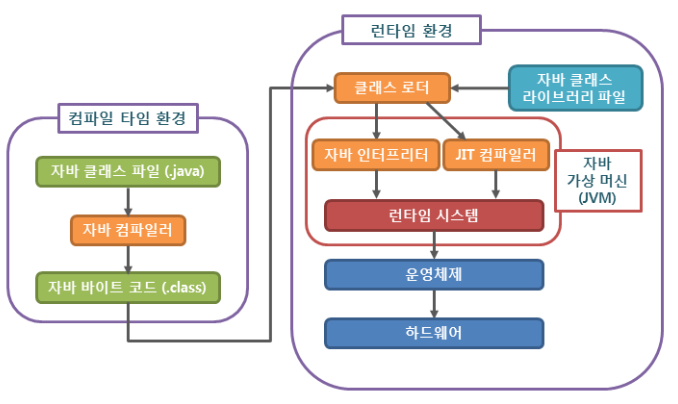
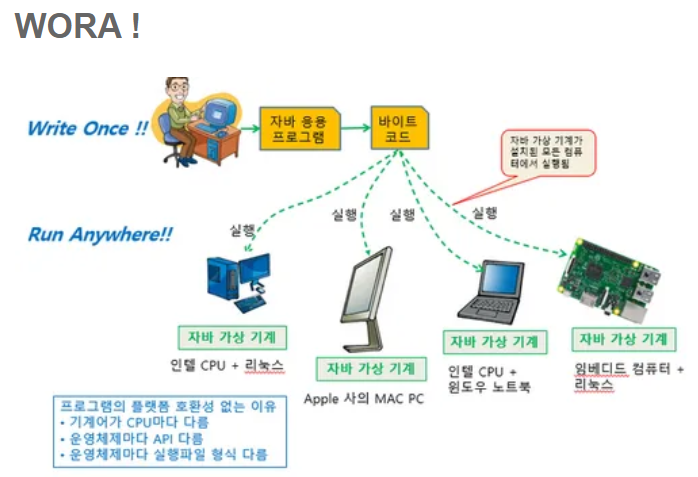
java란
자바 가상머신(JVM)으로 어떤 환경에서도 사용 가능함
- java 수업 블로그
https://blog.naver.com/drv98
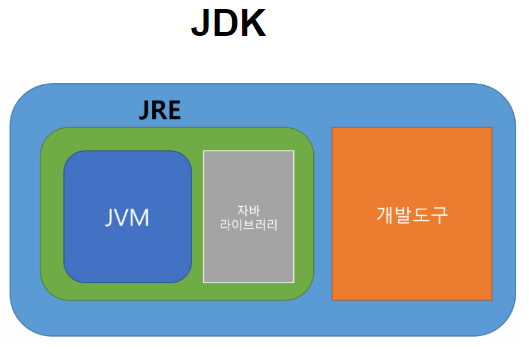
JDK : 개발자가 사용
JRE : 개발 코드만 보고 싶은 이용자가 사용
이클립스 jdk 설치 후 기본 세팅
D 또는 C 드라이브에 폴더 생성
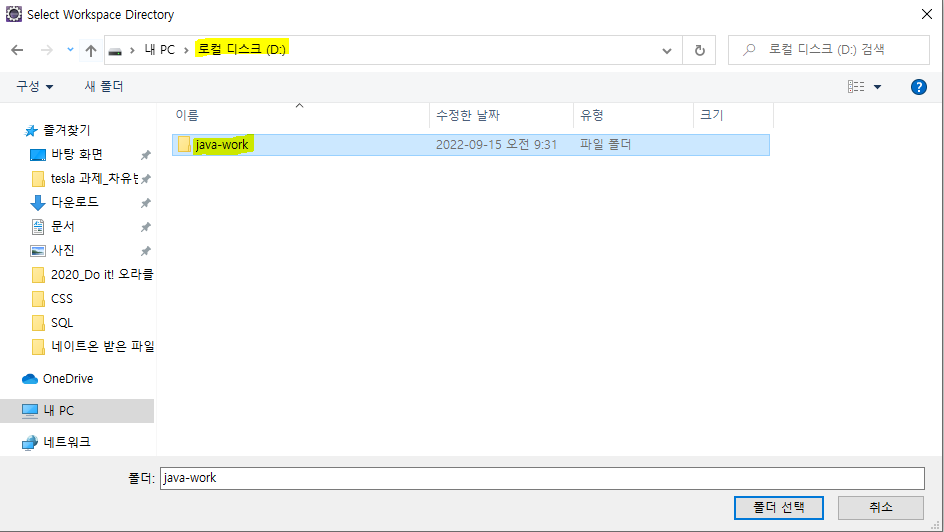
- cmd에서 jdk 버전 확인 가능
- 만든 코드(확장자가 .java)는 src 폴더로, 컴파일한 파일(확장자가 .class)은 bin 폴더로 들어감
- pakage는 class(자바 최소 단위)를 모아두는 저장소(더 큰 단위)
(보통 pakage는 소문자, 프로젝트 이름과 class는 대문자로 시작함) - ctrl + shift +/- (화면 글자 크기 조정)
- 코드 실행 단축키 : ctrl + F11
- 명령문 끝에 세미콜론(;) 꼭 붙여야 실행 됨
- ★ ctrl + shift + F : 코드 자동 줄 맞춤
- ctrl + Alt + 화살표 ↓ : 코드 복사
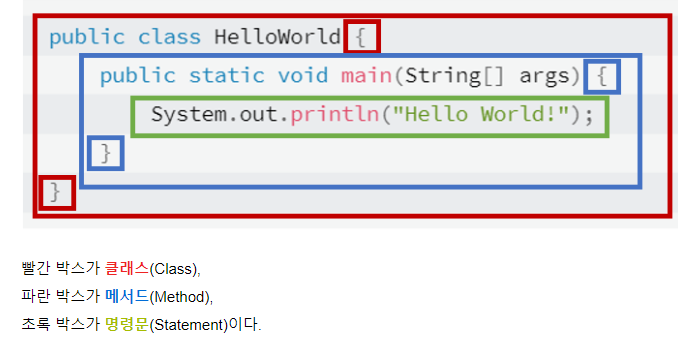
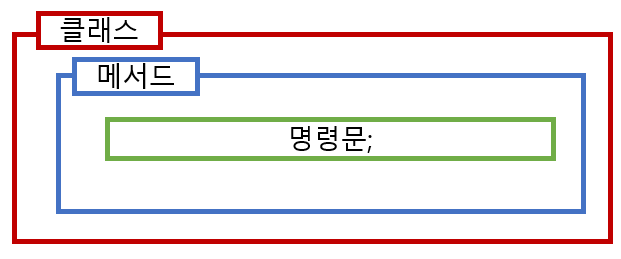

- 패키지 내의 다른 패키지 (상위 패키지.하위 패키지 이름) 으로 생성
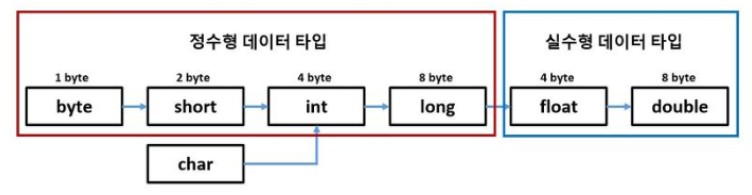
- 컴퓨터 구조
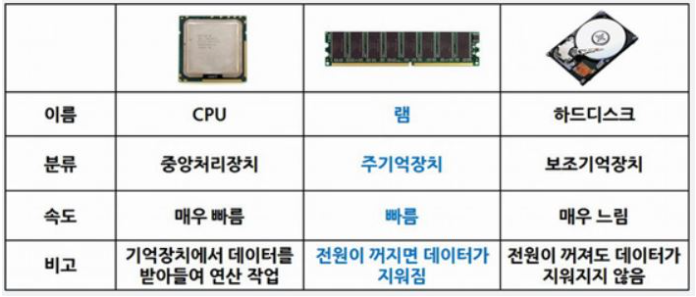
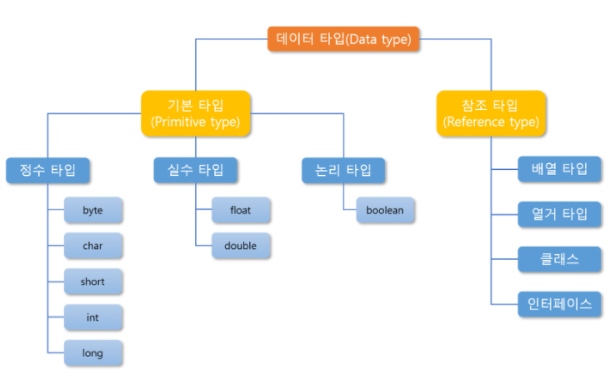
변수 INT(정수)
- 변수 : 하나의 값을 저장할 수 있는 상자
package 정수;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 변수 만들기 : 1. 변수 선언(자료형) 2. 변수 초기화
int x; //int(정수) 선언
x = 7; //초기값 입력 (초기화)
int y = 10; //선언과 동시에 초기화
System.out.println("헬로우월드!");
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
}
}데이터 타입
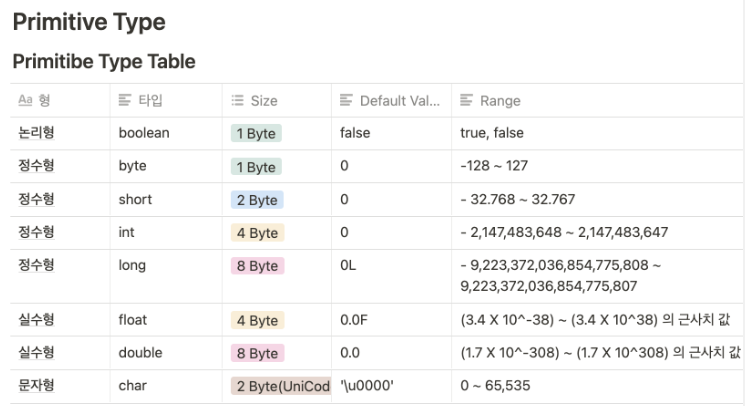
- 주로 쓰는 타입

문자열 + 변수 출력
package 정수;
public class PrintOutput {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 문자열 + 숫자 => 문자열
int x = 5;
int y = 7;
int z = x + y;
