First Thoughts: 현재 index에 있는 값 기준으로 그 이후에 subarray에서 나오는 maximum value 를 찾았다. 둘의 차이가 profit. 문제: 시간 효율성이 너무 떨어진다... -> array traverse 할 때 마다 값은 의미를 갖는다. 만약 가격이 떨어진 것이라면 minPrice update. 아니라면 차이가 벌어질 수 있느냐를 확인해야하므로 maxProfit update할 수 있는지 확인...아직도 감을 못 잡았다면 가격을 직접 plot 해봐라.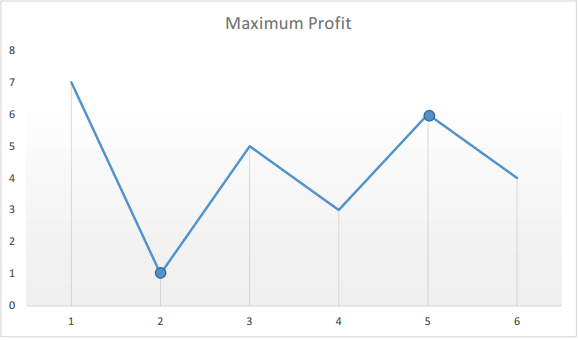
여기서 우리가 관심있는 것은 오르막길의 최대 간격. 만약 minPrice가 그대로라면, min 보다 비싼 가격이므로 profit 계산해서 profit 크기 비교. 만약 profit이 날 수 없는 상황 -> min보다 낮은 가격이면 update minPrice (intuitively, you can't calculate maxProfit if you subtract something bigger from something smaller)
My Solution: exceeds execution time (garbish time complexity)
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
ArrayList<Integer> profits = new ArrayList<>();
int sellPriceIndex = findMax(prices, -1);
for (int i=0; i<prices.length; i++) {
int buyPrice = prices[i];
if (i>sellPriceIndex) {
sellPriceIndex = findMax(prices, i);
}
profits.add(prices[sellPriceIndex]-buyPrice);
}
for (int num : profits) {
if (num>0) {
return Collections.max(profits);
}
}
return 0;
}
//returns maximum price after specified index
public int findMax(int[] prices, int currIndex) {
int maxPrice = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int maxIndex = currIndex;
for (int i=0; i<prices.length; i++) {
if (prices[i]>maxPrice && i> currIndex) {
maxPrice = prices[i];
maxIndex = i;
}
}
return maxIndex;
}
}Ideal Solution: one pass array (keeping track of maxProfit, updating minPrice)
int minPrice = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int maxProfit = 0;
for (int i=0; i<prices.length; i++) {
if (prices[i]<minPrice) {
minPrice = prices[i];
}
else if (prices[i]-minPrice > maxProfit) {
maxProfit = prices[i]-minPrice;
}
}
return maxProfit;Catch Point
-
Update minPrice and maxProfit along (first) traversal of array. This is done by updating minPrice if current Price is lower than previous minPrice -> possibility of larger profit.
-
No worry of losing and missing maxProfit as maxProfit only updated only if current calculated profit is greater than previous maxProfit.
