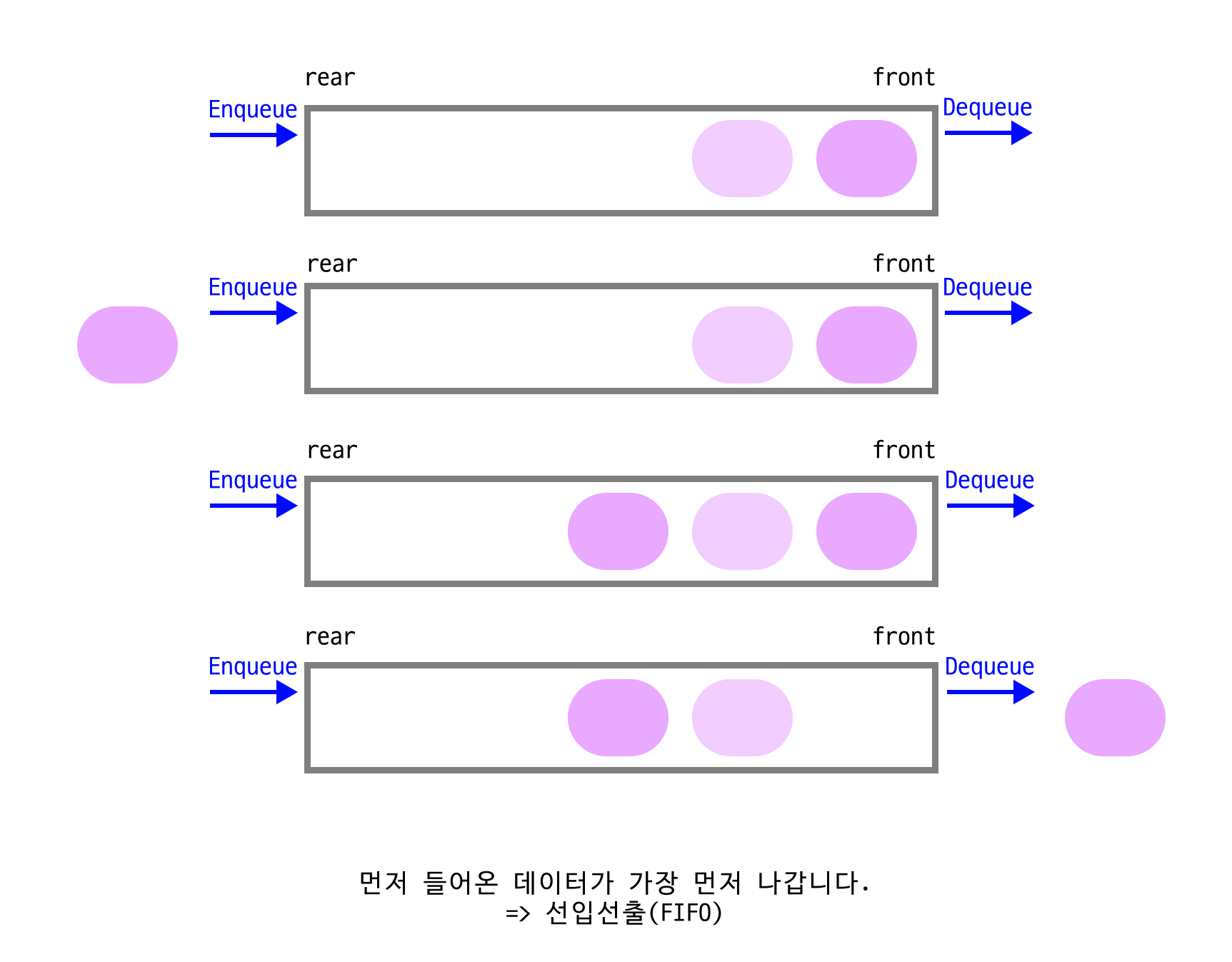
- front: 큐의 앞부분을 나타내며,
Dequeue연산만 수행됩니다. - rear: 큐의 뒷부분을 나타내며,
Enqueue연산만 수행됩니다. - Enqueue: 큐의 rear에 원소를 추가합니다. 큐가 꽉 차면 Overflow condition이 발생합니다.