System.out.println("x + y의 값은? " + z);
}
}실수
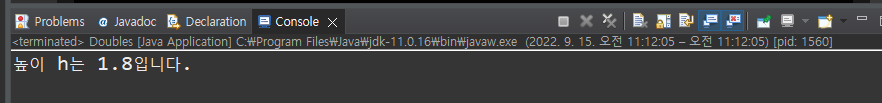
public class Doubles {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 실수 타입 변수 선언
double h = 1.8;
System.out.println("높이 h는 " + h + "입니다.");
}
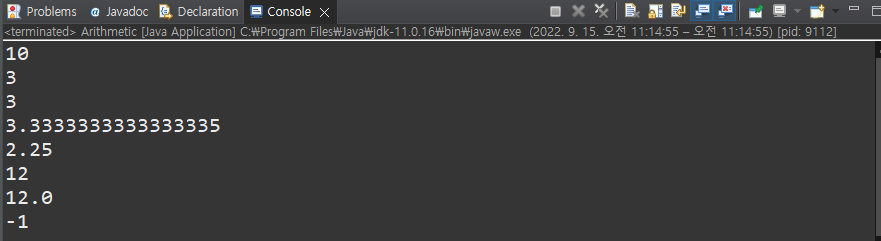
산술연산
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 숫자 산술연산(정수 : int, 실수 : Double)
System.out.println(7+3);
System.out.println(9/3);
System.out.println(10/3); // 정수/정수=정수 이므로 답 3으로 나옴
System.out.println(10.0/3.0); // 실수 double 이므로 답 3.33..
System.out.println(9/4.0); // 하나는 실수로 변환해줌(9를 변환)
System.out.println(3*4);
System.out.println(3*4.0); // 하나는 실수로 변환
System.out.println(3-4);
} 
> 변수 재할당
package 정수;
public class VariableAssignment {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 변수 재할당 : 변수에 다른 값 입력 가능
int x = 8;
int y = 3;
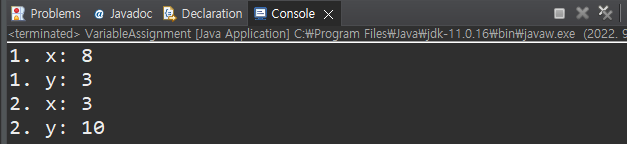
System.out.println("1. x: " + x);
System.out.println("1. y: " + y);
//변수 값 재할당
x = y;
y = 10;
System.out.println("2. x: " + x);
System.out.println("2. y: " + y);
}
}
온도 변환(섭씨 화씨 변환)
package 온도변환;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// (0°C × 9/5) + 32 = 32°F
double c = 25; //섭씨
double f = (c*9/5)+32; //화씨 (변환공식)
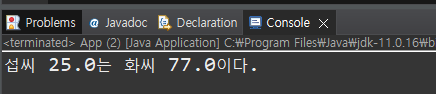
System.out.println("섭씨 " + c + "는 화씨 " + f +"이다.");
}
}
연습문제
연습문제 1
package 자바시작하기;
public class Profile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 연습문제 1
//1. 이름을 출력하시오.
