
프로젝트를 진행하다 보면 예기치 못한 예외가 발생할 수 있다.
그렇다면 이런 예외들은 어떻게 처리해야 할까?

Exception Handelr를 사용한다. 이것은 프로그램이 실행 중에 예기치 않은 오류가 발생했을 때 이를 처리하는 매커니즘이다. 스프링에서는 예외 처리를 관리하는 여러가지 기능을 제공하고 있다.
오늘은 예외를 처리하는 방법에 대해 알아보고, 실제 내가 프로젝트에서 적용한 것과 그 당시 했던 고민을 포스팅 해보려 한다.
1. 예외는 어떻게 처리할까?
웹에서는 예외가 발생했을 때, 클라이언트에게 어떤 문제가 발생했는지 상황을 전달하는 경우가 대부분이다. 즉, 예외를 복구하는 것보다 예외를 처리하는 것이다.
예외를 처리하는 상황은 밑에 처럼 크게 2가지 이다. 지금부터, 이 2가지 상황에서 각각 어떻게 예외를 처리하는지 알아보자.
(1) 모든 컨트롤러에서 예외 처리
(2) 특정 컨트롤러에서 예외 처리
1-1. 특정 Controller 안에서 발생하는 예외
@ExceptionHandler는 스프링에서 예외 처리를 담당하는 어노테이션으로, Controller 클래스 내에서 예외가 발생했을 때 해당 예외를 처리할 메서드를 정의하는데 사용한다.
(1) 일반적인 예외 발생 시키기
- 클라이언트가
/controller-null경로로 요청을 보냄 - 해당 요청을 처리하는 Controller 메소드가 실행하고, 이 메소드 내에서
NullPointerException이 발생 - 예외가 발생하면, 등록된 예외 처리 핸들러(@ExceptionHandler)가 이를 가로채 처리
@Controller
public class ExceptionHandlerController {
@GetMapping("/controller-null")
public String nullPointerExceptionTest() {
String str = null;
// 의도적으로 NullPointerException 발생
System.out.println(str.charAt(0));
return "/";
}
@ExceptionHandler(NullPointerException.class)
public String nullPointerExceptionHandler(NullPointerException e){
// Exception 객체가 가지고 있는 정보를 가져오는게 가능함
System.out.println("지역 범위의 Exception Handler 동작");
System.out.println("message : " + e.getMessage());
return "error/nullPointer";
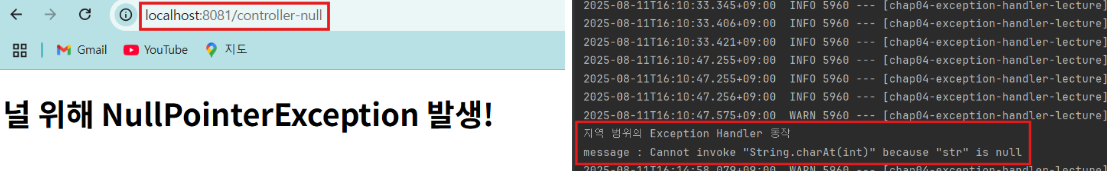
}✅ 실제 결과 확인
밑에 사진 처럼 controller-null 경로로 들어갔을 때, 예외가 발생하는 것과 콘솔에서 내용이 찍히는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
(2) 사용자 정의 예외 발생 시키기
MemberRegistException은 실제로 지원하는 예외가 아니고, 사용자 정의 예외이다. 사용자 정의 예외는 자바에서 기본적으로 제공하는 것이 아닌 개발자가 직접 만든 예외이다.
/* 사용자 정의 Exception 클래스 */
public class MemberRegistException extends Exception {
public MemberRegistException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}예외가 발생하는 흐름은 위에서 살펴봤던 것과 같다.
- 클라이언트가
/controller-user경로로 요청을 보냄 - 해당 요청을 처리하는 Controller 메소드가 실행하고, 이 메소드 내에서
MemberRegistException이 발생 - 예외가 발생하면, 등록된 예외 처리 핸들러(@ExceptionHandler)가 이를 가로채 처리
@Controller
public class ExceptionHandlerController {
@GetMapping("/controller-user")
public String userExceptionTest() throws MemberRegistException{
boolean check = true;
if(check){
throw new MemberRegistException("당신 같은 사람은 회원으로 받을 수 없습니다.");
}
return "/";
}
@ExceptionHandler(MemberRegistException.class)
public String userExceptionHandler(MemberRegistException e, Model model){
System.out.println("지역 범위의 Exception Handler 동작");
System.out.println("message : " + e.getMessage());
model.addAttribute("exception", e);
return "error/memberRegist";
}
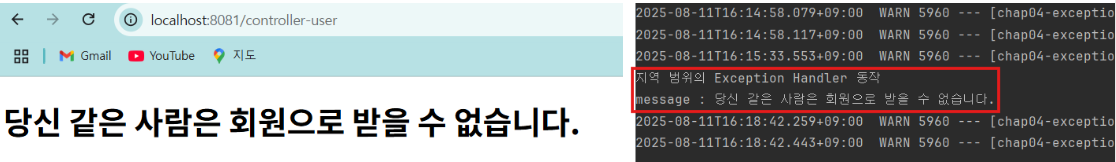
}✅ 실제 결과 확인
밑에 사진 처럼 controller-user 경로로 들어갔을 때, 예외가 발생하는 것과 콘솔에서 내용이 찍히는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
1-2. 여러 Controller에서 공통적으로 발생하는 예외
@ControllerAdvice어노테이션은 스프링에서 예외 처리를 담당하는 어노테이션이다.@ControllerAdvice어노테이션이 붙은 클래스는 전역 예외 처리를 담당하게 된다.