- Dequeue: 큐의 front에서 원소를 제거합니다. 큐가 비어있으면 Underflow condition이 발생합니다.
특징
- 스택과 달리 들어오는 순서대로 나갑니다. (FIFO - 선입선출)
LinkedList를 이용하여 구현하는 것이 적합하며,ArrayDeque와 같은 다른 구현도 사용될 수 있습니다.
메서드
boolean offer() 와 boolean add()
원소를 큐에 삽입할 때 사용하는 메서드입니다.
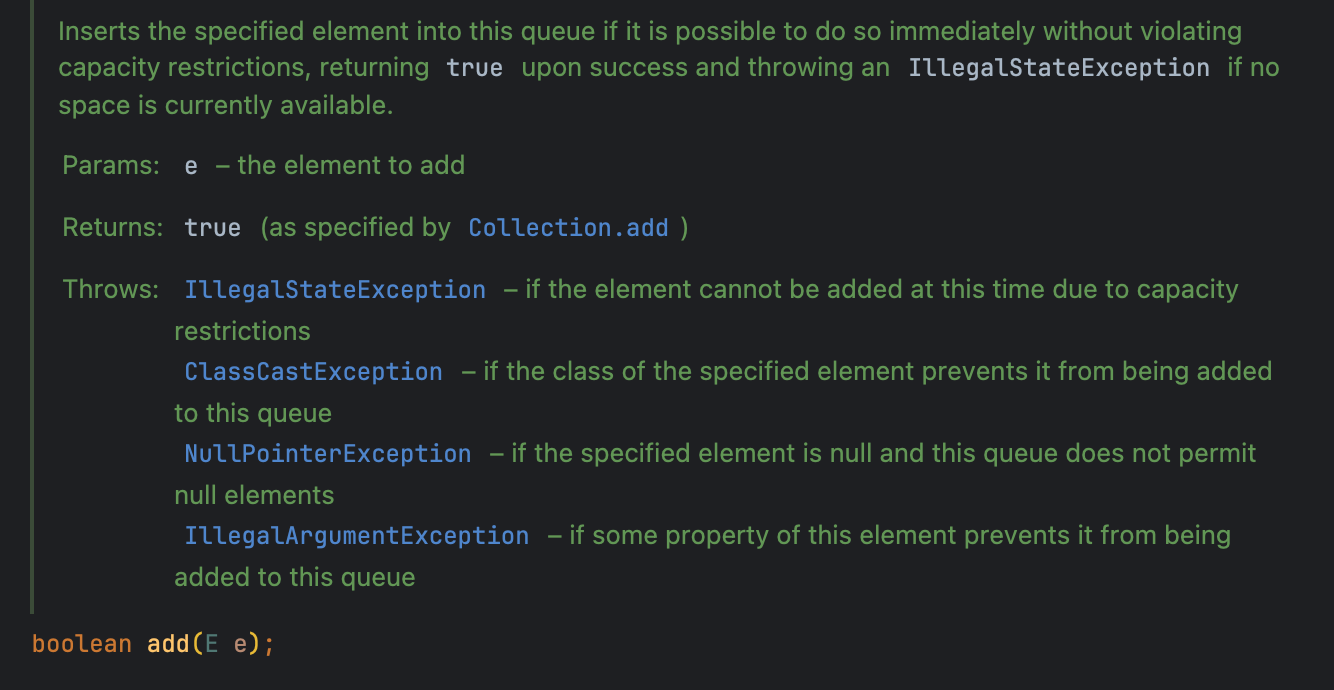

- add(): 큐에 원소를 추가하며, 큐가 꽉 차면
IllegalStateException을 발생시킵니다. - offer(): 큐에 원소를 추가하며, 큐가 꽉 차면
false를 반환합니다.
IllegalStateException- 용량 초과 시ClassCastException- 잘못된 클래스 타입NullPointerException- null 요소를 허용하지 않을 때IllegalArgumentException- 요소 속성에 의해 추가 불가
E poll() 와 E remove()
큐의 front 원소를 제거하고 반환하는 메서드입니다.