String name = "홍팍";
//2. 나이를 출력하시오.
int age = 20;
//3. 키를 출력하시오.
double height = 180.52;
//4. 자바 입문 여부를 출력하시오.
boolean isStarted = true;
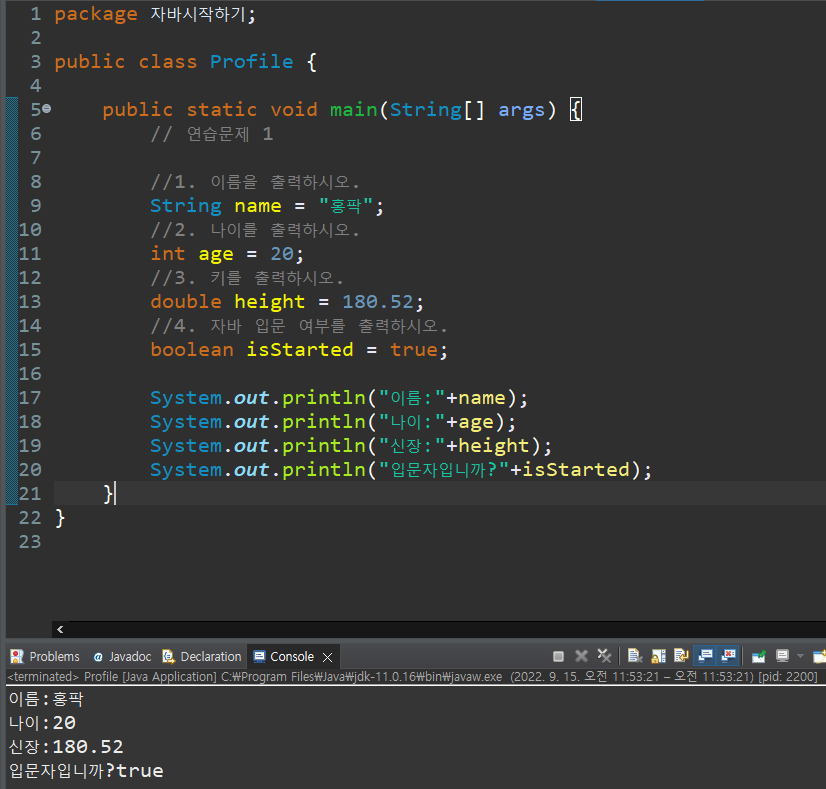
System.out.println("이름:"+name);
System.out.println("나이:"+age);
System.out.println("신장:"+height);
System.out.println("입문자입니까?"+isStarted);
}
}
연습문제 2
package 자바시작하기;
public class Score {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 연습문제 2
int math = 96;
int sience = 88;
int english = 76;
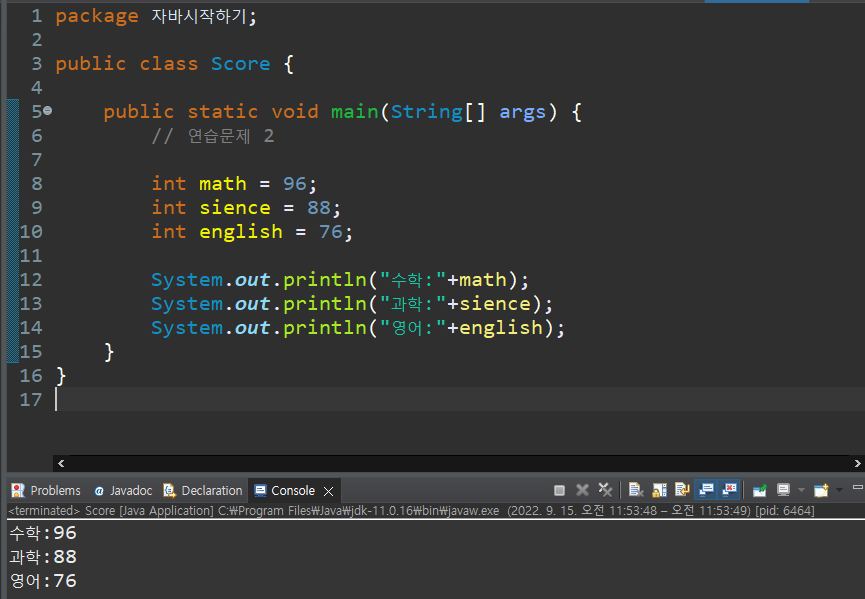
System.out.println("수학:"+math);
System.out.println("과학:"+sience);
System.out.println("영어:"+english);
}
}
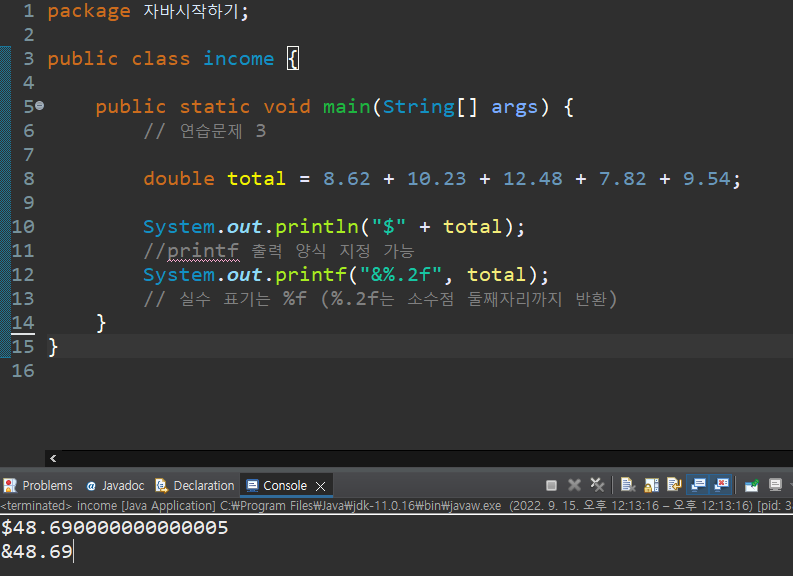
연습문제 3
package 자바시작하기;
public class income {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 연습문제 3
double total = 8.62 + 10.23 + 12.48 + 7.82 + 9.54;
System.out.println("$" + total);
//printf 출력 양식 지정 가능
System.out.printf("&%.2f", total);
// 실수 표기는 %f (%.2f는 소수점 둘째자리까지 반환)
}
}
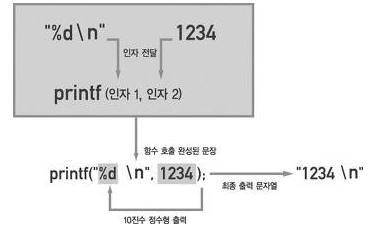
- printf에서 사용하는 서식 문자
%c : 문자 표기
%s : 문자열 표기
%f, %lf : 실수 표기
%u : 10진 정수 (부호 없음)
%d : 10진 정수 (부호 있음)
%o : 8진 정수 (부호 없음)
%x : 16진 정수 (부호 없음)
%lu : long 타입 (부호 없음)
%ld : long 타입 (부호 있음)
%llu : long long 타입 (부호 없음)
%lld : long long 타입 (부호 있음)
%p : 메모리 주소 표기
%% : 기호 % 표기