- 여러 개의 컨트롤러에서 발생하는 예외를 일괄적으로 처리하기 위해 사용
@ControllerAdvice를 사용하면 모든 컨트롤러에서 발생하는 예외를 한 곳에서 처리할 수 있어 코드의 중복 방지
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(NullPointerException.class)
public String nullPointerExceptionHandler(NullPointerException e){
System.out.println("전역 범위의 Exception Handler 동작");
System.out.println("message : " + e.getMessage());
return "error/nullPointer";
}
@ExceptionHandler(MemberRegistException.class)
public String userExceptionHandler(MemberRegistException e, Model model){
System.out.println("전역 범위의 Exception Handler 동작");
System.out.println("message : " + e.getMessage());
model.addAttribute("exception", e);
return "error/memberRegist";
}
/* 모든 타입의 Exception에 대응하기 위해 상위 타입으로 선언 된 핸들러 작성 */
/* 위에 구체적인 exception이 아니라면 여기에 작성한 exception이 발생함*/
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public String defaultExceptionHandler(Exception e){
return "error/default";
}
}이제 전역적으로 예외 처리를 담당한다. 이 때, 예외 처리는 지역 예외 처리 → 전역 예외 처리 순으로 동작한다. 지역적으로 선언된 핸들러가 우선 실행되는 것이다.
1-3. 전역 vs 지역 예외 처리
최종적으로 전역, 지역 예외 처리에 관해 정리해 보자.
(1) 전역 예외 처리
- 프로젝트 전반에서 발생할 수 있는 예외를 한 곳에서 관리
- 주로
@ControllerAdvice와@ExceptionHandler를 함께 사용 - 중복 코드 제거, 공통 로직 관리 용이
(2) 지역 예외 처리
- 특정 컨트롤러나 클래스 내부에서만 발생하는 예외 처리
- 해당 클래스에
@ExceptionHandler직접 선언 - 해당 기능에 특화된 예외 처리 가능
2. 실제 적용하기
2-1. Restful 하게 적용하기
우선 나는 RestAPI를 개발했기 때문에,
@RestController와 @RestControllerAdvice를 사용했다.
@RestController와 @RestControllerAdvice는
@ResponseBody가 포함되어 있어서, 반환 값이 JSON/XML 형태로 바로 변환된다.
반면 @Controller와 @ControllerAdvice는 기본적으로 뷰를 반환하고, JSON/XML을 내려주려면@ResponseBody를 따로 붙여야 한다.
✏️ 참고 사항
참고로 @RestControllerAdvice는 Spring 4.3부터, 그리고 @RestController는 Spring 4.0부터 생긴 어노테이션이다. 이 두가지 어노테이션이 나오기 전에는 @ResponseBody어노테이션을 함께 작성했다.
✅ 개발할 때
- Restful API 개발 → @RestController + @RestControllerAdvice 사용
- 뷰 렌더링 중심 웹 개발 → @Controller + @ControllerAdvice 사용
2-2. 적용 예시
(1) 사용자 정의 예외 클래스 만들기 : ApproveException
@Getter
public class ApproveException extends RuntimeException {
private final ErrorCode errorCode;
public ApproveException(ErrorCode errorCode) {
super(errorCode.getMessage());
this.errorCode = errorCode;
}
}RuntimeException을 상속하여 Unchecked Exception (예외 처리를 강제하지 않음)으로 설계- 예외마다 ErrorCode를 포함시켜 코드, 메시지, HTTP 상태를 함께 관리
- 이렇게 하면 예외 처리 시 에러 정보를 한 번에 꺼내 쓸 수 있음
(2) ErrorCode enum 정의
NOT_EXIST_APPROVE("30002", "존재하지 않는 결재 내역입니다.", HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
private final String code;
private final String message;
private final HttpStatus httpStatus;- 예외 상황을 코드, 메시지, HTTP 상태로 표준화
- 하나의 Enum 값이 하나의 예외 상황을 대표
- 결재 내역이 없을 경우 30002 코드, BAD_REQUEST 상태 반환
(3) 전역 예외 처리하기 : @RestControllerAdvice
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(ApproveException.class)
public ResponseEntity<ApiResponse<Void>> handleApproveException(ApproveException e){
ErrorCode errorCode = e.getErrorCode();
ApiResponse<Void> response
= ApiResponse.failure(errorCode.getCode(), errorCode.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity<>(response,errorCode.getHttpStatus());
}
}@RestControllerAdvice로 전역에서 발생하는 예외를 JSON 형태로 처리@ExceptionHandler(ApproveException.class)를 통해ApproveException 전용 처리 로직- 예외 객체에서 ErrorCode를 꺼내, 실패 응답(ApiResponse.failure) 생성
- ResponseEntity로 HTTP 상태와 함께 반환
이렇게 하면 예외가 발생했을 때, 다음과 같은 형식으로 메세지가 발생하게 된다. 이렇게 했을 경우 예외를 확실하게 확인할 수 있다.
{
"success": false,
"errorCode": "30002",
"message": "존재하지 않는 결재 내역입니다.",
"timestamp": "2025-08-11T16:25:43"
}