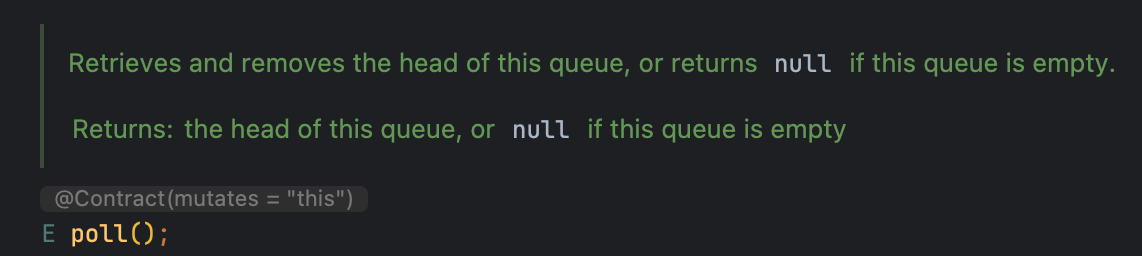
- poll(): 큐에서 원소를 제거하고 반환하며, 큐가 비어있으면
null을 반환합니다. - remove(): 큐에서 원소를 제거하고 반환하며, 큐가 비어있으면
NoSuchElementException을 발생시킵니다.
E peek() 와 E element()
큐의 front 원소를 검색하여 반환하는 메서드입니다.
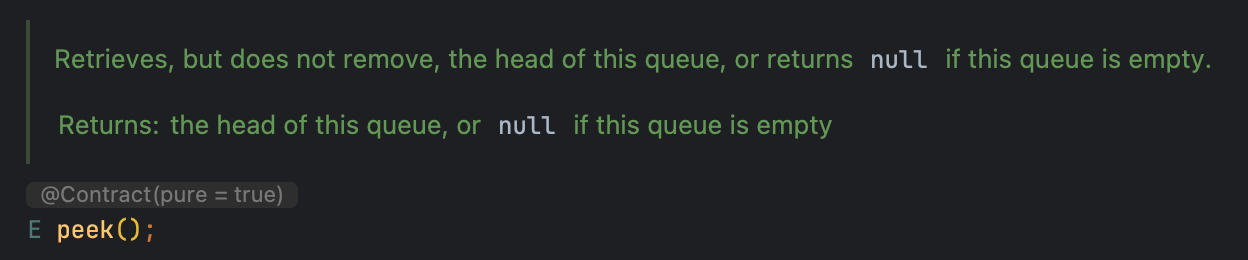
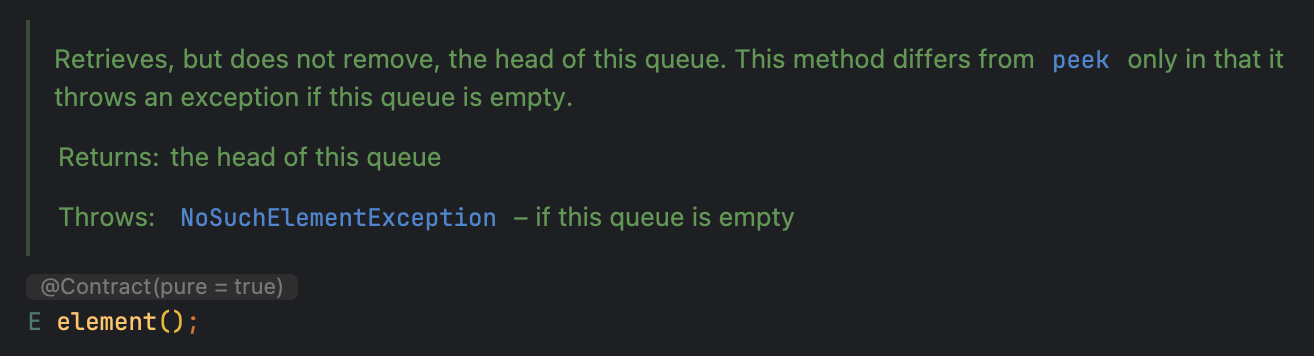
- peek(): 큐의 front 원소를 검색하여 반환하며, 큐가 비어있으면
null을 반환합니다. - element(): 큐의 front 원소를 검색하여 반환하며, 큐가 비어있으면
NoSuchElementException을 발생시킵니다.