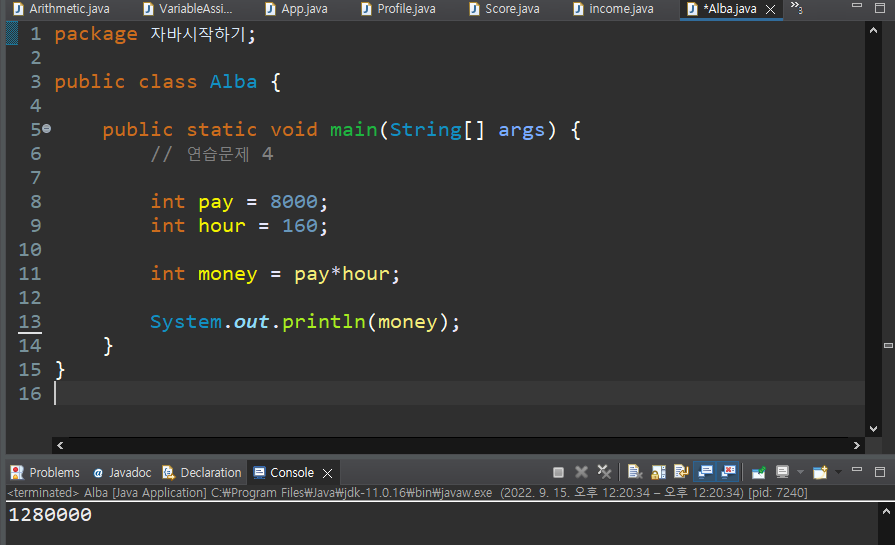
연습문제 4
package 자바시작하기;
public class Alba {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 연습문제 4
int pay = 8000;
int hour = 160;
int money = pay*hour;
System.out.println(money);
}
}
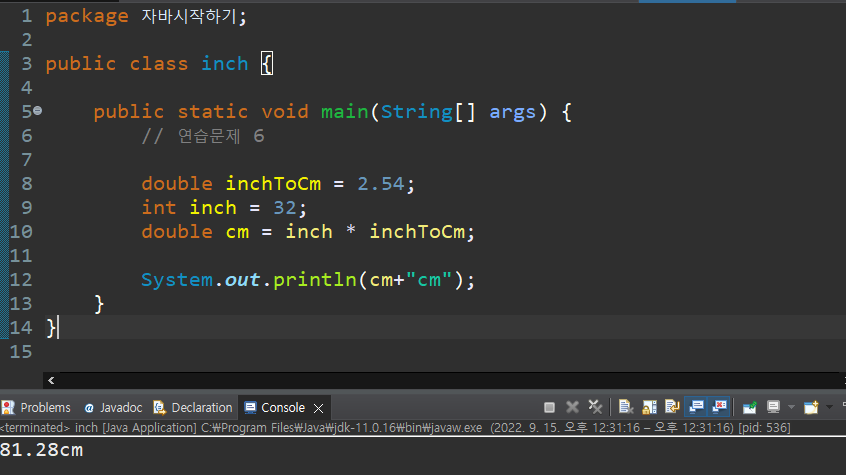
연습문제 6
package 자바시작하기;
public class inch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 연습문제 6
double inchToCm = 2.54;
int inch = 32;
double cm = inch * inchToCm;
System.out.println(cm+"cm");
}
}
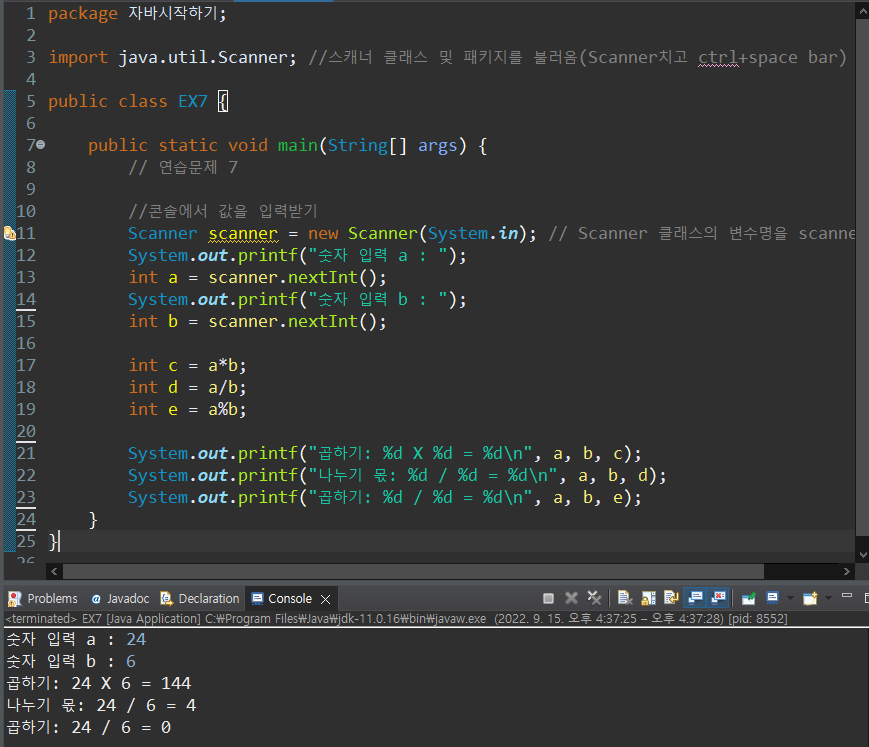
연습문제 7
package 자바시작하기;
import java.util.Scanner; //스캐너 클래스 및 패키지를 불러옴(Scanner치고 ctrl+space bar)
public class EX7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 연습문제 7
//콘솔에서 값을 입력받기
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); // Scanner 클래스의 변수명을 scanner라고 지정
System.out.printf("숫자 입력 a : ");
int a = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.printf("숫자 입력 b : ");
int b = scanner.nextInt();
int c = a*b;
int d = a/b;
int e = a%b;
System.out.printf("곱하기: %d X %d = %d\n", a, b, c);
System.out.printf("나누기 몫: %d / %d = %d\n", a, b, d);
System.out.printf("곱하기: %d / %d = %d\n", a, b, e);
}
}
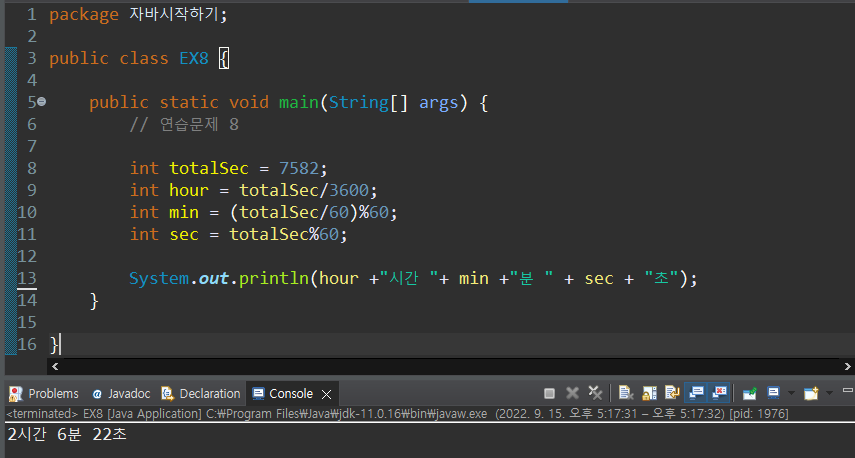
연습문제 8
package 자바시작하기;
public class EX8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 연습문제 8
int totalSec = 7582;
