JAVA 공부중
- 자바의 예외 처리 키워드 :
try,catch,finally,throw,throws
예외
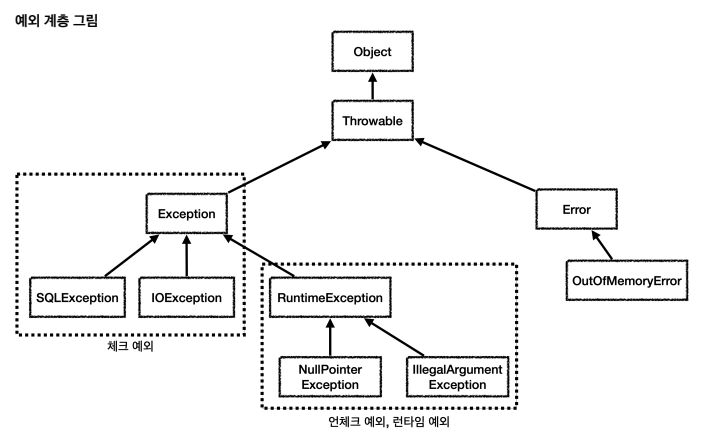
- Throwable: 최상위 예외
- Error : 메모리 부족, 시스템 오류와 같이 애플리케이션 복구 불가능 시스템 예외.(애플리케이션 개발자는 이 에러를 잡으면 안됨)
- Exception : 체크 예외. 로직에서 사용할 수 있는 최상위 예외. 하위는 모두 컴파일러가 체크하는 체크 예외 (RuntimeException은 예외)
- RuntimeException(=런타임 예외): 언체크 예외, 런타임 예외. 컴파일러가 체크하지않는 언체크 예외.
예외 기본 규칙
- 예외를 잡아서 처리하거나 밖으로 던져야함. (밖으로만 던지면 시스템 종료)
- 예외를 잡아서 던질 때 지정한 예외뿐만 아니라 그 예외의 자식들도 함께 처리할 수 있음
ex) Exception을 catch로 잡으면 하위 예외들도 모두 catch가능
ex) Exception 을 throws로 던지면 하위 예외들도 모두 throw 가능
체크예외
- Exception과 하위 예외는 컴파일러가 체크하는 체크 예외.(RuntimeException은 예외)
- 장점: 실수로 예외를 누락하지 않도록 컴파일러를 통해 문제를 잡아주는 안정장치
- 단점: 모든 체크 예외를 잡거나 던지도록 처리해야하므로 번거로움.
package exception.basic;
// 예외 클래스를 만들려면 Exception을 상속받으면 됨.
// Exception을 상속받은 예외는 "체크 예외"가 됨.
public class MyCheckedException extends Exception{
public MyCheckedException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}package exception.basic;
public class Client {
public void call() throws MyCheckedException { //여기서 해결못하니 밖으로 던지겠음
// throw예외라고 하면 새로운 예외를 발생시킬 수 있음.
// 예외도 객체이기때문에 객체를 먼저 new생성 후 예외발생시켜야함.
// throws 에외는 발생시킨 예외를 메서드 밖으로 던질 때 사용.
throw new MyCheckedException("예외발생");
}
}package exception.basic;
public class Service {
Client client = new Client();
// 체크예외를 catch하는 코드
public void callCatch() {
try {
client.call();
} catch (MyCheckedException e) {
// super(msg)로 상위클래스인 Throwable로 올린 메시지는
// Throwable의 detailMessage에 보관이 되어 getMessage로 조회가능.
System.out.println("예외 처리, message = " + e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("정상 흐름");
}
// 체크예외를 throw하는 코드
public void callThrow() throws MyCheckedException{
client.call();
}
}package exception.basic;
public class CheckedCatchMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Service service = new Service();
service.callCatch();
System.out.println("정상 종료");
}
}package exception.basic;
public class CheckedThrowMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws MyCheckedException {
Service service = new Service();
service.callThrow();
System.out.println("정상 종료");
}
}언체크 예외
-
컴파일러가 예외를 체크 X
-
체크예외와 차이점이 있다면 throws를 선언하지 않고, 생략가능. 자동으로 예외를 던짐.
