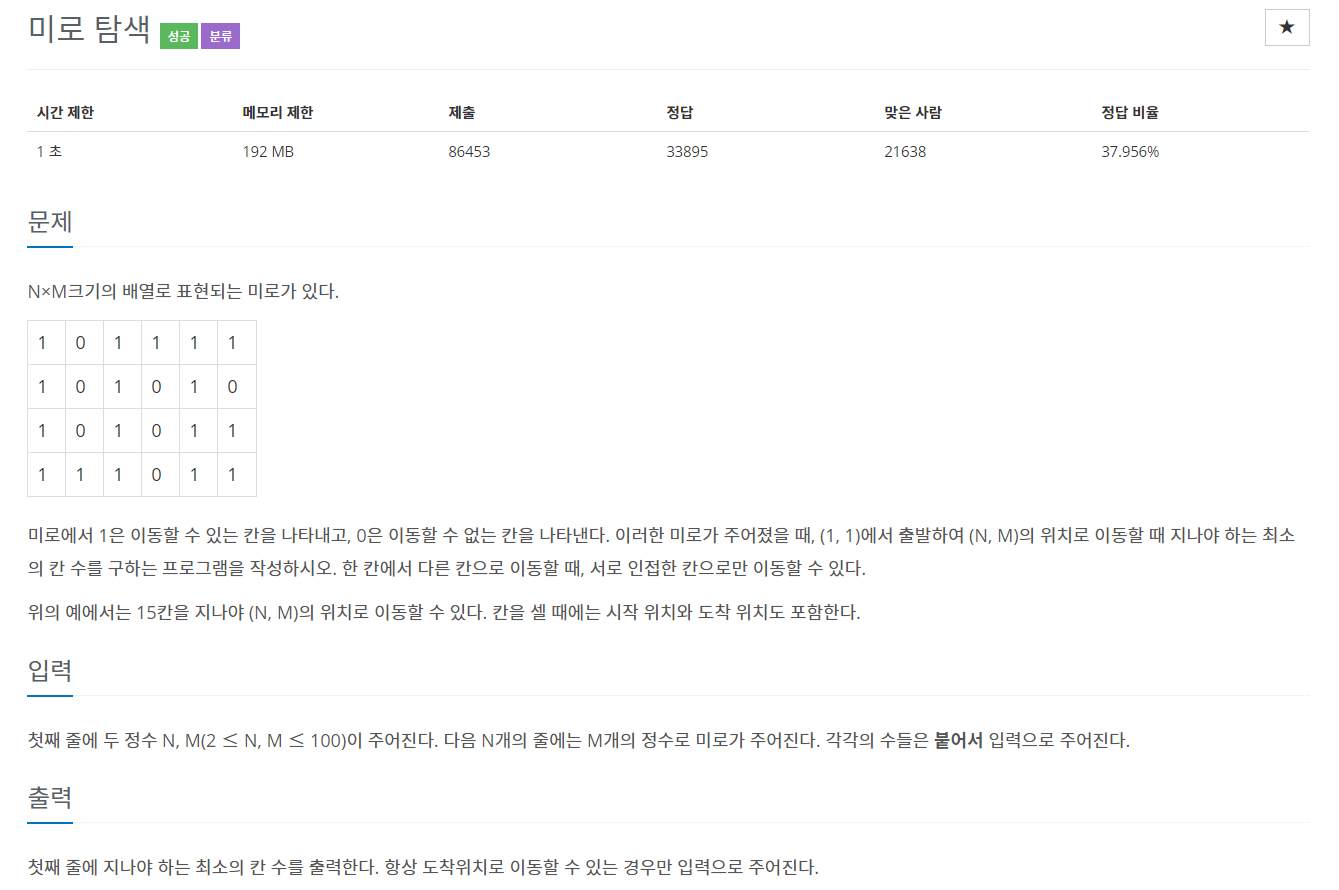
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
// #include <cstring> // memset
using namespace std;
#define MAX 101
// 미로 탐색
// scanf로 받아놓고 ios::sync_with_stdio(0); 쓰지 않도록 조심하기
int N, M;
int road[MAX][MAX] = {0, };
bool visited[MAX][MAX];
int cnt[MAX][MAX] = {0, }; // 그 경로까지 얼마나 걸렸는지를 길에 저장
int dx[4] = { 1, 0, -1, 0 };
int dy[4] = { 0, 1, 0, -1 };
void bfs(int y, int x) {
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push(make_pair(y, x));
// 일단 방문했기 때문에 true, cnt++
visited[y][x] = true;
cnt[y][x] = 1;
while(!q.empty()) {
// 큐가 빌 때까지
// 큐의 현재 원소를 꺼낸 후 삭제
y = q.front().first;
x = q.front().second;
q. pop();
// 위치의 상하좌우를 확인
for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
// 유효한 길이고 방문하지 않았다면
if(0 <= nx && 0 <= ny && nx < M && ny < N) {
if(road[ny][nx] == 1 && visited[ny][nx] == false) {
visited[ny][nx] = true;
// 그 전에 저장되어있던 칸 수에서 1을 더해 (지금 위치 배열에) 저장
cnt[ny][nx] = cnt[y][x]+1;
q.push(make_pair(ny, nx));
}
}
}
}
}
int main() {
// ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
// memset(road, false, sizeof(road));
// memset(visited, false, sizeof(visited));
// memset(cnt, false, sizeof(cnt));
cin >> N >> M;
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<M; j++) {
scanf("%1d", &road[i][j]);
}
}
// for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
// for(int j=0; j<M; j++) {
// if(road[j][i] == 1 && visited[j][i] == false) {
// bfs(j, i);
// }
// }
// }
bfs(0, 0);
// 0부터 경로가 저장됐으므로 (N-1, M-1)이 목적지
cout << cnt[N-1][M-1] << '\n';
return 0;
}
if문 범위 설정할 때 부등호를 잘못했었는지 시간낭비도 하고 입력 받을 때 scanf로 받아놓고 ios::sync_with_stdio(0);를 써 틀렸었음.