int hour = totalSec/3600;
int min = (totalSec/60)%60;
int sec = totalSec%60;
System.out.println(hour +"시간 "+ min +"분 " + sec + "초");
}
}
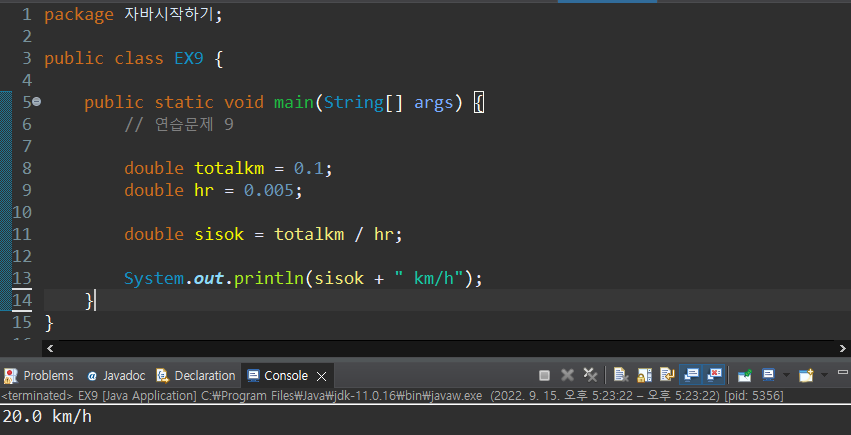
연습문제 9
package 자바시작하기;
public class EX9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 연습문제 9
double totalkm = 0.1;
double hr = 0.005;
double sisok = totalkm / hr;
System.out.println(sisok + " km/h");
}
}
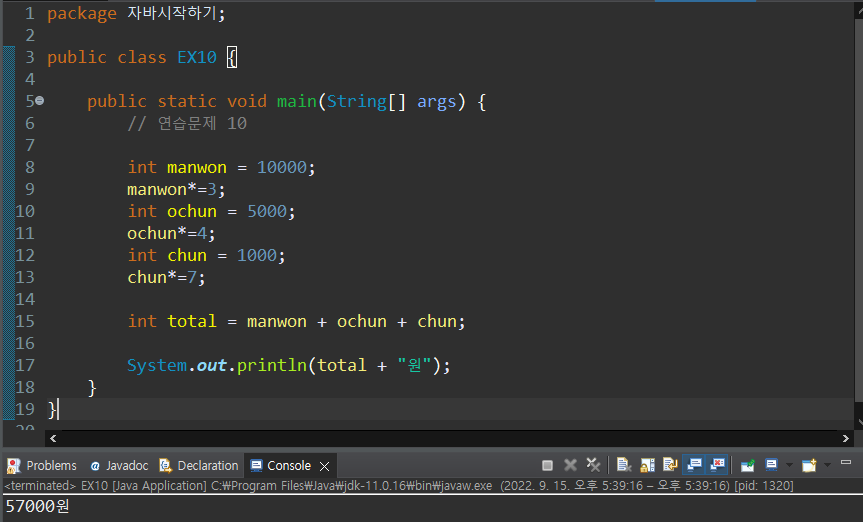
연습문제 10
package 자바시작하기;
public class EX10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 연습문제 10
int manwon = 10000;
manwon*=3;
int ochun = 5000;
ochun*=4;
int chun = 1000;
chun*=7;
int total = manwon + ochun + chun;
System.out.println(total + "원");
}
}
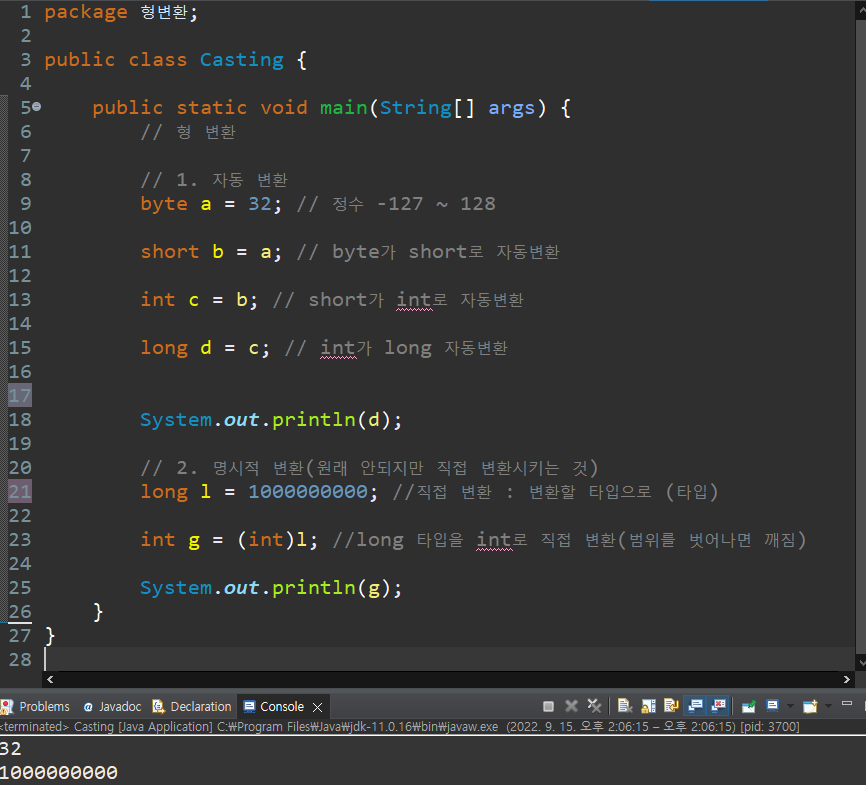
형 변환 Casting
- 범위가 작은 타입에서 큰 타입으로 변환 가능(큰->작은 은 안됨)
package 형변환;
public class Casting {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 형 변환
// 1. 자동 변환
byte a = 32; // 정수 -127 ~ 128
short b = a; // byte가 short로 자동변환
int c = b; // short가 int로 자동변환
long d = c; // int가 long 자동변환
System.out.println(d);
// 2. 명시적 변환(원래 안되지만 직접 변환시키는 것)
long l = 1000000000; //직접 변환 : 변환할 타입으로 (타입)
int g = (int)l; //long 타입을 int로 직접 변환(범위를 벗어나면 깨짐)
System.out.println(g);
}
}
명시적 변환
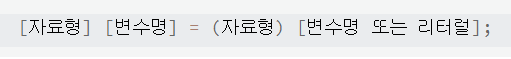
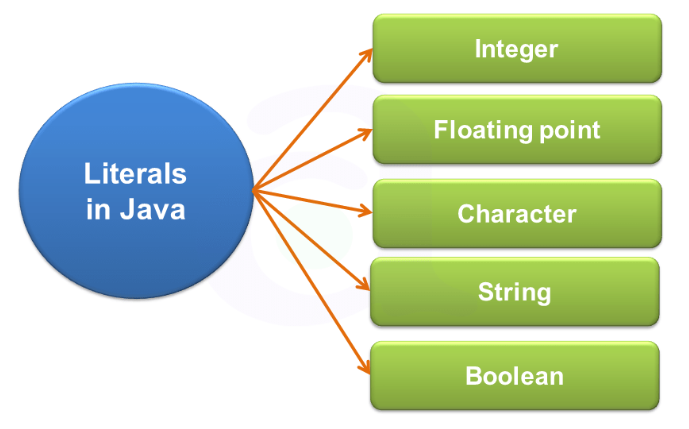