-
체크 예외: throws 키워드 이용->명시적으로 예외처리
-
언체크 예외: throws 키워드 생략 -> 자동 처리
-
장점: throws예외 생략 가능
-
단점: 개발자가 예외를 누락할 수 있음
package exception.basic.unchecked;
// RuntimeException을 상속받은 예외는 언체크 예외.
public class MyUncheckedException extends RuntimeException{
public MyUncheckedException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}package exception.basic.unchecked;
public class Client {
public void call() {
throw new MyUncheckedException("예외발생(언체크)");
}
}package exception.basic.unchecked;
public class Service {
Client client = new Client();
// catch 방법 : 필요한 경우 예외 잡아 처리
public void callCatch() {
try {
client.call();
} catch (MyUncheckedException e) {
System.out.println("예외 처리, message = " + e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("정상 로직");
}
// 예외를 잡지않아도 자연스럽게 상위(Main)으로 넘어감
// 체크예외와 다르게 throws 예외 선언 안해도 됨.
public void callThrow() {
client.call();
}
}package exception.basic.unchecked;
public class UncheckedCatchMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Service service = new Service();
service.callCatch();
System.out.println("정상 종료");
}
}package exception.basic.unchecked;
public class UncheckedThrowMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Service service = new Service();
service.callThrow();
System.out.println("정상 종료");
}
}try~catch~finally
- finally 블록은 반드시 호출되며 주로 try에서 사용한 자원을 해제할 때 주로 사용.
try {
//정상 흐름
} catch {
//예외 흐름
} finally {
//반드시 호출해야 하는 마무리 흐름
}package exception.ex2;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MainV2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NetworkClientExceptionV2 {
NetworkServiceV2_5 networkService = new NetworkServiceV2_5();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("전송할 문자: ");
String input = scanner.nextLine();
if(input.equals("exit")){
break;
}
networkService.sendMessage(input);
}
System.out.println("프로그램을 정상 종료합니다.");
}
}package exception.ex2;
public class NetworkClientExceptionV2 extends Exception{
private String errorCode;
public NetworkClientExceptionV2(String errorCode, String message) {
super(message);
this.errorCode = errorCode;
}
public String getErrorCode() {
return errorCode;
}
}package exception.ex2;
public class NetworkClientV2 {
private final String address;
public boolean connectError; //boolean 초기값 : false
public boolean sendError;
public NetworkClientV2(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public void connect() throws NetworkClientExceptionV2 {
if (connectError) {
throw new NetworkClientExceptionV2("connectError", address + "서버 연결 실패");
}
System.out.println(address + "서버 연결 성공");
}
public void send(String data) throws NetworkClientExceptionV2 {
if (sendError) {
// throw new NetworkClientExceptionV2("sendError", address + "서버에 데이터 전송 실패");
// 중간 예상 불가 예외 발생
throw new RuntimeException("런타임 예외");
}
System.out.println(address + "서버에 데이터 전송: " + data);
}
public void disconnect() {
System.out.println(address + "서버 연결 해제");
}
public void initError(String data) {
if(data.contains("error1")) {
connectError = true;
}
if (data.contains("error2")){
sendError = true;
}
}
}package exception.ex2;
public class NetworkServiceV2_5 {
public void sendMessage(String data) throws NetworkClientExceptionV2 {
String address = "http://example.com";
NetworkClientV2 client = new NetworkClientV2(address);
client.initError(data);
try {
//하나의 try안에 정상 흐름을 다 담는다.
client.connect();
client.send(data);
} catch (NetworkClientExceptionV2 e) {
System.out.println("[오류] 코드: " + e.getMessage() + ", 메시지: " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
client.disconnect();
}
}
}예외의 계층화
- 위와 같은 코드의 예외를 계층화하여 관리할 수 있음
//예외 클래스 1/3
package exception.ex3.exception;
// NetworkClient에서 발생하는 모든 예외는 이 클래스의 자식들.
public class NetworkClientExceptionV3 extends Exception{
public NetworkClientExceptionV3(String message) {
super(message);
}
}//예외 클래스 2/3
package exception.ex3.exception;
// 전송 실패시 발생하는 예외.
public class SendExceptionV3 extends NetworkClientExceptionV3 {
private final String sendData;
public SendExceptionV3(String sendData, String message) {
super(message);
this.sendData = sendData;
}
public String getSendData() {
return sendData;
}
}//예외 클래스 3/3
package exception.ex3.exception;
// 연결 실패 시 발생하는 예외
public class ConnectExceptionV3 extends NetworkClientExceptionV3{
private final String address;
public ConnectExceptionV3(String address, String message){
super(message);
this.address = address;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
}package exception.ex3;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MainV3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NetworkServiceV3_1 networkService = new NetworkServiceV3_1();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("전송할 문자: ");
String input = scanner.nextLine();
if(input.equals("exit")){
break;
}
networkService.sendMessage(input);
}
System.out.println("프로그램을 정상 종료합니다.");
}
}package exception.ex3;
import exception.ex3.exception.ConnectExceptionV3;
import exception.ex3.exception.SendExceptionV3;
public class NetworkClientV3 {
private final String address;
public boolean connectError; //boolean 초기값 : false
public boolean sendError;
public NetworkClientV3(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public void connect() throws ConnectExceptionV3 {
if (connectError) {
throw new ConnectExceptionV3(address, address + " 서버 연결 실패");
}
System.out.println(address + "서버 연결 성공");
}
public void send(String data) throws SendExceptionV3 {
if (sendError) {
throw new SendExceptionV3(data, address+ " 서버 데이터 전송 실패");
}
System.out.println(address + "서버에 데이터 전송: " + data);
}
public void disconnect() {
System.out.println(address + "서버 연결 해제");
}
public void initError(String data) {
if (data.contains("error1")) {
connectError = true;
}
if (data.contains("error2")) {
sendError = true;
}
}
}package exception.ex3;
import exception.ex3.exception.ConnectExceptionV3;
import exception.ex3.exception.SendExceptionV3;
public class NetworkServiceV3_1 {
public void sendMessage(String data) {
String address = "http://example.com";
NetworkClientV3 client = new NetworkClientV3(address);
client.initError(data);
try {
//하나의 try안에 정상 흐름을 다 담는다.
