
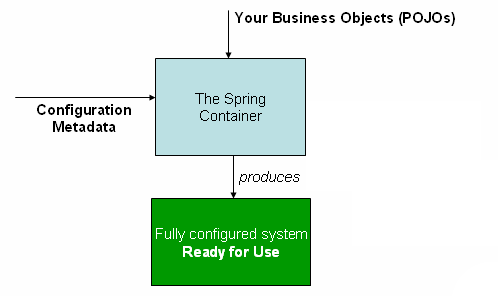
우리는 Spring IoC Container에게 객체(Bean)를 어떤 방식으로 만드는지에 관한 정보를 전달해줘야 한다. 이 때, POJO와 Configuration Metadata를 전달해주는데 이 Configuration Metadata를 전달하는 방법에는 3가지 방법이 있다. 오늘은 이에 관해 알아 볼 것이다.
0. 공통으로 사용하는 MemberDTO - POJO
package com.dbwls.common;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.ToString;
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
@AllArgsConstructor
public class MemberDTO {
private int sequence; //회원번호
private String id; //아이디
private String pwd; //비밀번호
private String name; //이름
}1. XML
1-1. XML 파일로, bean이라는 태그를 이용한다.
⚙️태그 내용
- bean 태그 : Configuration Metadate로 MemberDTO(POJO) 객체를 Bean으로 등록하고 그 객체를 생성할 때 전달할 인자들을 설정하는 역할
- constructor-arg 태그 : 생성자를 통해 객체를 만들 때 사용하는 태그
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- id는 bean의 식별자이고, class에서 이 Bean이 어떤 클래스로 생성될지 정의 -->
<bean id="member" class="com.dbwls.common.MemberDTO" >
<!-- index로 지정해도 되고, name을 통해서 지정해도 된다. -->
<!-- 생성자를 호출할 때 전달할 인자를 정의
아무것도 작성하지 않으면 기본 생성자를 사용한다는 의미-->
<constructor-arg index="0" value="1"/>
<constructor-arg name="id" value="user01"/>
<constructor-arg index="2"><value>pass01</value></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="name"><value>홍길동</value></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>1-2 Application : 실행 파일
⚙️ GenericXmlApplicationContext : 구현 클래스
XML 설정 메타 정보를 전달하기 때문에, GenericXmlApplicationContext이라는 클래스를 이용해 ApplicationContext(이게 IoC Container)를 생성한다.
import com.dbwls.common.MemberDTO;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* GenericXmlApplicationContext 클래스를 이용해 ApplicationContext를 생성한다.
* 생성자에 XML 설정 메타 정보를 인자로 전달한다. */
ApplicationContext applicationContext =
new GenericXmlApplicationContext("section01/xmlconfig/spring-context.xml");
// 여기에서 핵심은 우리가 직접 memberDTO 객체를 생성하지 않은 것!
// 1. Bean의 이름을 통해서 가져옴
// MemberDTO member = (MemberDTO)applicationContext.getBean("member");
// 2. Bean의 타입을 통해서 가져옴
// MemberDTO member = applicationContext.getBean(MemberDTO.class);
// 3. Bean의 이름과 타입을 통해 가져옴
// MemberDTO 타입이 여러 개가 있다면 이렇게 2가지를 전달해서 사용하면 됨
MemberDTO member = applicationContext.getBean("member",MemberDTO.class);
System.out.println(member);
}
}1-3 XML 파일을 이용해 전달했을 때 흐름
1) POJO (Plain Old Java Object)
- 처음에
MemberDTO라는 POJO 클래스를 만들었다. 이 클래스는 데이터만을 담는 객체로, 어떤 패턴이나 상속, 구현이 없는 순수한 클래스라고 생각하면 된다.
2) Configuration Metadata
- 그 다음, Configuration Metadata인 XML 설정 파일을 통해 이
MemberDTO클래스를 Spring 컨테이너에 등록하기 위해 Bean 정의를 작성한다. - 이때
class="com.dbwls.common.MemberDTO"로MemberDTO클래스가 Bean의 타입으로 지정되어 있다.
3) Bean의 생성과 인자 전달
- 이 설정 정보에서
constructor-arg를 통해MemberDTO객체가 생성될 때 필요한 인자값들을 전달했다. 예를 들어,index="0" value="1"은MemberDTO생성자의 첫 번째 인자로1을 전달하는 것이고,name="id" value="user01"은id라는 이름의 인자에user01값을 전달하는 방식이다.
2. Java @Bean
2-1 자바 코드를 이용해 전달하기
@Bean을 이용해 getMember() 메소드의 반환값을 spring Bean으로 등록한다.
import com.dbwls.common.MemberDTO;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
public class ConfigurationContext1 {
/* @Bean 사용 시 name 속성을 생략하면 메소드명이 bean 이름이 된다.