리터럴
- 변수에 넣는 데이터 값 그 자체를 말함 (즉 변수에 넣는 변하지 않는 데이터)
- 변수 데이터 타입에 따라 접미사가 있는 것은 붙여줘야 함
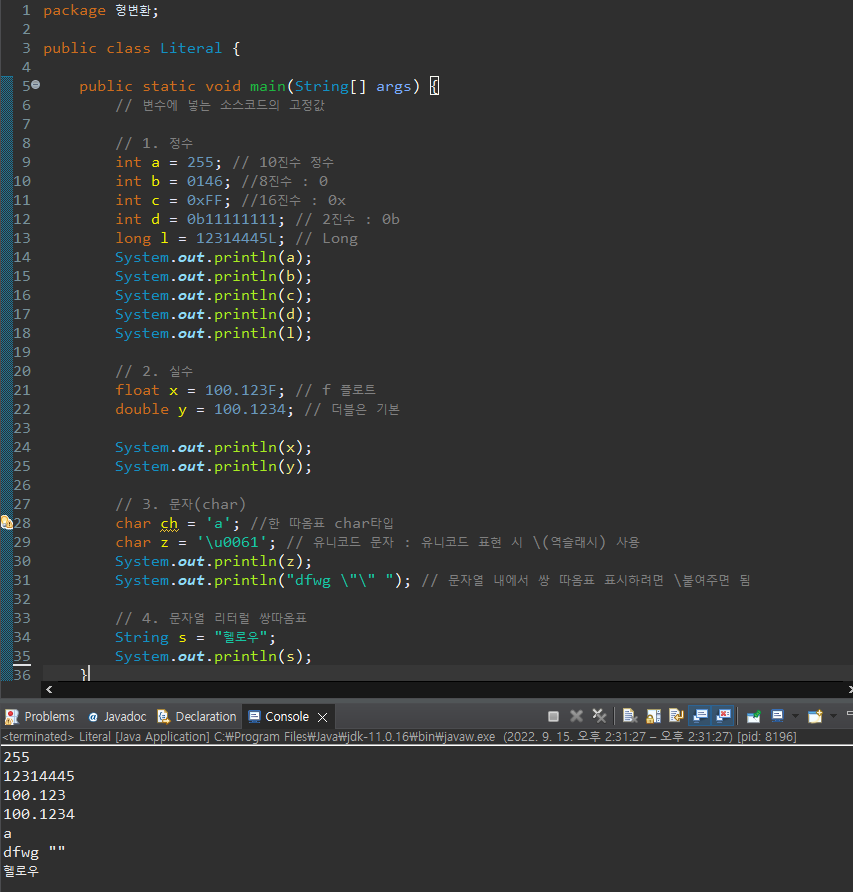
package 형변환;
public class Literal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 변수에 넣는 소스코드의 고정값
// 1. 정수
int a = 255; // 10진수 정수
int b = 0146; //8진수 : 0
int c = 0xFF; //16진수 : 0x
int d = 0b11111111; // 2진수 : 0b
long l = 12314445L; // Long
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(c);
System.out.println(d);
System.out.println(l);
// 2. 실수
float x = 100.123F; // f 플로트
double y = 100.1234; // 더블은 기본
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
// 3. 문자(char)
char ch = 'a'; //한 따옴표 char타입
char z = '\u0061'; // 유니코드 문자 : 유니코드 표현 시 \(역슬래시) 사용
System.out.println(z);
System.out.println("dfwg \"\" "); // 문자열 내에서 쌍 따옴표 표시하려면 \붙여주면 됨
// 4. 문자열 리터럴 쌍따옴표
String s = "헬로우";
System.out.println(s);
}
}
문자열
- 문자열 String 타입은 기본 타입이 아닌 클래스 타입(String이라는 class 자동 생성됨 색깔도 다름)
- 문자열+문자열=문자열 출력
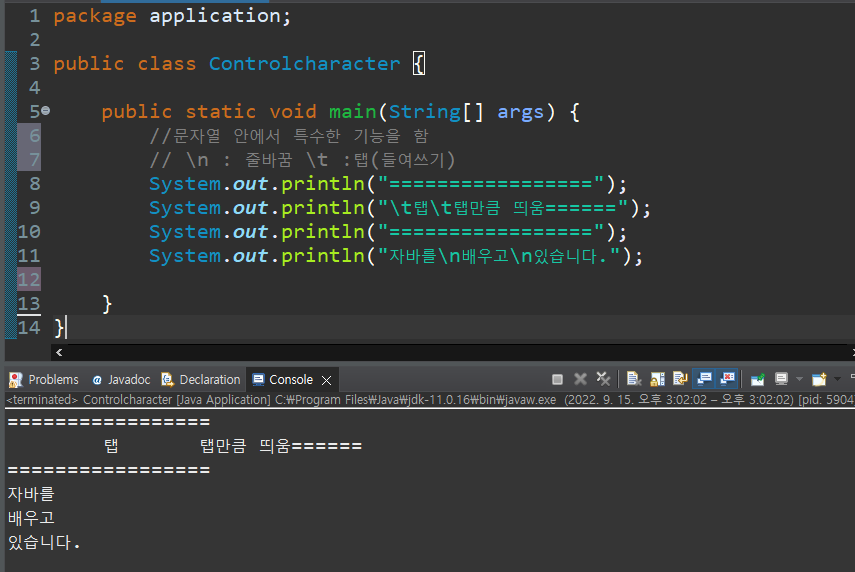
제어문자
package application;
public class Controlcharacter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//문자열 안에서 특수한 기능을 함
// \n : 줄바꿈 \t :탭(들여쓰기)
System.out.println("=================");
System.out.println("\t탭\t탭만큼 띄움======");
System.out.println("=================");