정리
| 예외 발생 | 값 출력 | |
|---|---|---|
| 삽입 | add() | offer() |
| 제거 | remove() | poll() |
| 검색 | element() | peek() |
코드로 보기
public class QueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
System.out.println("=====삽입=====");
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.add(3);
queue.add(4);
System.out.println(queue);
System.out.println("=====제거=====");
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.remove());
System.out.println("=====검색=====");
System.out.println(queue.peek());
System.out.println(queue.element());
}
}

예외 상황 코드로 보기
public class QueueExceptionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// add 예외 상황을 위해 큐의 크기를 2로 설정
Queue<Integer> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2);
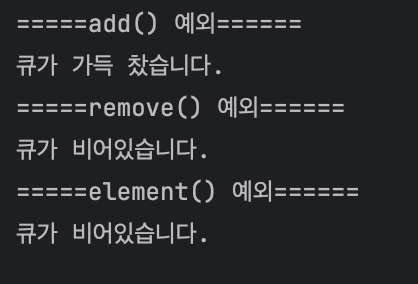
System.out.println("=====add() 예외======");
try {
queue.add(1);
queue.add(2);
queue.add(3);
} catch (IllegalStateException e) {
System.out.println("큐가 가득 찼습니다.");
}
System.out.println("=====remove() 예외======");
try {
queue.remove();
queue.remove();
queue.remove();
} catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
System.out.println("큐가 비어있습니다.");
}
System.out.println("=====element() 예외======");
try {
queue.element();
} catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
System.out.println("큐가 비어있습니다.");
}
}
}
활용 예시
- 작업 스케줄링: 운영체제의 프로세스나 프린터 작업을 순서대로 처리합니다.
- 버퍼링: 네트워크 패킷이나 입출력 작업을 임시로 저장하고 처리합니다.
- 데이터 스트리밍: 실시간 데이터나 미디어 스트림을 순서대로 처리합니다.
- 알고리즘 구현: 너비 우선 탐색(BFS)과 레벨 오더 트리 순회에서 사용됩니다.
- 게임 개발: 비동기 작업 처리와 사용자 입력 관리에 활용됩니다.
이 외에도 다양한 곳에서 큐가 활용됩니다.
종류
순환 큐 (Circular Queue)
선형큐를 구현할 시에 rear가 max size에 도달하게 되면 큐의 시작 부분이 빈 공간이 생길 수 있습니다. 빈 공간은 다시 사용될 수 없기 때문에 메모리가 낭비됩니다. 순환큐는 이러한 단점을 보완해줍니다.
순환큐도 FIFO 방식으로 front와 rear의 역할은 동일합니다.
