[Algorithm] NSL/NSR - Monotonic stack - leetcode 84
NSL : Nearest Smaller to Left
NSR : Nearest Smaller to Right
순차적 대소 비교
스트림내에서 단일값에 대해 가장 가까운 최소값 / 최대값을 찾을 때
전체 데이터에서 그다음 나오는 가장 가까운 작은값 / 큰값을 찾을 때
NSL : Nearest Smaller to Left
function NSL(nums: number[]) {
const nearestMinLeft = [];
const stack = [];
// index move like left To right but find value on the left side
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
while (stack.length && nums[stack[stack.length - 1]] >= nums[i]) {
stack.pop();
}
nearestMinLeft[i] = stack[stack.length - 1] ?? -1;
stack.push(i);
}
return nearestMinLeft;
}
NSR : Nearest Smaller to Right
function NSR(nums: number[]) {
const nearestMinRight = [];
const stack = [];
// index move like left To right but find value on the right side
for (let i = nums.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (stack.length && nums[stack[stack.length - 1]] >= nums[i]) {
stack.pop();
}
nearestMinRight[i] = stack[stack.length - 1] ?? nums.length;
stack.push(i);
}
return nearestMinRight;
}
Usage - monotonic stack - leetcode 84
Solution-1
/**
* Analyzing + NSL/NSR Algorithm : O(n)
* 전체 배열(히스토그램)의 특정 요소를 기준으로 왼쪽과 오른쪽에 대해서 해당 알고리즘을 바탕으로
* 가장 가까운 작은 요소의 위치를 찾아 이를 저장한다
* 그 다음엔 전체 요소에 대해서 다음 식을 반복하는데, 해당 식은
* (현재 요소의 높이 * (해당 요소의 가장 가까운 오른쪽의 값 - 해당 요소의 가장 가까운 왼쪽의 값 - 1)이다.
* */
export function largestRectagleAreaWithAnalysis(heights: number[]) {
let maxArea = 0;
let nearestMinLeft = [],
nearestMinRight = [];
let stack = [];
function NSL(nums: number[]) {
const nearestMinLeft = [];
const stack = [];
// index move like left To right but find value on the left side
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
while (stack.length && nums[stack[stack.length - 1]] >= nums[i]) {
stack.pop();
}
nearestMinLeft[i] = stack[stack.length - 1] ?? -1;
stack.push(i);
}
return nearestMinLeft;
}
function NSR(nums: number[]) {
const nearestMinRight = [];
const stack = [];
// index move like left To right but find value on the right side
for (let i = nums.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (stack.length && nums[stack[stack.length - 1]] >= nums[i]) {
stack.pop();
}
nearestMinRight[i] = stack[stack.length - 1] ?? nums.length;
stack.push(i);
}
return nearestMinRight;
}
nearestMinLeft = NSL(heights);
nearestMinRight = NSR(heights);
/// 자신의 높이 * (오른쪽의 가장 가까운 작은 값 인덱스 - 왼쪽의 가장 가까운 작은 값 인덱스 - 1)
for (let i = 0; i < heights.length; i++) {
const h = heights[i];