System.out.println("자바를\n배우고\n있습니다.");
}
}
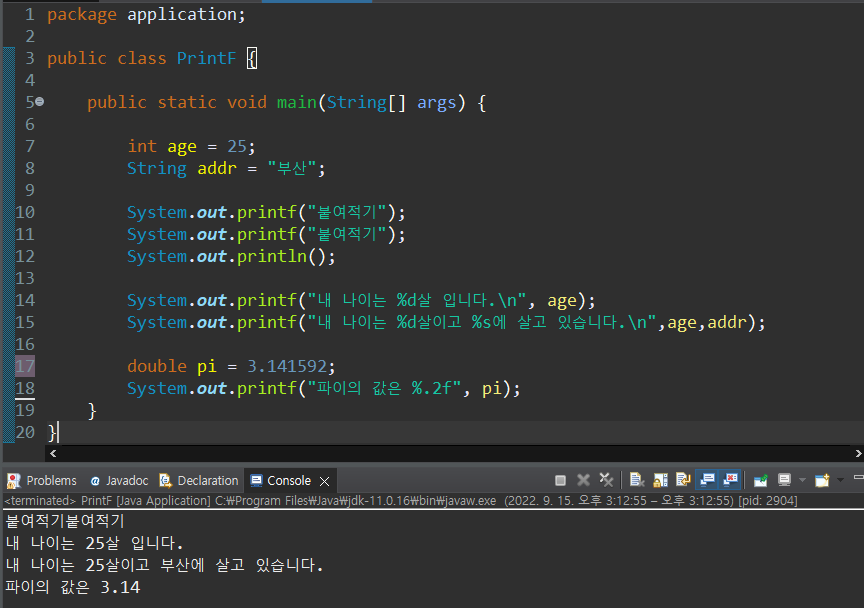
출력포맷 Printf()
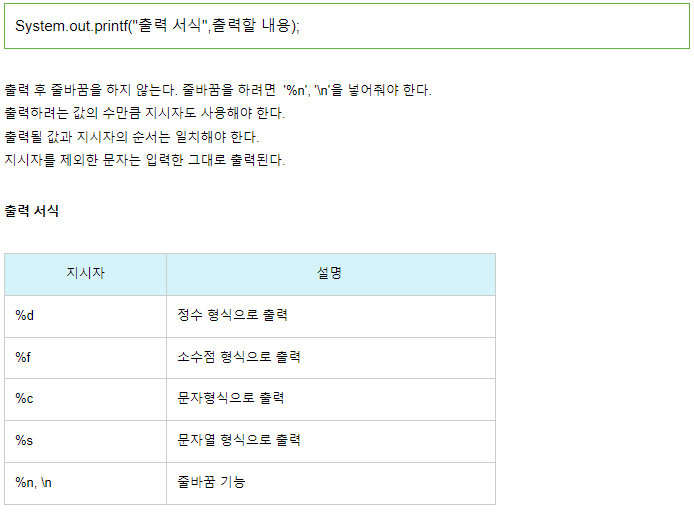
package application;
public class PrintF {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int age = 25;
String addr = "부산";
System.out.printf("붙여적기");
System.out.printf("붙여적기");
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("내 나이는 %d살 입니다.\n", age);
System.out.printf("내 나이는 %d살이고 %s에 살고 있습니다.\n",age,addr);
double pi = 3.141592;
System.out.printf("파이의 값은 %.2f", pi);
}
}
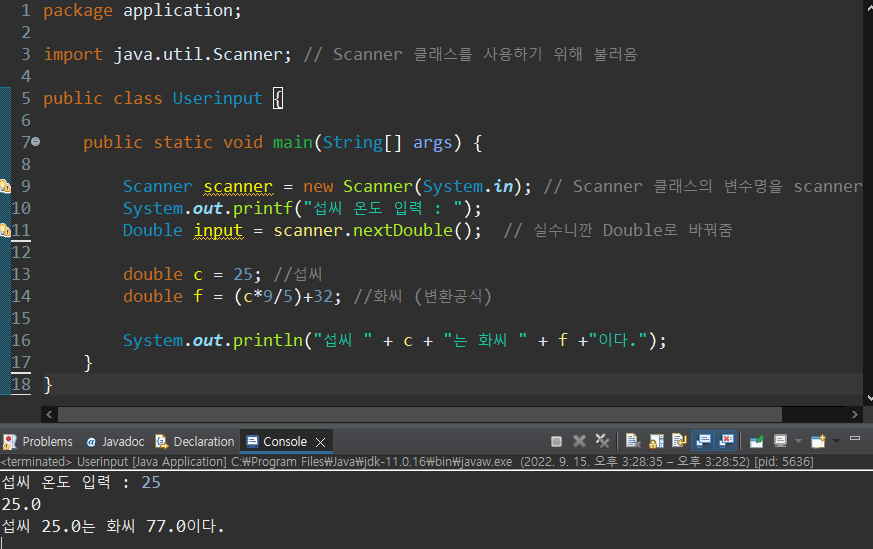
유저입력 input()
- Console 창에 사용자가 직접 입력 값을 기입하고 입력 값을 코드가 받아서 사용
- Scanner 클래스를 사용
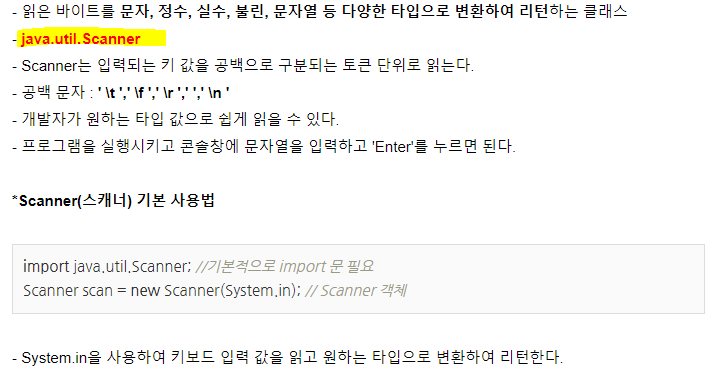
package application;
import java.util.Scanner; // Scanner 클래스를 사용하기 위해 불러옴
public class Userinput {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); // Scanner 클래스의 변수명을 scanner라고 지정
System.out.printf("섭씨 온도 입력 : ");
Double input = scanner.nextDouble(); // 실수니깐 Double로 바꿔줌
double c = 25; //섭씨
double f = (c*9/5)+32; //화씨 (변환공식)
System.out.println("섭씨 " + c + "는 화씨 " + f +"이다.");
}
}
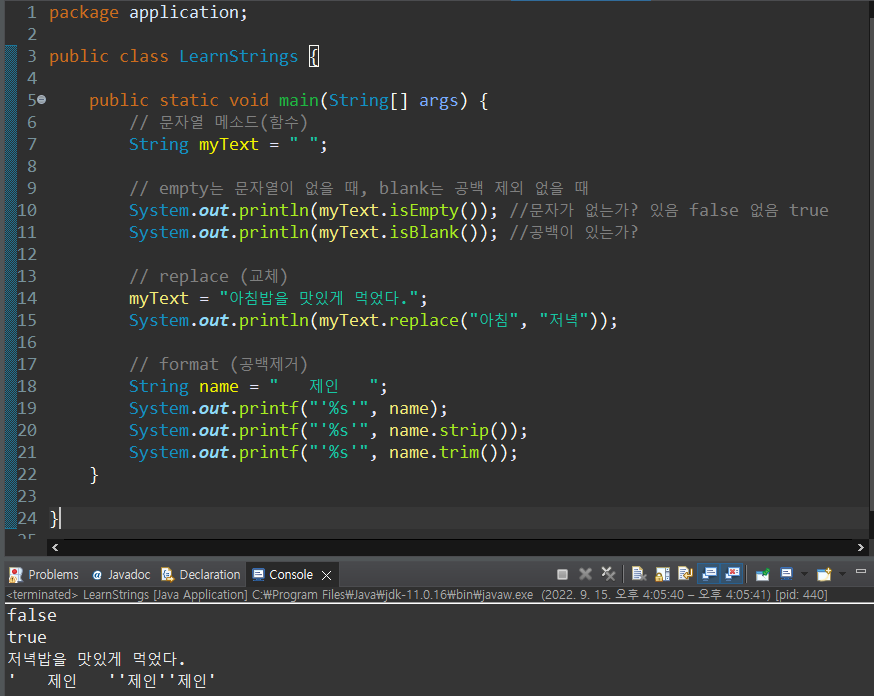
empty, blank, replace, strip & strip
package application;
public class LearnStrings {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 문자열 메소드(함수)