 출처:Circular Queue using Array in C
출처:Circular Queue using Array in C
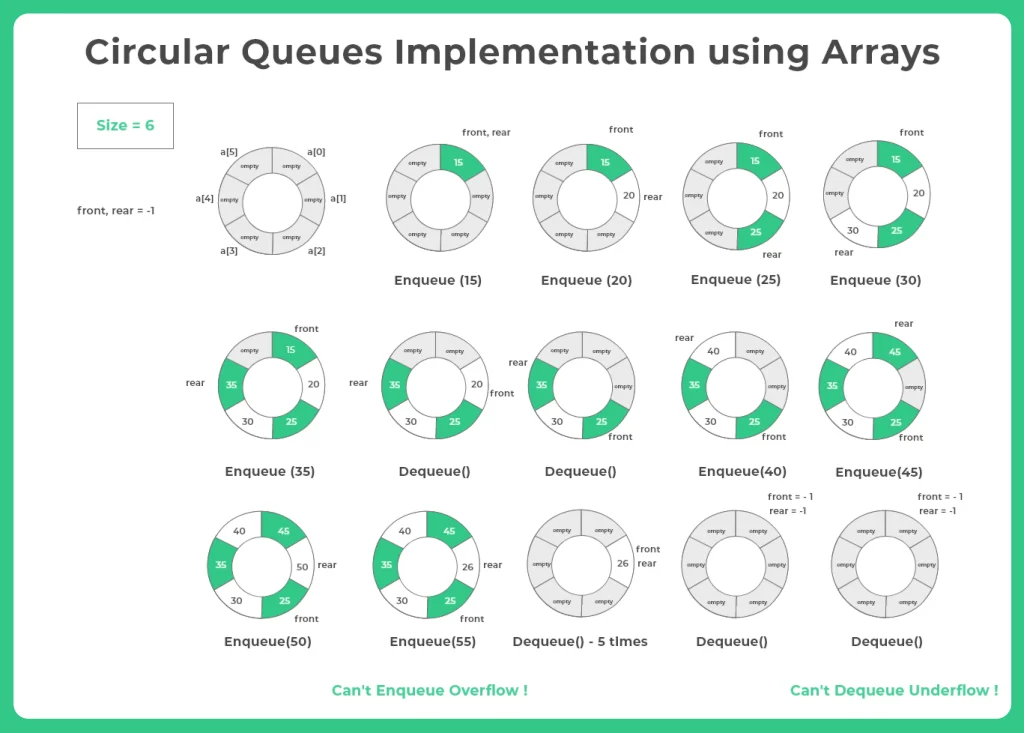
enqueue() 작업
1단계: 큐가 꽉 찼는지 확인합니다.
rear + 1 % max_size = front
2단계: 큐가 가득 찬 경우 Overflow가 발생합니다.
3단계: 큐가 비어 있는지 확인하고 front와 rear를 모두 0으로 설정합니다.
4단계: rear = max_size - 1 & front != 0 (rear가 큐의 끝에 있고 front가 0번째 인덱스에 없는 경우)이면 rear = 0으로 설정합니다.
5단계: 그렇지 않은 경우 rear = (rear + 1) % max_size로 설정합니다.
6단계: 큐에 요소를 삽입합니다. Queue[Rear] = x
dequeue() 작업
1단계 : 큐가 비어있는지 확인합니다.
2단계 : 큐가 비어있다면 Underflow가 발생합니다.
3단계 : 비어있지 않다면 Element = Queue[front]로 설정합니다.
4단계 : 큐에 요소가 하나만 있는 경우(front = rear)에는 모두 -1로 설정합니다.
5단계 : front = max_size - 1이면, front = 0으로 설정합니다.
6단계 : 그렇지 않다면 front = front + 1로 설정합니다.
코드로 보기
public class CircularQueue {
private int[] queue;
private int front;
private int rear;
private int size;
private int maxSize;
// 큐 초기화
public CircularQueue(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
queue = new int[maxSize];
front = -1;
rear = -1;
size = 0;
}
// 큐가 비어 있는지 확인
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
// 큐가 가득 찼는지 확인
public boolean isFull() {
return size == maxSize;
}
// 큐에 원소를 추가 (Enqueue)
public boolean enqueue(int element) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("큐가 가득 찼습니다.");
return false;
}
// 큐가 비어 있는 경우 front와 rear를 초기화
if (isEmpty()) {
front = 0;
}
// rear를 원형 큐의 다음 위치로 이동
rear = (rear + 1) % maxSize;
queue[rear] = element;
size++;
return true;
}
// 큐에서 원소를 제거하고 반환 (Dequeue)
public int dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("큐가 비어 있습니다.");
return -1;
}
int element = queue[front];
front = (front + 1) % maxSize;
size--;
// 큐가 비어 있는 경우 front와 rear를 초기화
if (isEmpty()) {
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
return element;
}
// 큐의 앞부분 원소를 반환 (삭제하지 않음)
public int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("큐가 비어 있습니다.");
return -1;
}
return queue[front];
}
// 큐의 내용을 출력
public void display() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("큐가 비어 있습니다.");
return;
}
System.out.print("큐 : ");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
System.out.print(queue[(front + i) % maxSize] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircularQueue cq = new CircularQueue(5);
cq.enqueue(10);
cq.enqueue(20);
cq.enqueue(30);
cq.enqueue(40);
cq.enqueue(50);
cq.display(); // 큐: 10 20 30 40 50
System.out.println("Dequeue: " + cq.dequeue()); // Dequeue: 10
System.out.println("Dequeue: " + cq.dequeue()); // Dequeue: 20
cq.display(); // 큐: 30 40 50
cq.enqueue(60);
cq.enqueue(70);
cq.display(); // 큐 : 30 40 50 60 70
// 큐가 가득 찼기 때문에 enqueue(80)는 실패합니다.