client.connect();
client.send(data);
} catch (ConnectExceptionV3 e) {
System.out.println("[연결 오류] 주소 : " + e.getAddress() + ", 메시지: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SendExceptionV3 e) {
System.out.println("[전송 오류] 전송 데이터 : " + e.getSendData() + ", 메시지: " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
client.disconnect();
}
}
}추가 - 모든 Exception 잡기
- 모든 예외를 잡으려면 마지막에 Exceptionㅇ르 두면 됨.
- catch로 잡는 예외는 디테일한 자식부터 잡아가야함.
package exception.ex3;
import exception.ex3.exception.ConnectExceptionV3;
import exception.ex3.exception.NetworkClientExceptionV3;
import exception.ex3.exception.SendExceptionV3;
public class NetworkServiceV3_2 {
public void sendMessage(String data) {
String address = "http://example.com";
NetworkClientV3 client = new NetworkClientV3(address);
client.initError(data);
try {
//하나의 try안에 정상 흐름을 다 담는다.
client.connect();
client.send(data);
} catch (ConnectExceptionV3 e) {
System.out.println("[연결 오류] 주소 : " + e.getAddress() + ", 메시지: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (NetworkClientExceptionV3 e) {
System.out.println("[네트워크 오류] 전송 데이터 : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("[알 수 없는 오류] 메시지: " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
client.disconnect();
}
}
}실무 예외 처리 방안
-
처리할 수 없는 예외
- ( 네트워크 연결 오류, DB 접속 오류 ) : 예외를 잡아도 해결할 수 있는게 거의 없음. 고객에게 시스템 문제 사실 알리는 alert를 띄우거나 내부 개발자가 문제상황을 빠르게 인지하도록 오류에 대한 로그를 남겨둬야함. -
체크 예외의 부담
- 실무에서 수많은 라이브러리 사용. 서비스는 호출하는 곳에서 던지는 체크 예외들을 처리해야하는 부담이 커짐. 처리불가능이면 던질 대상 모두 다 밖으로 던져야함.
=> 본인이 해결할 수 있는 예외는 잡아서 처리하고, 해결할 수 없는 예외는 신경 쓰지 않는 것이 더 나은 선택일 수 있음.
=> 처리할 수 없는 예외는 공통으로 처리할 수 있는 곳을 만들어 한곳에서 해결하면됨.
Try with resources
-finally 구문을 사용하는 이유 중 하나는 외부 자원을 해제하기 위함이지만 자바7부터 Try with resources 구문을 도입함.
- 리소스 누락 방지 : 모든 리소스가 제대로 닫히도록 함.
- 조금 더 빠른 자원 해제 : try~catch~finally를 다 통과한 다음 자원이 해제되었으나 try with resources는 try블럭이 끝나면 즉시 close()를 호출함.
package exception.ex4;
import exception.ex4.exception.ConnectExceptionV4;
import exception.ex4.exception.SendExceptionV4;
// AutoCloseable 인터페이스 구현
public class NetworkClientV5 implements AutoCloseable{
private final String address;
public boolean connectError;
public boolean sendError;
public NetworkClientV5(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public void connect() {
if (connectError) {
throw new ConnectExceptionV4(address, address + " 서버 연결 실패");
}
System.out.println(address + " 서버 연결 성공");
}
public void send(String data) {
if (sendError) {
throw new SendExceptionV4(data, address + " 서버에 데이터 전송 실패: " + data);
}
System.out.println(address + " 서버에 데이터 전송: " + data);
}
public void disconnect() {
System.out.println(address + " 서버 연결 해제");
}
public void initError(String data) {
if (data.contains("error1")) {
connectError = true;
}
if (data.contains("error2")) {
sendError = true;
}
}
// 추가
@Override
public void close() {
System.out.println("NetworkClientV5 닫기~");
disconnect();
}
}package exception.ex4;
public class NetworkServiceV5 {
public void sendMessage(String data) {
String address = "https://example.com";
try (NetworkClientV5 client = new NetworkClientV5(address)){
client.initError(data);
client.connect();
client.send(data);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("[예외 확인] : " + e.getMessage());
throw e;
}
}
}