array (LeetCode #215)
Using min-heap
function findKthLargest(nums: number[], k: number): number {
const heap = nums.slice(0, k);
// min-heap
function heapify (_heap: number[], idx: number) {
let minIdx = idx;
const left = 2 * idx + 1;
const right = 2 * idx + 2;
if(left < _heap.length && _heap[left] < _heap[minIdx]){
minIdx = left;
}
if(right < _heap.length && _heap[right] < _heap[minIdx]){
minIdx = right;
}
if(minIdx !== idx){
[_heap[idx] , _heap[minIdx]] = [_heap[minIdx], _heap[idx]]
heapify(_heap, minIdx)
}
}
// buildMinHeap(heap)
for(let i = Math.floor(heap.length / 2) ; i>= 0 ; i-- ){
heapify(heap, i);
}
//go through rest of the items
for (let i=k; i< nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > heap[0])
{
heap[0] = nums[i];
heapify(heap, 0)
}
}
return heap[0]
};
Using max-heap
function kthLargestEl() {
let nums = [3, 2, 3, 1, 2, 4, 5, 5, 6],
k = 4;
const heap: number[] = [];
function heapify(i: number, before?: number) {
console.log("parent ==== ", i, before);
// findLargestNumIndex
const leftIdx = i * 2 + 1;
const rightIdx = i * 2 + 2;
let largestIdx = i;
if (leftIdx < heap.length && heap[leftIdx] > heap[largestIdx]) {
largestIdx = leftIdx;
}
if (rightIdx < heap.length && heap[rightIdx] > heap[largestIdx]) {
largestIdx = rightIdx;
}
// swap
if (largestIdx !== i) {
[heap[largestIdx], heap[i]] = [heap[i], heap[largestIdx]];
heapify(largestIdx, i);
}
}
// buildHeap : O(k) better than O(n) with ...nums entire element.
heap.push(...nums.slice(0,k));
for (let i = Math.floor(heap.length / 2); i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(i);
}
console.log(heap);
let result = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {
result = heap.pop()!;
}
console.log(heap, result);
}
Using Map
function findKthLargest(nums: number[], k: number): number {
const map = new Map();
for (const num of nums) {
map.set(num, (map.get(num) || 0) + 1);
}
const minNum = Math.min(...nums);
const maxNum = Math.max(...nums);
let count = 0;
for (let i = maxNum; i >= minNum; i--) {
if (map.has(i)) {
count += map.get(i);
}
if (count >= k) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}QuickSelect Algorithm
duplicate values 많은 경우 느림 TLE발생(Time Limit Exceeded)
export function findKthLargest(nums: number[], k: number): number {
const targetIndex = nums.length - k;
function partition(left: number, right: number): number {
const pivot = nums[right];
let i = left;
for (let j = left; j < right; j++) {
if (nums[j] <= pivot) {
// swap elements
[nums[i], nums[j]] = [nums[j], nums[i]];
i++;
}
}
[nums[i], nums[right]] = [nums[right], nums[i]];
return i;
}
function quickSelect(left: number, right: number): number {
const pivotIndex = partition(left, right);
if (pivotIndex === targetIndex) {
return nums[pivotIndex];
} else if (pivotIndex < targetIndex) {
return quickSelect(pivotIndex + 1, right);
} else {
return quickSelect(left, pivotIndex - 1);
}
}
return quickSelect(0, nums.length - 1);
}QuickSelect Algorithm
function findKthLargest(nums: number[], k: number): number {
const targetIndex = nums.length - k;
function partition(left: number, right: number): [number, number] {
const randomIndex = left + Math.floor(Math.random() * (right - left + 1));
[nums[randomIndex], nums[right]] = [nums[right], nums[randomIndex]];
const pivot = nums[right];
let i = left,
j = left,
n = right;
while (j <= n) {
if (nums[j] < pivot) {
[nums[i], nums[j]] = [nums[j], nums[i]];
i++;
j++;
} else if (nums[j] > pivot) {
[nums[j], nums[right]] = [nums[right], nums[j]];
n--;
} else {
j++;
}
}
return [i, n];
}
function quickSelect(left: number, right: number): number {
const [low, high] = partition(left, right);
if (targetIndex >= low && targetIndex <= high) {
return nums[targetIndex];
} else if (targetIndex < low) {
return quickSelect(left, low - 1);
} else {
return quickSelect(high + 1, right);
}
}
return quickSelect(0, nums.length - 1);
}Using MaxHeap Class
function findKthLargest4WithClass(nums: number[], k: number): number {
let heap = new MaxHeap(nums);
let result: number = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {
result = heap.pop();
}
return result;
}
class MaxHeap {
heap: number[] = [];
constructor(nums: number[]) {
this.heap = [];
this.buildHeap(nums);
}
leftChildIndx(parent: number) {
return parent * 2 + 1;
}
rightChildIndex(parent: number) {
return parent * 2 + 2;
}
swap(a: number, b: number) {