const w = nearestMinRight[i] - nearestMinLeft[i] - 1;
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, h * w);
}
return maxArea;
}
why -1? nearestMinRight[i] - nearestMinLeft[i] - 1;
Phase
(Phase 1)
let heights = [ 2, 4, 5, 3, 1 ]
let index = 0 ;
let nearestMinLeft = [ -1, 0, 1, 0, -1 ]
let nearestMinRight =[ 4, 3, 3, 4, 5 ];
let h = heights[index];
let left = nearestMinLeft[index]
let right = nearestMinRight[index];
`${right} -(${left}) -1 : ${right - left - 1}`
width: '4 -(-1) -1 : 4'
(Phase 2)
let heights = [ 2, 4, 5, 3, 1 ]
let index = 1 ;
let nearestMinLeft = [ -1, 0, 1, 0, -1 ]
let nearestMinRight =[ 4, 3, 3, 4, 5 ];
let h = heights[index];
let left = nearestMinLeft[index]
let right = nearestMinRight[index];
`${right} -(${left}) -1 : ${right - left - 1}`
width: '3 -(0) -1 : 2'
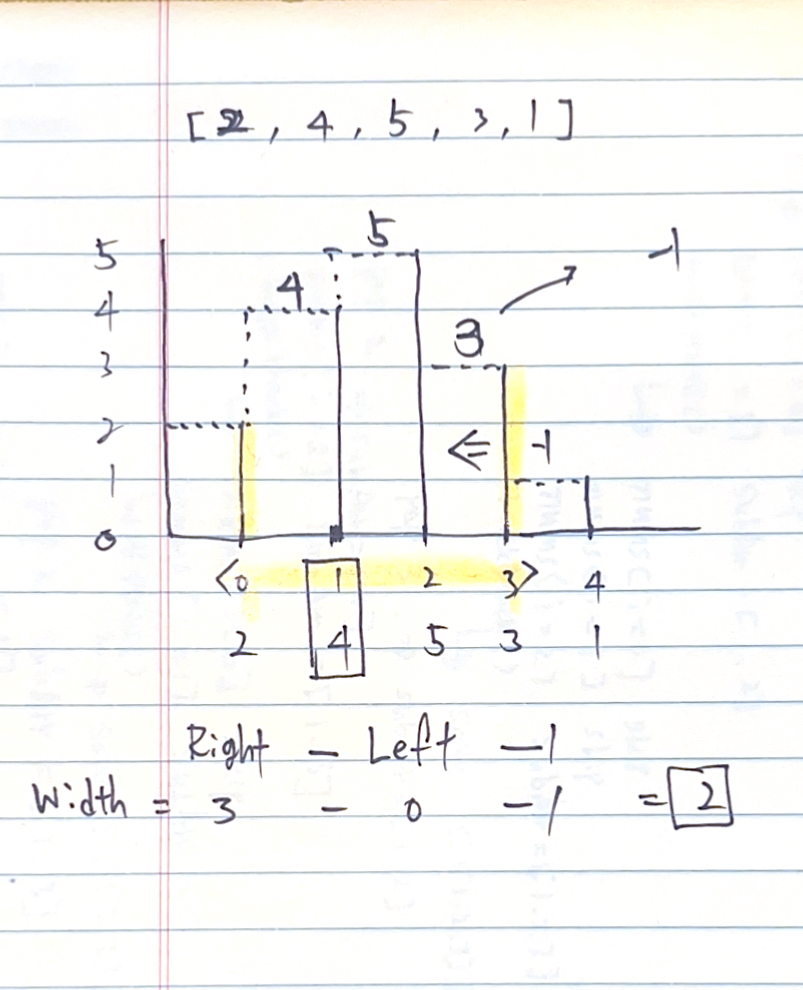
(Phase 3)
let heights = [ 2, 4, 5, 3, 1 ]
let index = 2;
let nearestMinLeft = [ -1, 0, 1, 0, -1 ]
let nearestMinRight =[ 4, 3, 3, 4, 5 ];
let h = heights[index];
let left = nearestMinLeft[index]
let right = nearestMinRight[index];
`${right} -(${left}) -1 : ${right - left - 1}`
width: '3 -(1) -1 : 1'
(Phase 4)
let heights = [ 2, 4, 5, 3, 1 ]
let index = 3;
let nearestMinLeft = [ -1, 0, 1, 0, -1 ]
let nearestMinRight =[ 4, 3, 3, 4, 5 ];
let h = heights[index];
let left = nearestMinLeft[index]
let right = nearestMinRight[index];
`${right} -(${left}) -1 : ${right - left - 1}`
width: '4 -(0) -1 : 3'
(Phase 5)
let heights = [ 2, 4, 5, 3, 1 ]
let index = 4;
let nearestMinLeft = [ -1, 0, 1, 0, -1 ]
let nearestMinRight =[ 4, 3, 3, 4, 5 ];
let h = heights[index];
let left = nearestMinLeft[index]
let right = nearestMinRight[index];
`${right} -(${left}) -1 : ${right - left - 1}`
width: '5 -(-1) -1 : 5'Solution-2
// this one is east to understand and explain
export function largestRectangleAreaPassed(heights: number[]): number {
const stack: [number, number][] = [];
let maxArea = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < heights.length; i++) {
let start = i;
const currH = heights[i];
while (stack.length > 0 && stack[stack.length - 1][1] > currH) {
const [index, height] = stack.pop()!;
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, height * (i - index));
start = index;
}
stack.push([start, currH]);
}
for (const [index, height] of stack) {
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, height * (heights.length - index));
}
return maxArea;
}