if (!cq.enqueue(80)) {
System.out.println("원소 80을 추가할 수 없습니다. 큐가 가득 찼습니다.");
}
System.out.println("Peek: " + cq.peek()); // Peek: 30
cq.dequeue();
cq.dequeue();
cq.dequeue();
cq.dequeue();
cq.dequeue(); // 모든 원소를 제거
cq.display(); // 큐가 비어 있습니다.
}
}
시간복잡도
모든 메서드가 포인터 이동과 조건 확인과 같은 단순한 작업만 하기 때문에 상수시간O(1) 내에 동작합니다.
우선순위 큐 (Priority Queue)
선형큐의 FIFO 방식과 다르게 들어온 순서에 상관없이 우선순위가 높은 데이터가 먼저 나옵니다. 일반적으로 힙(Heap)을 이용하여 구현을 많이 합니다.
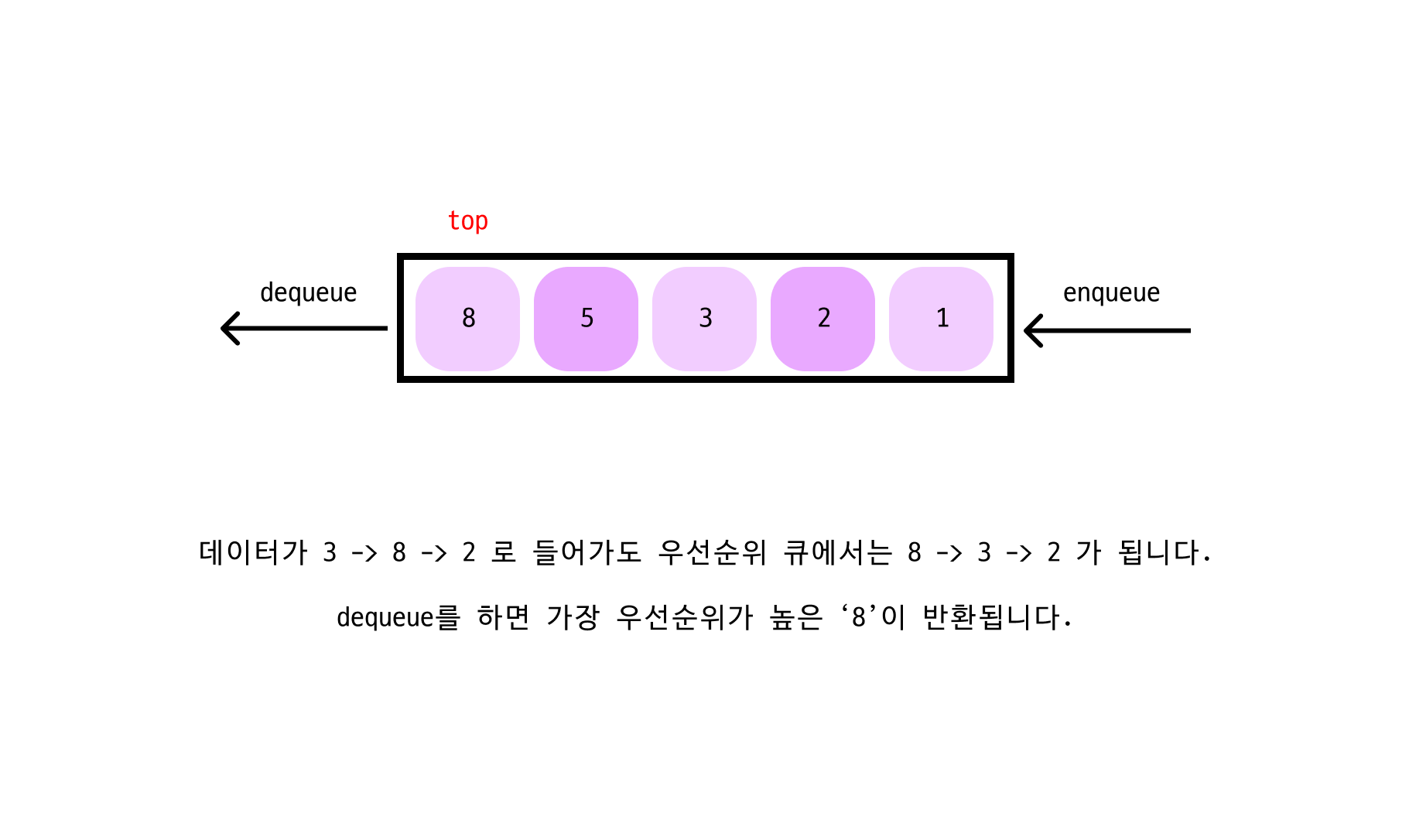
왜 힙을 많이 사용할까?
- 배열: 배열은 새로운 요소를 삽입할 때 적절한 위치를 찾기 위해 최악의 경우 모든 요소를 이동시켜야 하기 때문에
O(n)의 시간 복잡도를 초래합니다. 특히 삽입 연산이 빈번할 때 비효율적입니다.- 연결 리스트: 연결 리스트는 중간에 요소를 삽입하거나 삭제할 때
O(1)의 시간이 걸릴 수 있지만, 최대/최소값을 찾기 위해서는 리스트를 탐색해야 하므로 최악의 경우O(n)이 소요됩니다.그럼 힙은 효율적인가?
- 효율적인 삽입 & 추출 : 삽입과 추출 연산 모두
O(log n)의 시간복잡도로 효율적으로 처리할 수 있습니다.
항상 이진 트리 구조를 유지하기 때문에 새로운 요소가 추가되거나 루트 노드가 제거될 때마다 힙의 구조를 유지하기 위한 최소한의 비교와 교환만 필요합니다.- 빠른 접근 : 최대 힙이나 최소 힙을 사용하면 항상 루트 노드가 최대값과 최소값이 되기 떄문에 우선순위가 가장 높은 요소를 빠르게 접근 가능합니다.