[this.heap[a], this.heap[b]] = [this.heap[b], this.heap[a]];
}
findLargestIndex(parent: number) {
const left = this.leftChildIndx(parent);
const right = this.rightChildIndex(parent);
let largest = parent;
if (left < this.heap.length && this.heap[left] > this.heap[largest]) {
largest = left;
}
if (right < this.heap.length && this.heap[right] > this.heap[largest]) {
largest = right;
}
return largest;
}
filterDown() {
let index = 0;
while (index < this.heap.length) {
let largest = this.findLargestIndex(index);
if (largest !== index) {
this.swap(index, largest);
index = largest;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
pop() {
let result = this.heap[0];
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop()!;
this.filterDown();
return result;
}
buildHeap(arr: number[]) {
this.heap.push(...arr);
const n = arr.length;
const heapify = (index: number) => {
let largest = this.findLargestIndex(index);
if (largest !== index) {
this.swap(largest, index);
heapify(largest);
}
};
for (let i = Math.floor(n / 2); i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(i);
}
}
}2. Top K Frequent Elements (LeetCode #347)
Using heap
// heap
export function topKFrequentHeap(nums: number[], k: number): number[] {
const freqMap = new Map<number, number>();
for (const num of nums) {
freqMap.set(num, (freqMap.get(num) || 0) + 1);
}
const maxHeap: HeapItem[] = Array.from(freqMap.entries()).map(
([num, freqCnt]) => ({ num, freqCnt })
);
function findBiggerChildIdx(parentIdx: number) {
let largest = parentIdx;
const left = parentIdx * 2 + 1;
const right = parentIdx * 2 + 2;
if (
left < maxHeap.length &&
maxHeap[left].freqCnt > maxHeap[largest].freqCnt
) {
largest = left;
}
if (
right < maxHeap.length &&
maxHeap[right].freqCnt > maxHeap[largest].freqCnt
) {
largest = right;
}
return largest;
}
function heapify(parentIdx: number) {
const largestChildIdx = findBiggerChildIdx(parentIdx);
if (largestChildIdx !== parentIdx) {
[maxHeap[parentIdx], maxHeap[largestChildIdx]] = [
maxHeap[largestChildIdx],
maxHeap[parentIdx],
];
heapify(largestChildIdx);
}
}
function pop() {
const largest = maxHeap[0];
if (maxHeap.length > 1) {
maxHeap[0] = maxHeap.pop()!;
let index = 0;
while (index < maxHeap.length) {
const largestChildIdx = findBiggerChildIdx(index);
if (index !== largestChildIdx) {
[maxHeap[index], maxHeap[largestChildIdx]] = [
maxHeap[largestChildIdx],
maxHeap[index],
];
index = largestChildIdx;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
return largest.num;
}
// build heap
for (let i = Math.floor(maxHeap.length / 2) - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(i);
}
const result = [];
for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {
result.push(pop());
}
return result;
}Using map and sort
function topKFrequent(nums: number[], k: number): number[] {
const freq = new Map<number, number>();
for (const num of nums) {
freq.set(num, (freq.get(num) || 0) + 1);
}
return Array.from(freq)
.sort((a, b) => b[1] - a[1])
.slice(0, k)
.map((val) => Number(val[0]));
}
3. Find K Pairs with Smallest Sums (LeetCode #373)
Using min-heap
// (a,b) => a[0] - b[0]
type CompareFn<T> = (a: T, b: T) => number;
class BinaryMinHeap<T> {
heap: T[];
compare: CompareFn<T>;
constructor(compareFn: CompareFn<T>) {
this.heap = [];
this.compare = compareFn;
}
pop(): T | undefined {
if (this.heap.length < 2) {
return this.heap.pop();
}
const samllest = this.heap[0];
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop()!;
this.sinkDown(this.heap, this.compare, 0);
return samllest;
}
push(value: T): number {
const length = this.heap.push(value);
this.bubbleUp(this.heap, this.compare, length - 1);
return length;
}
bubbleUp<T>(arr: Array<T>, compareFn: CompareFn<T>, index: number) {
const value = arr[index];
while (index > 0) {
// Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
const parentIndex = (index - 1) >> 1;
if (compareFn(arr[parentIndex], value) <= 0) {
break;
}
arr[index] = arr[parentIndex];
index = parentIndex;
}
arr[index] = value;
}
// sinkDown<T>(arr: Array<T>, compareFn: CompareFn<T>, parentIdx: number) {
// const N = arr.length;
// // Find the indices of the two children (left and right) of the parent
// const leftChildIdx = 2 * parentIdx + 1;
// const rightChildIdx = 2 * parentIdx + 2;
// // Find the index of the smallest (or largest in case of a max-heap) child
// let smallestChildIdx = parentIdx;