* 만약 이것을 원치 않는다면, name 속성을 적어주면 된다. */
@Bean(name = "member")
public MemberDTO getMember(){
return new MemberDTO(1,"user01","pass01", "홍길동");
}
}
2-2. Application : 실행 파일
⚙️ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext : 구현 클래스
Java 코드를 이용해 설정 메타 정보를 전달하기 때문에, AnnotationConfigApplicationContext이라는 클래스를 이용해 ApplicationContext(이게 IoC Container)를 생성한다.
import com.dbwls.common.MemberDTO;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. ApplicationContext 생성하기
ApplicationContext applicationContext
= new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ConfigurationContext1.class);
// 2. member라는 name의 bean을 가져오기
MemberDTO member = applicationContext.getBean("member", MemberDTO.class);
System.out.println(member);
}
}
2-3. 자바 코드를 이용해 정보를 전달했을 때의 흐름
1) Spring이 ConfigurationContext1 클래스를 로드한다.
- 이 클래스 안에
@Bean이 붙은 메서드가 있는지 확인한다.
2) getMember() 메서드를 실행하여 MemberDTO 객체를 생성한다.
- 메서드 내부에서
new MemberDTO(1, "user01", "pass01", "홍길동")을 호출하여 객체를 생성한다.
3) Spring 컨테이너가 이 객체를 "member"라는 이름으로 저장한다.
@Bean(name = "member")에 의해 해당 객체가"member"라는 이름의 Bean으로 등록된다.
4) 필요할 때 ApplicationContext에서 "member" Bean을 가져와 사용한다.
getBean("member", MemberDTO.class)을 호출하면 Spring 컨테이너에서 저장된MemberDTO객체를 반환한다.
3. @Component
@Component라는 annotation이 붙어 있다면, 이걸 스캔해서 bean으로 등록한다.<bean>태그와 동일한 역할이다.
3-1. MemberDAO (POJO)
: 이 클래스가 스캔되어 Bean 객체로 등록
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
// Component라는 어노테이션이 등록되어,
// 이 클래스가 스캔되어 빈 객체로 등록되는 것이다.
@Component
public class MemberDAO {
private final Map<Integer, MemberDTO> memberMap;
public MemberDAO() {
memberMap = new HashMap<>();
memberMap.put(1, new MemberDTO(1, "user01", "pass01", "홍길동"));
memberMap.put(2, new MemberDTO(2, "user02", "pass02", "유관순"));
}
/* 매개변수로 전달 받은 회원 번호를 map에서 조회 후 회원 정보를 리턴하는 메소드 */
public MemberDTO selectMember(int sequence) {
return memberMap.get(sequence);
}
/* 매개변수를 전달 받은 회원 정보를 map에 추가하고 성공 실패 여부를 boolean으로 리턴하는 메소드 */
public boolean insertMember(MemberDTO newMember) {
int before = memberMap.size();
memberMap.put(newMember.getSequence(), newMember);
int after = memberMap.size();
return after > before;
}
}
3-2. Java 코드를 이용하기
3-2-1. Java 코드
-
@Configuration("configurationContextJava")
: 이 annotation을 통해 이 파일이 componetMetadata라는 것을 알려줌 -
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.dbwls")
:com.dbwls패키지 아래에 있는 컴포넌트(Bean)들을 자동으로 검색해서 스프링 컨테이너에 등록하라는 의미
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/* @Configuration
: @Component의 구체화 어노테이션으로 설정 정보를 담는 클래스로
여기에 정의된 내용을 기반으로 Bean을 등록 */
@Configuration("configurationContextJava")
/* @ComponentScan : Componenet Scan과 관련된 설정을 기입하며, basePackages를 기입하지 않으면
* default는 현재 패키지 기준으로 Scan이 수행 된다. */
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.dbwls")
public class ConfigurationContext {
}
3-2-2. Application
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext
= new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ConfigurationContext.class);
String[] beanNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for(String beanName : beanNames){
System.out.println("beanName : " + beanName);
}
}
}3-3. XML 파일을 이용하기
3-3-1. XML 파일
⚙️context:component-scan
위에서 알아본 @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.dbwls")와 같은 역할이다.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- component를 스캔해라!-->
<context:component-scan base-package = "com.dbwls"/>
</beans>3-3-2. Application
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext
= new GenericXmlApplicationContext("section03/xmlconfig/spring-context.xml");
String[] beanNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for(String beanName : beanNames){
System.out.println("beanName : " + beanName);
}
}
}
4. 어떤 경우에? 어떤 방법으로?
지금까지 ConfigurationMetadata를 보내는 방식을 배웠다. 그렇다면 이 각각의 방법을 언제 어떤 상황에 사용하면 될까?
- XML 설정
- 전통적으로 사용하던 방식으로 최근에는 Java 설정이 선호된다.
- @Component 사용
- 개발자가 직접 컨트롤 가능한 Class인 경우에 사용한다.
- @Bean 사용
- 개발자가 직접 수정할 수 없는 외부 라이브러리에는 @Component를 붙일 수 없다. (이 어노 테이션은 해당 클래스에 직접 적어야 하기 때문에) 그렇기에 @Bean을 메소드에 사용하여 수동으로 빈 등록을 해야 한다.
- 다형성을 활용하고 싶은 경우에도 @Bean을 사용할 수 있다.
