
2차원 배열(Array)
● 1차원 배열에 단지 대괄호[] 하나만 더 붙인 상태이다.
● 1차원 배열에 * N개의 배열을 만들어 사용한다.배열 생성(선언)
// 2차원 배열 선언
변수타입[][] 변수이름;
// 2차원 배열 생성
변수이름 = new 타입[행길이][열길이]
int[][] arrs;
arrs = new int[3][4]; int[][] score = {
{100, 100, 100},
{20, 20, 20},
{30, 30, 30},
{40, 40, 40},
{50, 50, 50},
};
// 과목별 총점
int korTotal = 0, engTotal = 0, mathTotal = 0;
System.out.println("번호 국어 영어 수학 총점 평군");
System.out.println("=========================");
for (int i = 0; i < score.length; i++) {
int sum = 0; // 개인별 총점
float avg = 0f; // 개인별 평균
korTotal += score[i][0];
engTotal += score[i][1];
mathTotal += score[i][2];
System.out.printf("%3d", i+1);
for (int j = 0; j < score[i].length; j++) {
sum += score[i][j];
System.out.printf("%5d", score[i][j]);
}
avg = sum / (float)score[i].length;
System.out.printf("%5d %5.1f%n", sum, avg);
}
System.out.println("================================");
System.out.printf("총점:%3d %4d %4d%n", korTotal, engTotal, mathTotal);2차원 배열 예제1
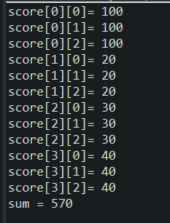
public class Array2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] score = {
{ 100, 100, 100},
{20, 20, 20},
{30 , 30 , 30},
{40, 40, 40}
};
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < score.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < score[i].length; j++) {
System.out.printf("score[%d][%d]= %d\n", i, j, score[i][j]);
sum += score[i][j];
}
}
System.out.println("sum = " + sum);
}
}
결과 값:
2차원 배열 예제2
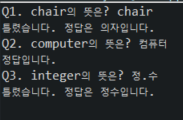
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Array2_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[][] words = {
{"chair", "의자"},
{"computer", "컴퓨터"},
{"integer", "정수"}
};
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
// 2차원 배열에서 chair, computer, integer을 말하는 것이다.
System.out.printf("Q%d. %s의 뜻은? ", i+1, words[i][0]);
String tmp = sc.nextLine();
if(tmp.equals(words[i][1])) {
System.out.printf("정답입니다.\n");
} else {
System.out.printf("틀렸습니다. 정답은 %s입니다.\n",words[i][1]);
}
}
}
}
결과 값:
- 1차원과 마찬가지로 선언 및 생성을 동시에 가능하다.
- 3차원 배열 이상의 고차원 배열의 선언도 이와같이
[]대괄호만 추가해주면 된다.
Arrays로 배열 다루기
배열의 비교와 출력 - toString(), equals()
toString()은 배열의 모든 요소를 문자열로 편하게 출력할 수 있다. 다만 일차원 배열에만 사용할 수 있고 다차원 배열에는 deepToString()을 사용해야 한다.
equals()는 두 배열에 저장된 모든 요소를 비교해서 같으면 true, 틀리면 false를 반환한다. 다차원 배열에서는 deepToEquals()를 사용해야 한다.
배열의 복사 - copyOf(), copyOfRange()
copyOf()는 배열 전체를, copyOfRange()는 배열의 일부를 복사해서 새로운 배열을 만들어 반환한다. 늘 그렇듯이 copyOfRange()에 지정된 범위의 끝은 포함되지 않는다.
배열의 정렬 - sort()
배열을 정렬할 때는 sort()를 사용한다.