// // Check if the left child exists and is smaller than the current element
// if (
// leftChildIdx < N &&
// compareFn(arr[leftChildIdx], arr[smallestChildIdx]) < 0
// ) {
// smallestChildIdx = leftChildIdx;
// }
// // Check if the right child exists and is smaller than the current element
// if (
// rightChildIdx < N &&
// compareFn(arr[rightChildIdx], arr[smallestChildIdx]) < 0
// ) {
// smallestChildIdx = rightChildIdx;
// }
// // If the smallest child is different from the parent, swap and recursively heapify
// if (smallestChildIdx !== parentIdx) {
// [arr[parentIdx], arr[smallestChildIdx]] = [
// arr[smallestChildIdx],
// arr[parentIdx],
// ];
// // Recursively heapify the affected subtree
// this.sinkDown(arr, compareFn, smallestChildIdx);
// }
// }
sinkDown<T>(arr: Array<T>, compareFn: CompareFn<T>, index: number) {
const value = arr[index];
const N = arr.length;
const mid = Math.floor(arr.length / 2) - 1;
// const mid = (N - 1) / 2;
while (index <= mid) {
let childIndex = (index << 1) + 1;
// +(true) = 1 , +(false) = 0
childIndex += +(
childIndex + 1 < N &&
compareFn(arr[childIndex + 1], arr[childIndex]) <= 0
);
if (compareFn(value, arr[childIndex]) <= 0) {
break;
}
arr[index] = arr[childIndex];
index = childIndex;
}
arr[index] = value;
}
}
type HeapItem = [sum: number, nums1Value: number, nums2Index: number];
function kSmallestPairs(
nums1: number[],
nums2: number[],
k: number
): number[][] {
const result: number[][] = [];
if (nums1.length === 0 || nums2.length === 0 || k === 0) return result;
const minHeap = new BinaryMinHeap<HeapItem>((a, b) => a[0] - b[0]);
const N = Math.min(nums1.length, k);
const M = Math.min(nums2.length, k);
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
minHeap.push([nums1[i] + nums2[0], nums1[i], 0]);
}
while (k-- > 0 && minHeap.heap.length > 0) {
const [sum, nums1Value, nums2Index] = minHeap.pop()!;
result.push([nums1Value, sum - nums1Value]);
if (nums2Index + 1 < M) {
minHeap.push([
nums1Value + nums2[nums2Index + 1],
nums1Value,
nums2Index + 1,
]);
}
}
return result;
}
Using min-heap2
function kSmallestPairs(
nums1: number[],
nums2: number[],
k: number
): number[][] {
const result: number[][] = Array.from({ length: k }, () => []);
const length = result.length;
const minHeap = new MinHeap();
for (let i = 0; i < Math.min(nums1.length, k); ++i) {
minHeap.insert({
sum: nums1[i] + nums2[0],
num1: nums1[i],
num2: nums2[0],
index2: 0,
});
}
while (k > 0 && !minHeap.isEmpty()) {
const { num1, num2, index2 } = minHeap.pop();
result[length - k] = [num1, num2];
const nextIndex2 = index2 + 1;
if (nextIndex2 < nums2.length) {
minHeap.insert({
sum: num1 + nums2[nextIndex2],
num1,
num2: nums2[nextIndex2],
index2: nextIndex2,
});
}
--k;
}
return result;
}
interface INode {
sum: number;
num1: number;
num2: number;
index2: number;
}
class MinHeap {
private nodes: INode[] = [];
constructor() {
this.nodes = [];
}
private swap(a: number, b: number) {
[this.nodes[a], this.nodes[b]] = [this.nodes[b], this.nodes[a]];
}
private shouldSwap(parentIdx: number, childIdx: number) {
if (parentIdx < 0 || parentIdx >= this.size()) {
return false;
}
if (childIdx < 0 || childIdx >= this.size()) {
return false;
}
return this.nodes[parentIdx].sum > this.nodes[childIdx].sum;
}
private heapifyUp(startIdx: number) {
let childIndex = startIdx;
let parentIndex = Math.floor((childIndex - 1) / 2);
while (this.shouldSwap(parentIndex, childIndex)) {
this.swap(parentIndex, childIndex);
childIndex = parentIndex;
parentIndex = Math.floor((childIndex - 1) / 2);
}
}
private heapifyDown(startIdx: number) {
const length = this.size();
const leftChildIndex = 2 * startIdx + 1;
const rightChildIndex = 2 * startIdx + 2;
let samllest = startIdx;
if (
leftChildIndex < length &&
this.nodes[leftChildIndex].sum < this.nodes[samllest].sum
) {
samllest = leftChildIndex;
}
if (
rightChildIndex < length &&
this.nodes[rightChildIndex].sum < this.nodes[samllest].sum
) {
samllest = rightChildIndex;
}
if (samllest !== startIdx) {
this.swap(startIdx, samllest);
this.heapifyDown(samllest);
}
}
size() {
return this.nodes.length;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
insert(value: INode) {
this.nodes.push(value);
this.heapifyUp(this.size() - 1);
}
pop() {
if (this.size() === 1) {
return this.nodes.pop()!;
}
const minValue = this.nodes[0];
this.nodes[0] = this.nodes.pop()!;
this.heapifyDown(0);
return minValue;
}
}