- 메모리 효율 : 일반적으로 배열을 기반으로 구현되기 때문에 추가적인 연결 구조에 대한 메모리 오버헤드가 없습니다.
코드로 보기
Java의 PriorityQueue클래스를 이용하여 최소 힙(default)을 기반으로 동작하는 우선순위 큐를 생성합니다.
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class PriorityQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
priorityQueue.offer(5);
priorityQueue.offer(1);
priorityQueue.offer(3);
priorityQueue.offer(10);
priorityQueue.offer(2);
System.out.println("우선순위 큐: " + priorityQueue); // 우선순위 큐: [1, 2, 3, 10, 5]
System.out.println("가장 높은 요소 확인: " + priorityQueue.peek()); // 가장 높은 요소 확인: 1
System.out.println("가장 높은 요소 제거: " + priorityQueue.poll()); // 가장 높은 요소 제거: 1
System.out.println("제거 후 우선순위 큐: " + priorityQueue); // 제거 후 우선순위 큐: [2, 5, 3, 10]
while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("제거됨: " + priorityQueue.poll()); // 제거됨: 2, 제거됨: 3, 제거됨: 5, 제거됨: 10
}
System.out.println("모두 제거 후 우선순위 큐: " + priorityQueue); // 모두 제거 후 우선순위 큐: []
}
}
시간복잡도
- 삽입(offer):
O(log n) - 삭제(poll):
O(log n) - 최대/최소값 확인(peek):
O(1)