String myText = " ";
// empty는 문자열이 없을 때, blank는 공백 제외 없을 때
System.out.println(myText.isEmpty()); //문자가 없는가? 있음 false 없음 true
System.out.println(myText.isBlank()); //공백이 있는가?
// replace (교체)
myText = "아침밥을 맛있게 먹었다.";
System.out.println(myText.replace("아침", "저녁"));
// format (공백제거)
String name = " 제인 ";
System.out.printf("'%s'", name);
System.out.printf("'%s'", name.strip());
System.out.printf("'%s'", name.trim());
}
}
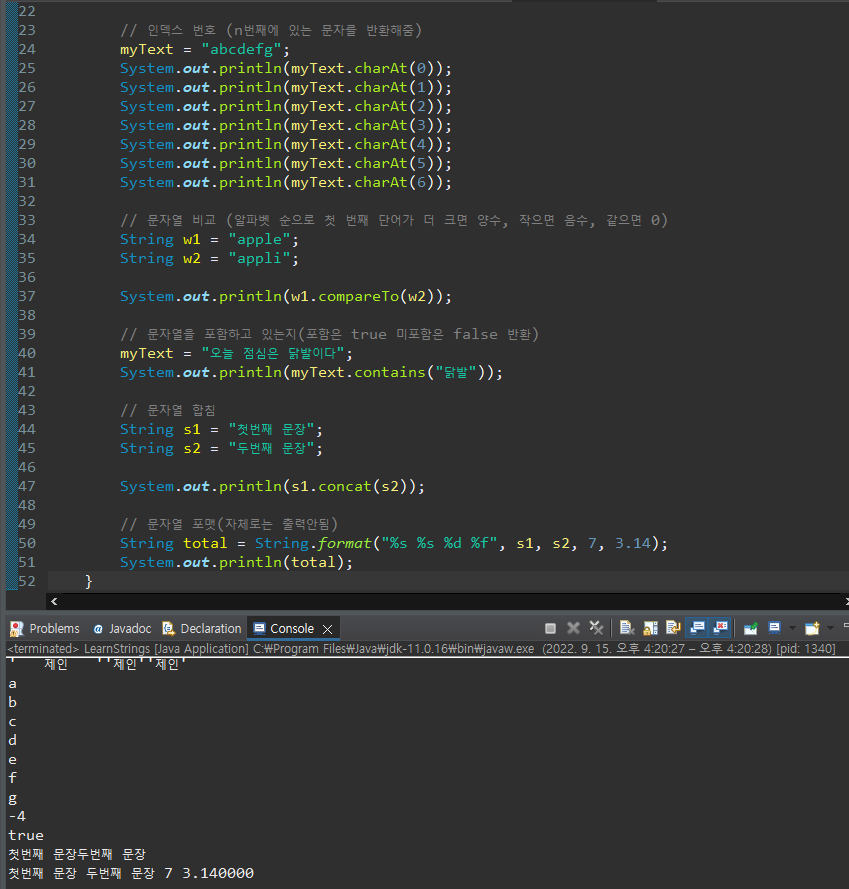
인덱스 번호(charAt), 비교(campareTo), 포함여부(contains), concat(합침)
// 인덱스 번호 (n번째에 있는 문자를 반환해줌)
myText = "abcdefg";
System.out.println(myText.charAt(0));
System.out.println(myText.charAt(1));
System.out.println(myText.charAt(2));
System.out.println(myText.charAt(3));
System.out.println(myText.charAt(4));
System.out.println(myText.charAt(5));
System.out.println(myText.charAt(6));
// 문자열 비교 (알파벳 순으로 첫 번째 단어가 더 크면 양수, 작으면 음수, 같으면 0)
String w1 = "apple";
String w2 = "appli";
System.out.println(w1.compareTo(w2));
// 문자열을 포함하고 있는지(포함은 true 미포함은 false 반환)
myText = "오늘 점심은 닭발이다";
System.out.println(myText.contains("닭발"));
// 문자열 합침
String s1 = "첫번째 문장";
String s2 = "두번째 문장";
System.out.println(s1.concat(s2));
// 문자열 포맷(자체로는 출력안됨)
String total = String.format("%s %s %d %f", s1, s2, 7, 3.14);
System.out.println(total);